Agilent 34401A ½ Digit Multimeter
U T I O N WA RN I N G
Safety Information
Protection Limits
Additional Notices
Declaration of Conformity
Convenient Bench-Top Features
Flexible System Features
Front Panel at a Glance
Menu Operation keys
SYStem Menu
Front-Panel Menu at a Glance
TRIGger Menu
Input / Output Menu
Key as you
Adrs Rmt Man Trig Hold Mem Ratio Math Error Rear Shift 4W
Display Annunciators
Rear Panel at a Glance
Use the front-panel Input / Output Menu to
This Book
Contents
Contents
Application Programs
Error Messages
Remote Interface Reference
Index Declaration of Conformity
Specifications
Measurement Tutorial
Quick Start
Quick Start
To Prepare the Multimeter for Use
Connect the power cord and turn on the multimeter
To Prepare the Multimeter for Use
Check the list of supplied items
Verify that the power-line fuse is good
Verify that there is ac power to the multimeter
Verify the power-line voltage setting
If the Multimeter Does Not Turn On
Replace the fuse-holder assembly in the rear panel
Bench-top viewing positions Carrying position
To Adjust the Carrying Handle
To Adjust the Carrying Handle
To Measure Voltage
To Measure Voltage
To Measure Resistance
To Measure Current
To Measure Current
To Measure Frequency or Period
To Test Continuity
To Test Continuity
To Check Diodes
To Select a Range
To Select a Range
To Set the Resolution
To Set the Resolution
Front-Panel Display Formats
To Rack Mount the Multimeter
To Rack Mount the Multimeter
Quick Start
Front-Panel Menu Operation
Front-Panel Menu Operation
Front-Panel Menu Reference
Front-Panel Menu Reference
Front-Panel Menu Reference SYStem Menu
Secured
Front-Panel Menu Tutorial
Front-Panel Menu Tutorial
Messages Displayed During Menu USE
Menu Bottom You pressed
Turn on the menu
Move across to the SYS Menu choice on this level
Save the change and turn off the menu
Move across to the Beep command on the commands level
Move down a level to the Beep parameter choices
Move across to the on choice
Use menu recall to return to the Beep command
Move down to the Beep parameter choices
Math Menu
Increment the first digit until 2 is displayed
Move down to edit the Null Value parameter
Make the number negative
Increase the displayed number by a factor
To Turn Off the Comma Separator
Move down a level and then across to the Comma command
To Turn Off the Comma Separator
Move across to the SYS Menu choice on the menus level
Result = reading null value
To Make Null Relative Measurements
To Make Null Relative Measurements
To Store Minimum and Maximum Readings
To Store Minimum and Maximum Readings
DB = reading in dBm relative value in dBm
To Make dB Measurements
To Make dB Measurements
DBm = 10 ⋅ Log10 reading2 / reference resistance / 1 mW
To Make dBm Measurements
To Make dBm Measurements
To Trigger the Multimeter
To Trigger the Multimeter
To Use Reading Hold
To Use Reading Hold
To Make dcvdcv Ratio Measurements
To Make dcvdcv Ratio Measurements
Move down to the parameter level
Move down a level and then across to the Ratio Func command
Meas Menu
To Use Reading Memory
Select the single trigger mode
Move down to a level to the Rdgs Store command
To Use Reading Memory
This takes you to the Saved Rdgs command in the SYS Menu
Turn off the menu
Move down a level to view the first stored reading
Move across to view the two remaining stored readings
Features and Functions
Features and Functions
Math Operations, starting on Triggering, starting on
Measurement Configuration
Measurement Configuration
AC Signal Filter
Applies to ac voltage and ac current measurements only
Continuity Threshold Resistance
See also To Test Continuity, on
DC Input Resistance
Input R Meas Menu
Resolution
Resolution Choices Integration Time
This is the 10 Vdc range, 51⁄2 digits are displayed
Remote Interface Operation You can set the resolution using
Resolution setting. The default mode is 5 digits slow
