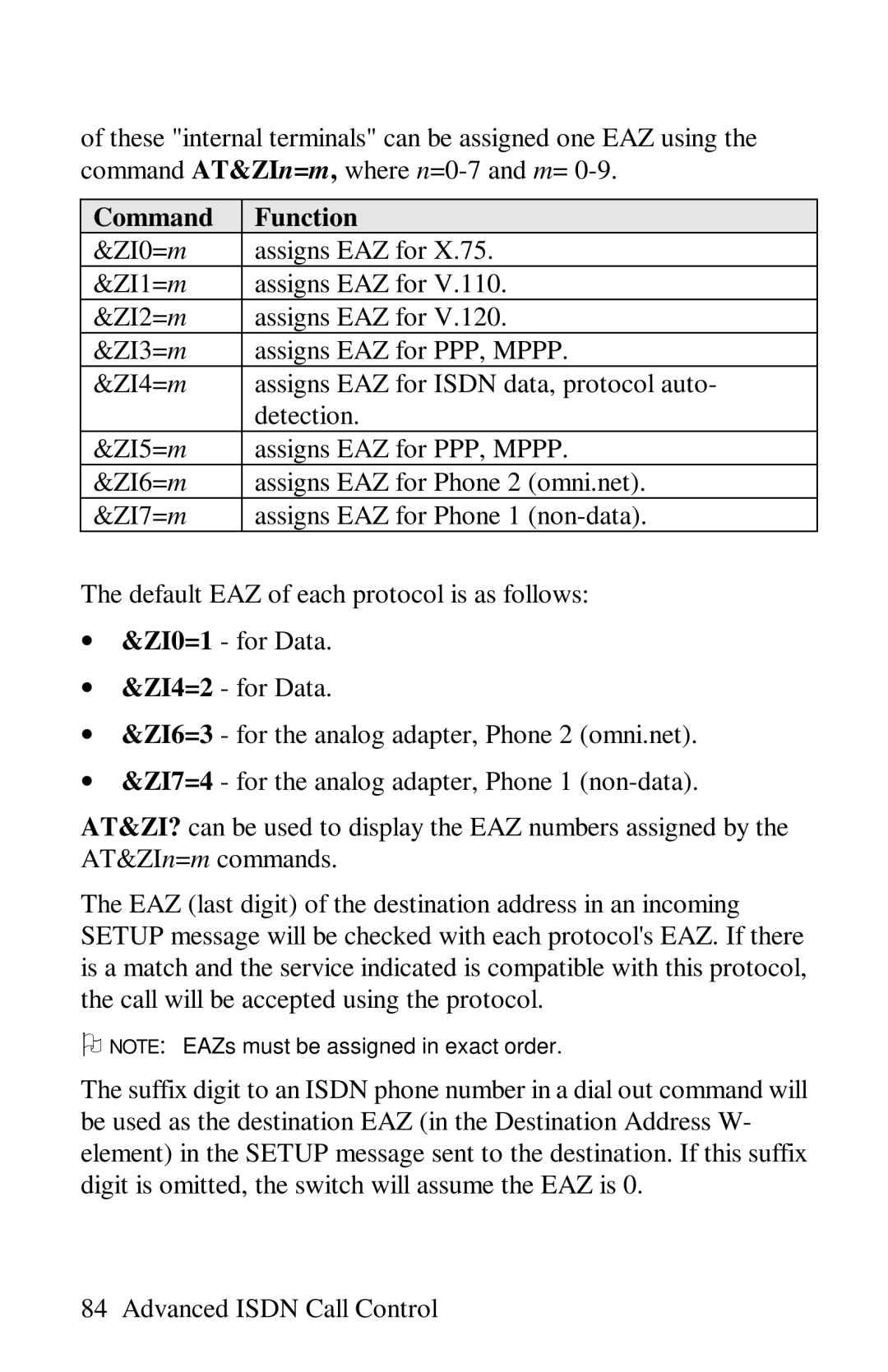
of these "internal terminals" can be assigned one EAZ using the command AT&ZIn=m, where
Command | Function |
&ZI0=m | assigns EAZ for X.75. |
&ZI1=m | assigns EAZ for V.110. |
&ZI2=m | assigns EAZ for V.120. |
&ZI3=m | assigns EAZ for PPP, MPPP. |
&ZI4=m | assigns EAZ for ISDN data, protocol auto- |
| detection. |
&ZI5=m | assigns EAZ for PPP, MPPP. |
&ZI6=m | assigns EAZ for Phone 2 (omni.net). |
&ZI7=m | assigns EAZ for Phone 1 |
The default EAZ of each protocol is as follows:
∙&ZI0=1 - for Data.
∙&ZI4=2 - for Data.
∙&ZI6=3 - for the analog adapter, Phone 2 (omni.net).
∙&ZI7=4 - for the analog adapter, Phone 1
AT&ZI? can be used to display the EAZ numbers assigned by the AT&ZIn=m commands.
The EAZ (last digit) of the destination address in an incoming SETUP message will be checked with each protocol's EAZ. If there is a match and the service indicated is compatible with this protocol, the call will be accepted using the protocol.
ONOTE: EAZs must be assigned in exact order.
The suffix digit to an ISDN phone number in a dial out command will be used as the destination EAZ (in the Destination Address W- element) in the SETUP message sent to the destination. If this suffix digit is omitted, the switch will assume the EAZ is 0.
84 Advanced ISDN Call Control