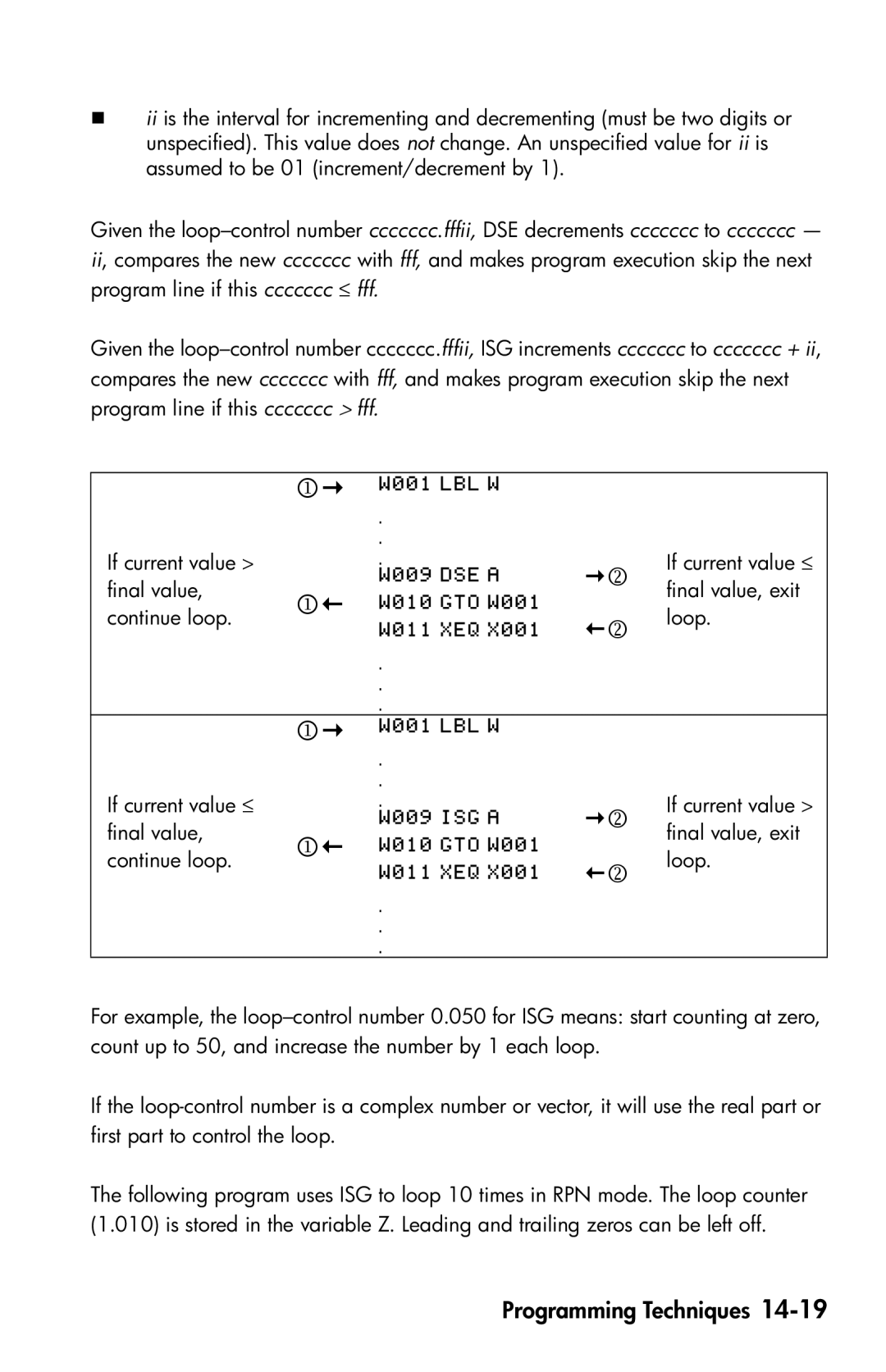
iiis the interval for incrementing and decrementing (must be two digits or unspecified). This value does not change. An unspecified value for ii is assumed to be 01 (increment/decrement by 1).
Given the
Given the
| 1 | |
|
| |
| . |
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
| . |
|
| |
If current value > |
| . | 2 | If current value ≤ | |
final value, |
| | final value, exit | ||
1 | | ||||
continue loop. |
| loop. | |||
| 2 | ||||
| | ||||
|
| . |
|
| |
|
| . |
|
| |
|
| . |
|
| |
| 1 | |
|
| |
| . |
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
| . |
|
| |
If current value ≤ |
| . | 2 | If current value > | |
final value, |
| | final value, exit | ||
1 | | ||||
continue loop. |
| loop. | |||
| 2 | ||||
| | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
.
.
.
For example, the
If the
The following program uses ISG to loop 10 times in RPN mode. The loop counter (1.010) is stored in the variable Z. Leading and trailing zeros can be left off.