See also To Set the Resolution, on
Following commands
Integration Time Resolution
Integration Time
Remote Interface Operation
Front / Rear Input Terminal Switching
Default 51⁄2 digits, or 1 second 61⁄2 digits
Returns Fron or Rear
Resolution Choices Integration Time Autozero
Autozero
Measurement Configuration Autozero
Front-panel settings
Ranging
Input voltage, not its frequency
Remote Interface Operation You can set the range using any
Autoranging or manual ranging. For frequency and period
See also To Select a Range, on
Freq Per Cont Diode Ratio Null Min-Max DBm Limit
Math Operations
Math Operations
See also To Store Minimum and Maximum Readings, on
Min-Max Operation
MIN-MAXMATH Menu
Null Relative Operation
See also To Make Null Relative Measurements, on
Math Operations Null Relative
Entering a null value also turns on the null function
See also To Make dB Measurements, on
DB Measurements
DB REL Math Menu
See also To Make dBm Measurements, on
DBm Measurements
DBm REF R Math Menu
Set the upper limit
Limit Testing
Enable or disable limit test
Set the lower limit
Reading that exceeds the upper or lower limit
Limit testing
More information
RS-232 interface circuitry may be damaged
Triggering
Triggering
Trigger
State
Wait-for
Front-panel
Key is disabled when in remote
Trigger Source Choices
Key is disabled when in remote Remote Interface Operation
See also External Trigger Terminal, on
TRIGgerSOURce IMMediate
Wait-for-Trigger State
Halting a Measurement in Progress
Number of Samples
Front-Panel Operation
Number of Triggers
Trigger Delay
Auto Delay
Trigger Delay
Zero Delay
DC Voltage and DC Current for all ranges
Automatic Trigger Delays
Resistance 2-wire and 4-wire
AC Voltage and AC Current for all ranges
See also To Use Reading Hold, on
Reading Hold
Read Hold Trig Menu
Voltmeter Complete Terminal
External Trigger Terminal
System-Related Operations
System-Related Operations
Reading Memory
SYS Menu
Error Conditions
Error SYS Menu
Returns 0 if the self-test is successful, or 1 if it fails
Self-Test
Test SYS Menu
Display SYS Menu
Disable/enable the display
Display Control
Display the string enclosed in quotes
Beeper Control
Issue a single beep immediately
Disable/enable beeper state
Beep SYS Menu
Comma SYS Menu
Comma Separators
Firmware Revision Query
See also To Turn Off the Comma Separator, on
Scpi Language Version Query
You cannot query the Scpi version from the front panel
Gpib Address
Remote Interface Configuration
Remote Interface Configuration
Gpib address can be set only from the front-panel
See also To Select the Remote Interface, on
Remote Interface Selection
Remote interface can be set only from the front-panel
Gpib RS-232
Parity I/O Menu
Baud Rate Selection RS-232
Parity Selection RS-232
Programming Language Selection
Language I/O Menu
Calibration Overview
Calibration Overview
Calibration Security
Characters
Calibration Security
Secured CAL Menu
Unsecured CAL Menu
Enter new code
Calibration Count
Unsecure with old code
Calibration Message
Operator Maintenance
Operator Maintenance
To Replace the Power-Line Fuse
To Replace the Current Input Fuses
Power-On and Reset State
Power-On and Reset State
102
Remote Interface Reference
Command Summary, starting on
Remote Interface Reference
Command Summary
Command Summary
106
107
See page 124 for more information
CALCulate
See page 127 for more information
See page 132 for more information
110
111
Simplified Programming Overview
MEASure? and CONFigure Preset States
Command MEASure? and CONFigure Setting
Simplified Programming Overview
Using the MEASure? Command
Using the CONFigure Command
You must specify a range to use the resolution parameter
Using the range and resolution Parameters
Using the READ? Command
Before sending the second query command
Using the INITiate and FETCh? Commands
To avoid this, do not send a query command without reading
MEASure?
Simplified Programming Overview CONFigure
MEASure? and CONFigure Commands
MEASure? and CONFigure Commands
MEASureCONTinuity?
MEASureDIODe?
CONFigureCURRentDC rangeMINMAXDEF,resolutionMINMAXDEF
CONFigure?
CONFigureCONTinuity
CONFigureDIODe
Measurement Configuration Commands
Measurement Configuration Commands
FREQuencyAPERture? MINimumMAXimum
FunctionRESolution resolutionMINimumMAXimum
FunctionRESolution? MINimumMAXimum
PERiodAPERture? MINimumMAXimum
SENSeZEROAUTO Offonceon
SENSeDETectorBANDwidth 320200MINimumMAXimum
SENSeDETectorBANDwidth? MINimumMAXimum
SENSeZEROAUTO?
Math Operation Commands
Math Operation Commands
CALCulateAVERageAVERage?
CALCulateAVERageMINimum?
CALCulateAVERageMAXimum?
CALCulateAVERageCOUNt?
DATAFEED?
See also Triggering, starting on page 71 in chapter
128
129
READ?
Triggering Commands
Triggering Commands
TRIGgerDELayAUTO Offon
TRIGgerDELay secondsMINimumMAXimum
TRIGgerDELay? MINimumMAXimum
TRIGgerDELayAUTO?
System-Related Commands
System-Related Commands
IDN?
RST
TST?
Scpi Status Model
What is an Event Register?
What is an Enable Register?
Scpi Status Model
Scpi Status System
Bit Decimal Definition Value
Status Byte
Bit Definitions Status Byte Register
Using Service Request SRQ and Serial Poll
U t i o n
To Determine When a Command Sequence is Completed
Using *STB? to Read the Status Byte
To Interrupt Your Bus Controller Using SRQ
How to Use the Message Available Bit MAV
Using *OPC to Signal When Data is in the Output Buffer
Standard Event Register
Bit Definitions Standard Event Register
Scpi Status Model
Questionable Data Register
Bit Definitions Questionable Data Register
143
CLS
Status Reporting Commands
Status Reporting Commands
ESE?
OPC?
ESR?
OPC
PSC?
Calibration Commands
Calibration Commands
CALibrationVALue value
CALibrationSTRing quoted string
CALibrationSTRing?
CALibrationVALue?
RS-232 Interface Configuration
RS-232 Interface Configuration
RS-232 Configuration Overview
Even / 7 data bits, factory setting or Odd / 7 data bits
RS-232 Data Frame Format
Connection to a Computer or Terminal
RS-232 Interface Configuration
DTR / DSR Handshake Protocol
Multimeter sets the DTR line False in the following cases
RS-232 Troubleshooting
RS-232 Interface Commands
RS-232 Interface Commands
SENSe
An Introduction to the Scpi Language
An Introduction to the Scpi Language
Command Format Used in This Manual
Command Separators
Using the MIN and MAX Parameters
Querying Parameter Settings
