B a s i c S e c u r i t y C o n f i g u r a t i o n s
There are two main decisions to be made when choosing wireless security: encryption method and authentication protocol. The encryption method determines the algorithm used to encrypt the message. The authentication type specifies how users are identified and verified on a network. Is the device seeking connection what (and who) it claims to be?
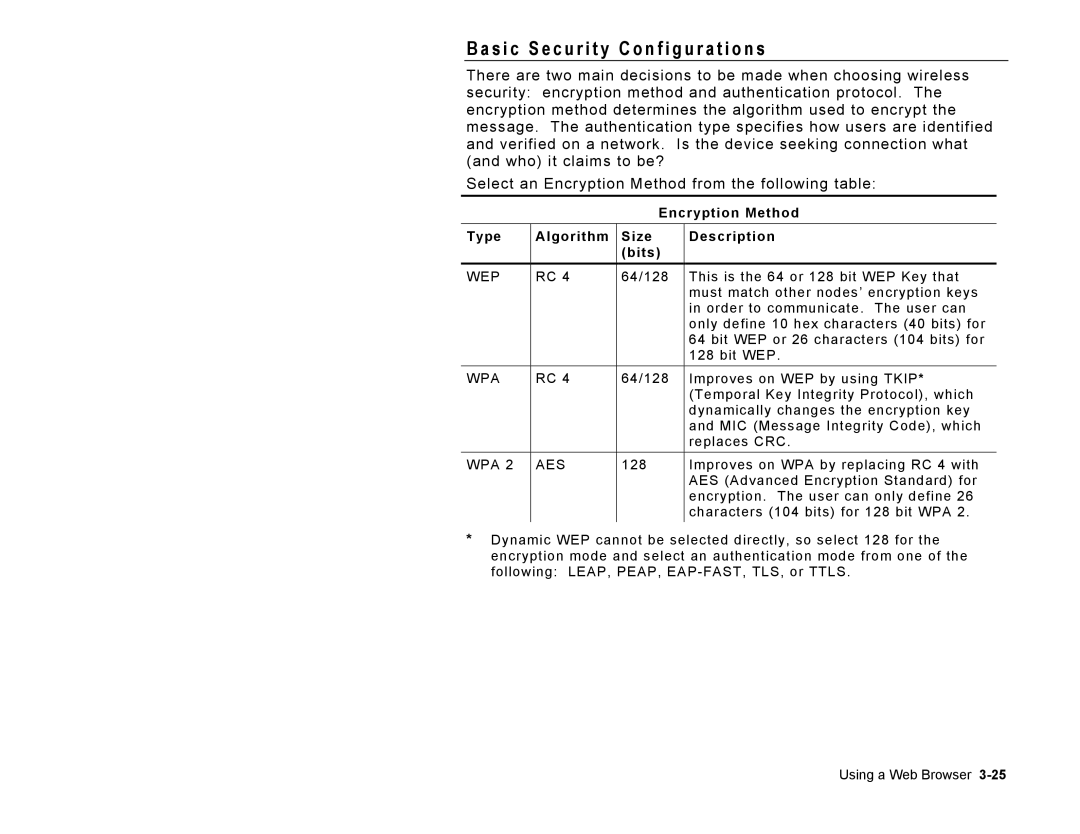
Select an Encryption Method from the following table:
Encryption Method
Type | Algorithm | Size | Description |
|
| (bits) |
|
WEP | RC 4 | 64/128 | This is the 64 or 128 bit WEP Key that |
|
|
| must match other nodes’ encryption keys |
|
|
| in order to communicate. The user can |
|
|
| only define 10 hex characters (40 bits) for |
|
|
| 64 bit WEP or 26 characters (104 bits) for |
|
|
| 128 bit WEP. |
WPA | RC 4 | 64/128 | Improves on WEP by using TKIP* |
|
|
| (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), which |
|
|
| dynamically changes the encryption key |
|
|
| and MIC (Message Integrity Code), which |
|
|
| replaces CRC. |
WPA 2 | AES | 128 | Improves on WPA by replacing RC 4 with |
|
|
| AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for |
|
|
| encryption. The user can only define 26 |
|
|
| characters (104 bits) for 128 bit WPA 2. |
*Dynamic WEP cannot be selected directly, so select 128 for the encryption mode and select an authentication mode from one of the following: LEAP, PEAP,