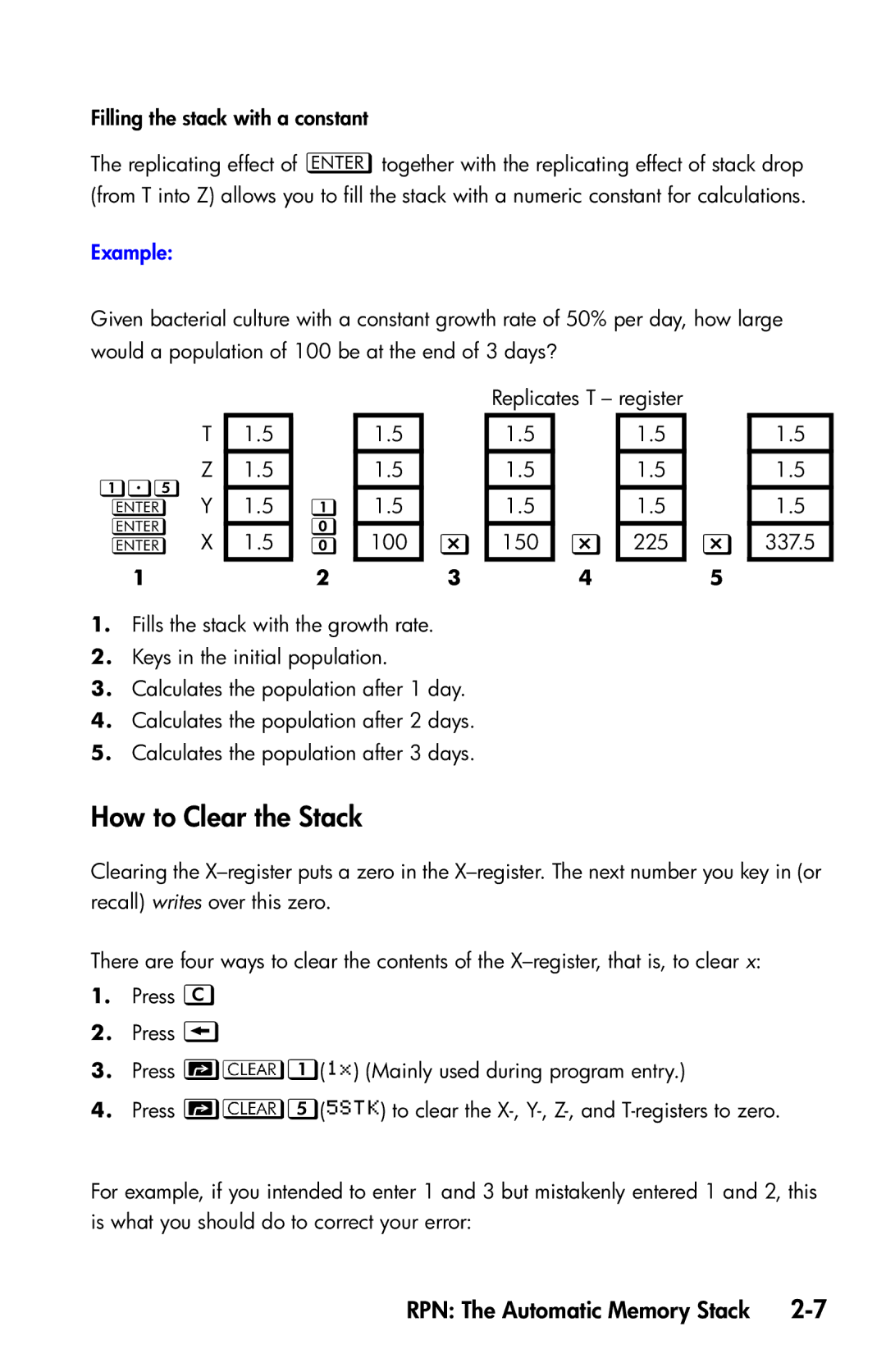
Filling the stack with a constant
The replicating effect of together with the replicating effect of stack drop (from T into Z) allows you to fill the stack with a numeric constant for calculations.
Example:
Given bacterial culture with a constant growth rate of 50% per day, how large would a population of 100 be at the end of 3 days?
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Replicates T – register |
|
|
| |||
| T | 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 | |
| Z | 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 | |
| 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
| 1.5 |
|
| 1.5 | ||
Y | |
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
X | 1.5 | 100 | | 150 | | 225 | |
| 337.5 | ||||
| |
| |||||||||||
1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
|
| |
1.Fills the stack with the growth rate.
2.Keys in the initial population.
3.Calculates the population after 1 day.
4.Calculates the population after 2 days.
5.Calculates the population after 3 days.
How to Clear the Stack
Clearing the
There are four ways to clear the contents of the
1.Press
2.Press
3.Press ![]() () (Mainly used during program entry.)
() (Mainly used during program entry.)
4.Press ![]() () to clear the
() to clear the
For example, if you intended to enter 1 and 3 but mistakenly entered 1 and 2, this is what you should do to correct your error: