TOC
TOC
INSTALLATION |
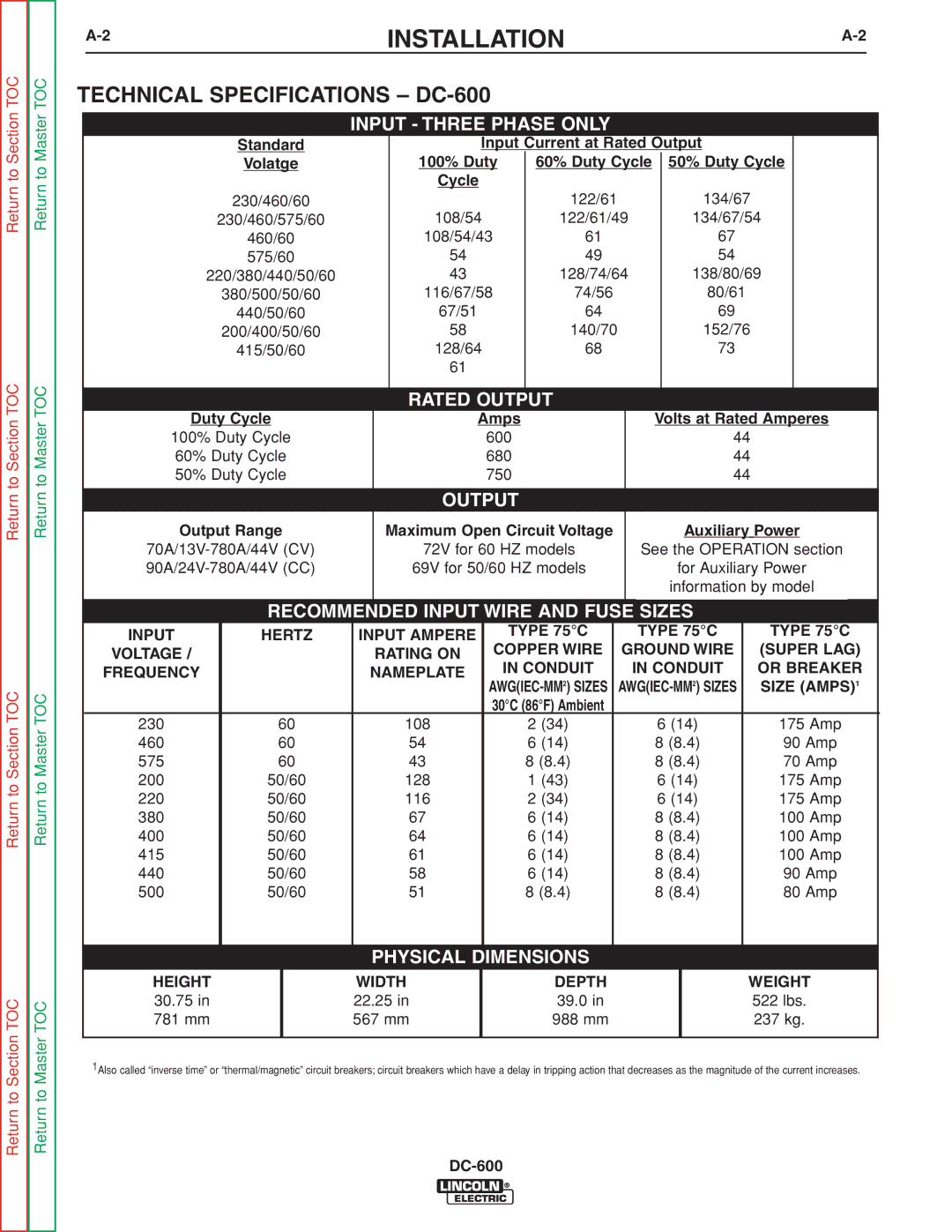
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – DC-600
INPUT - THREE PHASE ONLY
Return to Section
Return to Master
Standard
Volatge
230/460/60
230/460/575/60
460/60
575/60
220/380/440/50/60
380/500/50/60
440/50/60
200/400/50/60
415/50/60
Input Current at Rated Output
100% Duty 60% Duty Cycle 50% Duty Cycle
Cycle
| 122/61 | 134/67 |
108/54 | 122/61/49 | 134/67/54 |
108/54/43 | 61 | 67 |
54 | 49 | 54 |
43 | 128/74/64 | 138/80/69 |
116/67/58 | 74/56 | 80/61 |
67/51 | 64 | 69 |
58 | 140/70 | 152/76 |
128/64 | 68 | 73 |
61 |
|
|
TOC
TOC
RATED OUTPUT
Return to Section
Return to Master
Duty Cycle
100% Duty Cycle
60% Duty Cycle
50% Duty Cycle
Output Range
Amps
600
680
750
OUTPUT
Maximum Open Circuit Voltage
72V for 60 HZ models
69V for 50/60 HZ models
Volts at Rated Amperes
44
44
44
Auxiliary Power
See the OPERATION section
for Auxiliary Power
information by model
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
RECOMMENDED INPUT WIRE AND FUSE SIZES
INPUT | HERTZ | INPUT AMPERE | TYPE 75°C | TYPE 75°C | TYPE 75°C | |
COPPER WIRE | GROUND WIRE | (SUPER LAG) | ||||
VOLTAGE / |
| RATING ON | ||||
| IN CONDUIT | IN CONDUIT | OR BREAKER | |||
FREQUENCY |
| NAMEPLATE | ||||
| SIZE (AMPS)1 | |||||
|
|
| ||||
|
|
| 30°C (86°F) Ambient |
|
| |
230 | 60 | 108 | 2 (34) | 6 (14) | 175 Amp | |
460 | 60 | 54 | 6 (14) | 8 (8.4) | 90 Amp | |
575 | 60 | 43 | 8 (8.4) | 8 (8.4) | 70 Amp | |
200 | 50/60 | 128 | 1 (43) | 6 (14) | 175 Amp | |
220 | 50/60 | 116 | 2 (34) | 6 (14) | 175 Amp | |
380 | 50/60 | 67 | 6 (14) | 8 (8.4) | 100 Amp | |
400 | 50/60 | 64 | 6 (14) | 8 (8.4) | 100 Amp | |
415 | 50/60 | 61 | 6 (14) | 8 (8.4) | 100 Amp | |
440 | 50/60 | 58 | 6 (14) | 8 (8.4) | 90 Amp | |
500 | 50/60 | 51 | 8 (8.4) | 8 (8.4) | 80 Amp | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
HEIGHT | WIDTH | DEPTH | WEIGHT |
30.75 in | 22.25 in | 39.0 in | 522 lbs. |
781 mm | 567 mm | 988 mm | 237 kg. |
|
|
|
|
1Also called “inverse time” or “thermal/magnetic” circuit breakers; circuit breakers which have a delay in tripping action that decreases as the magnitude of the current increases.