Understanding IP Addressing
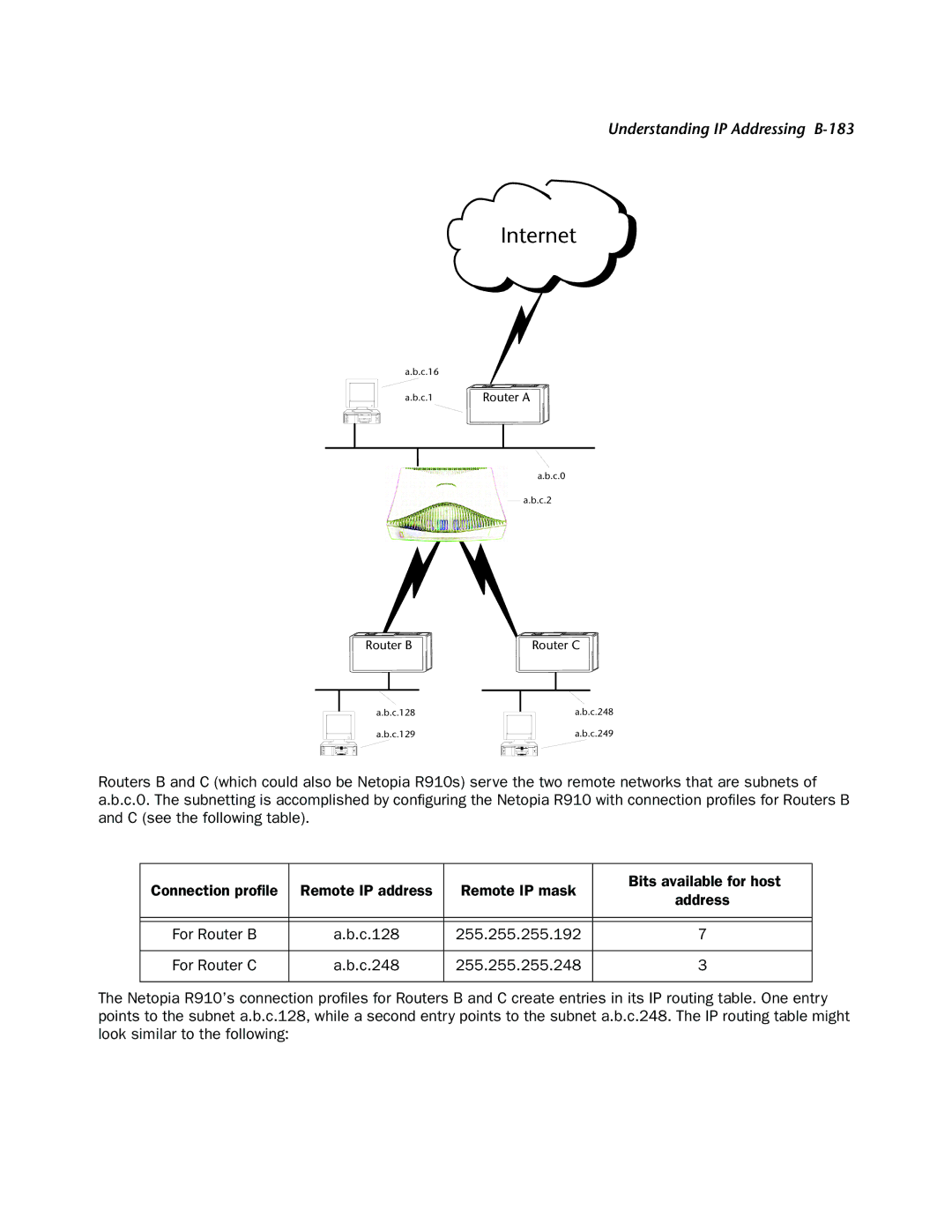
Internet
a.b.c.16
a.b.c.1 | Router A |
a.b.c.0
a.b.c.2
Router B
Router C
a.b.c.128
a.b.c.129
a.b.c.248
a.b.c.249
Routers B and C (which could also be Netopia R910s) serve the two remote networks that are subnets of a.b.c.0. The subnetting is accomplished by configuring the Netopia R910 with connection profiles for Routers B and C (see the following table).
Connection profile | Remote IP address | Remote IP mask | Bits available for host | |
address | ||||
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
For Router B | a.b.c.128 | 255.255.255.192 | 7 | |
|
|
|
| |
For Router C | a.b.c.248 | 255.255.255.248 | 3 | |
|
|
|
|
The Netopia R910’s connection profiles for Routers B and C create entries in its IP routing table. One entry points to the subnet a.b.c.128, while a second entry points to the subnet a.b.c.248. The IP routing table might look similar to the following: