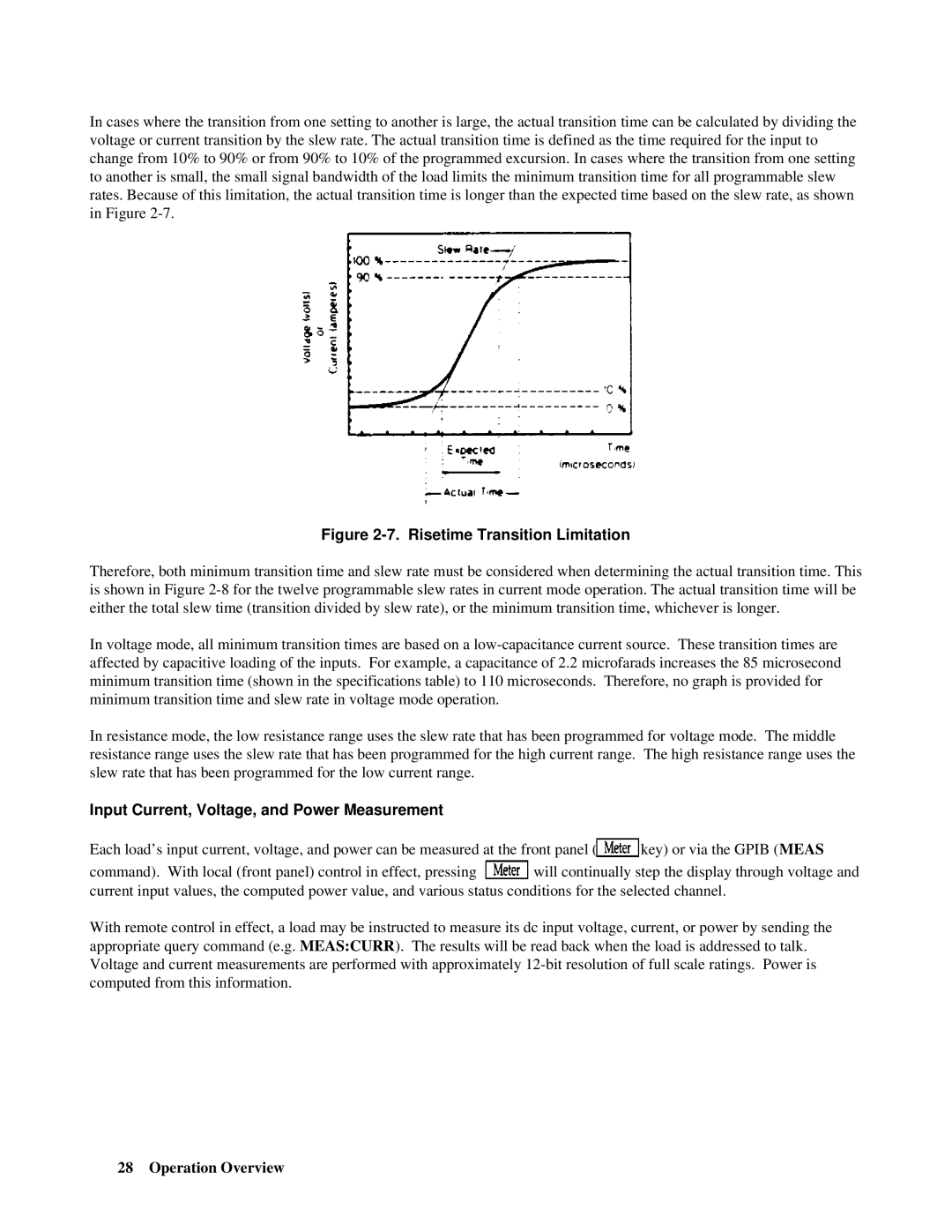
In cases where the transition from one setting to another is large, the actual transition time can be calculated by dividing the voltage or current transition by the slew rate. The actual transition time is defined as the time required for the input to change from 10% to 90% or from 90% to 10% of the programmed excursion. In cases where the transition from one setting to another is small, the small signal bandwidth of the load limits the minimum transition time for all programmable slew rates. Because of this limitation, the actual transition time is longer than the expected time based on the slew rate, as shown in Figure
Figure 2-7. Risetime Transition Limitation
Therefore, both minimum transition time and slew rate must be considered when determining the actual transition time. This is shown in Figure
In voltage mode, all minimum transition times are based on a
In resistance mode, the low resistance range uses the slew rate that has been programmed for voltage mode. The middle resistance range uses the slew rate that has been programmed for the high current range. The high resistance range uses the slew rate that has been programmed for the low current range.
Input Current, Voltage, and Power Measurement
Each load’s input current, voltage, and power can be measured at the front panel (![]() key) or via the GPIB (MEAS
key) or via the GPIB (MEAS
command). With local (front panel) control in effect, pressing ![]() will continually step the display through voltage and current input values, the computed power value, and various status conditions for the selected channel.
will continually step the display through voltage and current input values, the computed power value, and various status conditions for the selected channel.
With remote control in effect, a load may be instructed to measure its dc input voltage, current, or power by sending the appropriate query command (e.g. MEAS:CURR). The results will be read back when the load is addressed to talk. Voltage and current measurements are performed with approximately