Understanding Netopia NAT Behavior
Appendix C
Understanding Netopia NAT Behavior
This appendix describes how Network Address Translation (NAT) works within the Netopia R910. The Netopia R910 implements a powerful feature called Network Address Translation as specified in RFC 1631. NAT is used for IP address conservation and for security purposes since there will only be a single IP “presence” on the WAN. This appendix describes the NAT functionality within the Netopia R910 and provides examples for setup and use.
Network configuration
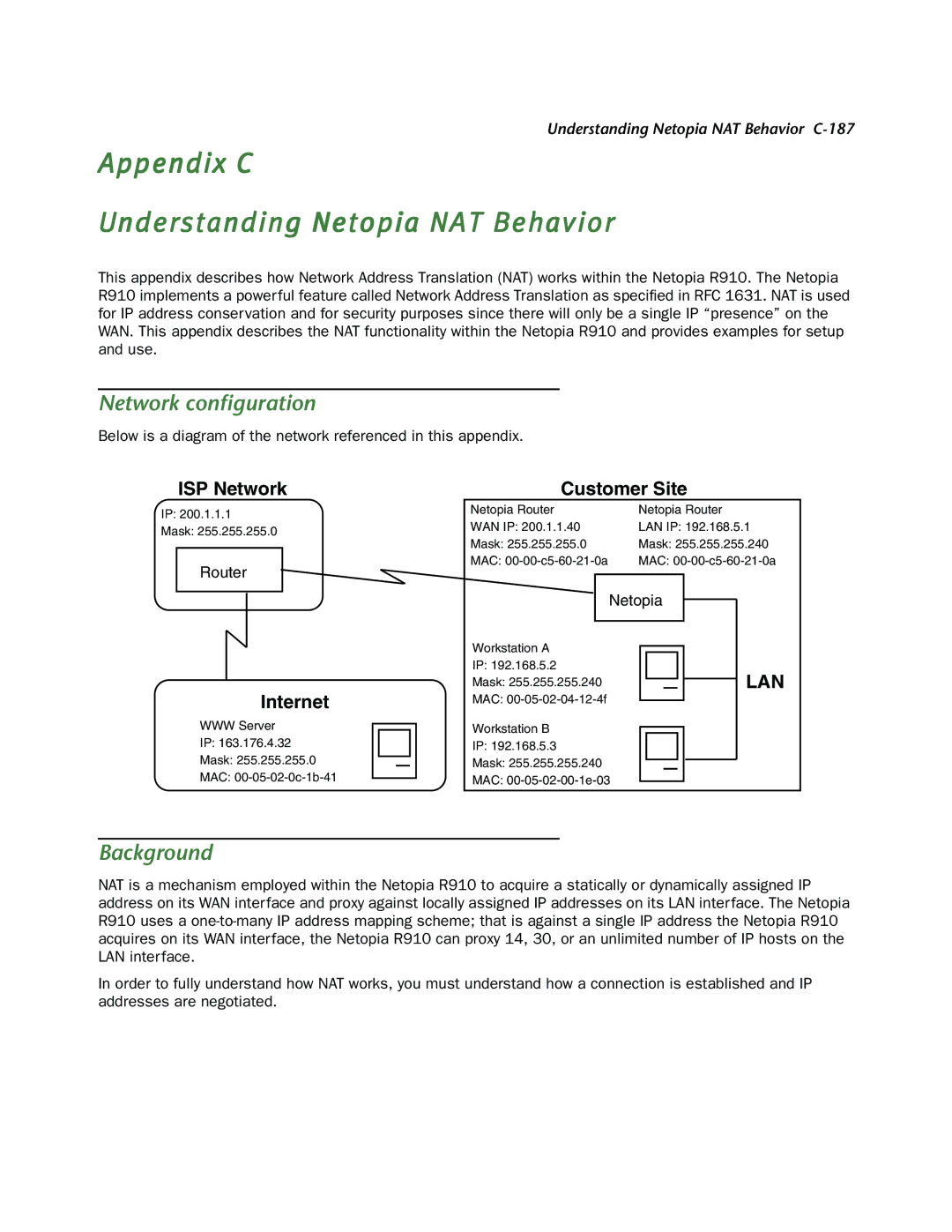
Below is a diagram of the network referenced in this appendix.
ISP Network
IP: 200.1.1.1
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Router
Internet
WWWServer
IP: 163.176.4.32
Mask: 255.255.255.0
MAC:
Customer Site
Netopia Router | Netopia Router | ||||||
WAN IP: 200.1.1.40 | LAN IP: 192.168.5.1 | ||||||
Mask: 255.255.255.0 | Mask: 255.255.255.240 | ||||||
MAC: | MAC: | ||||||
Workstation A | Netopia |
|
| ||||
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
IP: 192.168.5.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| LAN |
Mask: 255.255.255.240 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
MAC: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Workstation B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
IP: 192.168.5.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mask: 255.255.255.240 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
MAC:
Background
NAT is a mechanism employed within the Netopia R910 to acquire a statically or dynamically assigned IP address on its WAN interface and proxy against locally assigned IP addresses on its LAN interface. The Netopia R910 uses a
In order to fully understand how NAT works, you must understand how a connection is established and IP addresses are negotiated.