Scpi Command Terminators
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
Scpi Parameter Types
Type of Output Data Output Data Format
Output Data Formats
Output Data Formats
Talk only for Printers
Using Device Clear to Halt Measurements
Using Device Clear to Halt Measurements
To Set the Gpib Address
Move down a level to the HP-IB Addr command
To Set the Gpib Address
Turn on the front-panel menu
To Select the Remote Interface
Move down a level and then across to the Interface command
To Select the Remote Interface
Move down to the parameter level to select the interface
To Set the Baud Rate
Move down a level and then across to the Baud Rate command
To Set the Baud Rate
Move down to the parameter level to select the baud rate
To Set the Parity
Move down a level and then across to the Parity command
To Set the Parity
Move down to the parameter level to select the parity
To Select the Programming Language
Move down a level and then across to the Language command
To Select the Programming Language
O Menu
Alternate Programming Language Compatibility
Agilent 3478A Language Setting
Alternate Programming Language Compatibility
Fluke 8840A/8842A Language Setting
Fluke 8840A Description Agilent 34401A Action Command
Scpi Compliance Information
Scpi Compliance Information
IEEE-488 Compliance Information
Dedicated Hardware Lines Addressed Commands
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
IEEE-488 Compliance Information
170
Error Messages
Error Messages
Execution Errors
121
Execution Errors 112
113
123
158
Execution Errors 151
Invalid string data
String data not allowed
223
Execution Errors 221
222
224
420
Execution Errors 350
410
430
511
Execution Errors 501
502
512
602
Self-Test Errors
601
603
Calibration Errors
705
Calibration Errors 703
704
706
731
Calibration Errors 725
730
732
Application Programs
Application Programs
Gpib Operation Using Basic
Using MEASure? for a Single Measurement
Using MEASure? for a Single Measurement
Gpib Operation Using QuickBASIC
Using CONFigure with a Math Operation
Using CONFigure with a Math Operation
187
On next
Using the Status Registers
Using the Status Registers
Using the Status Registers Gpib Operation Using Basic
END While
Using the Status Registers Gpib Operation Using QuickBASIC
191
RS-232 Operation Using QuickBASIC
RS-232 Operation Using QuickBASIC
RS-232 Operation Using Turbo C
RS-232 Operation Using Turbo C
194
195
196
Measurement Tutorial
Thermal EMF Errors
Copper-to Approx. ∝V / C
Loading Errors dc volts
Loading Errors dc volts
Leakage Current Errors
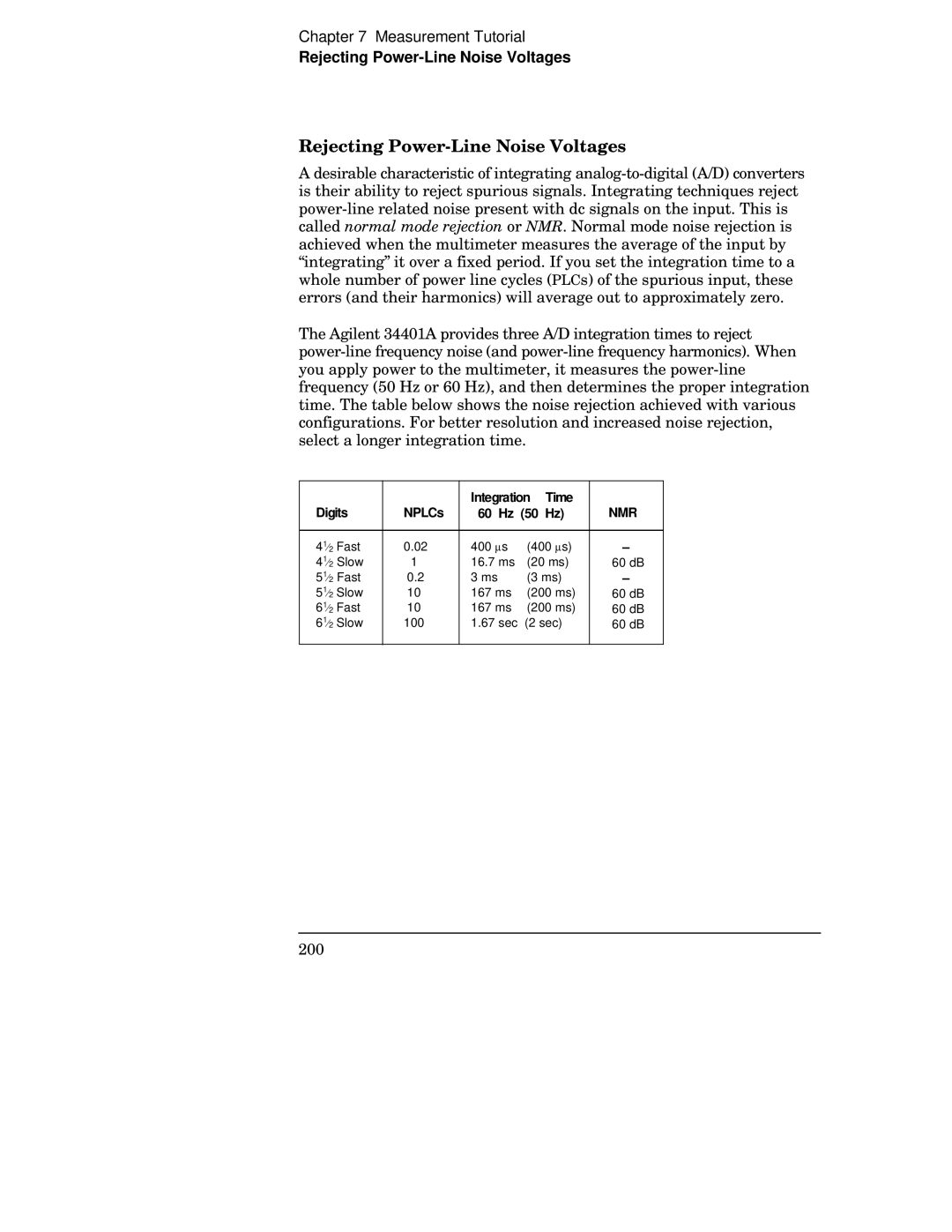
Digits NPLCs Integration Time
Rejecting Power-Line Noise Voltages
Rejecting Power-Line Noise Voltages
60 Hz 50 Hz
Noise Caused by Magnetic Loops
Common Mode Rejection CMR
Common Mode Rejection CMR
Noise Caused by Ground Loops
Noise Caused by Ground Loops
Resistance Measurements
Wire Ohms Measurements
Resistance Measurements
Removing Test Lead Resistance Errors
Removing Test Lead Resistance Errors
Power Dissipation Effects
Settling Time Effects
Errors in High Resistance Measurements
Errors in High Resistance Measurements
DC Current Measurement Errors
True RMS AC Measurements
True RMS AC Measurements
Ac + dc = √ ac2 + dc2
Crest Factor Errors non-sinusoidal inputs
Crest Factor Errors non-sinusoidal inputs
Bandwidth Error = C.F x F
Additional error for high frequencies
Loading Errors ac volts
Loading Errors ac volts
For low frequencies
Measurements Below Full Scale
High-Voltage Self-Heating Errors
Temperature Coefficient and Overload Errors
Measurements Below Full Scale
Voltage Measured = √
Low-Level Measurement Errors
Low-Level Measurement Errors
+ Noise
Common Mode Errors
Common Mode Errors
AC Current Measurement Errors
Making High-Speed DC and Resistance Measurements
Frequency and Period Measurement Errors
Frequency and Period Measurement Errors
Making High-Speed AC Measurements
Making High-Speed AC Measurements
Specifications
DC Characteristics
DC Characteristics
DC Characteristics Measuring Characteristics
Operating Characteristics
AC Characteristics
AC Characteristics
AC Characteristics Measuring Characteristics
Frequency and Period Characteristics
Frequency and Period Characteristics
Frequency and Period
Measurement Considerations
General Information
General Information
Product Dimensions
Product Dimensions
Range Input Level Reading Error
To Calculate Total Measurement Error
To Calculate Total Measurement Error
Range Input Level Range Error
Input error =
Ppm of input error =
100
Number of Digits and Overrange
Interpreting Multimeter Specifications
Interpreting Multimeter Specifications
Sensitivity
Specification Probability Criteria Failure
Accuracy
Hour Accuracy
Temperature Coefficients
Transfer Accuracy
Day and 1-Year Accuracy
Configuring for Highest Accuracy Measurements
Configuring for Highest Accuracy Measurements
230
Index
Ext Trig, 5 VM Comp, 5
Index
233
234
235
236