B-184 User’s Reference Guide
|
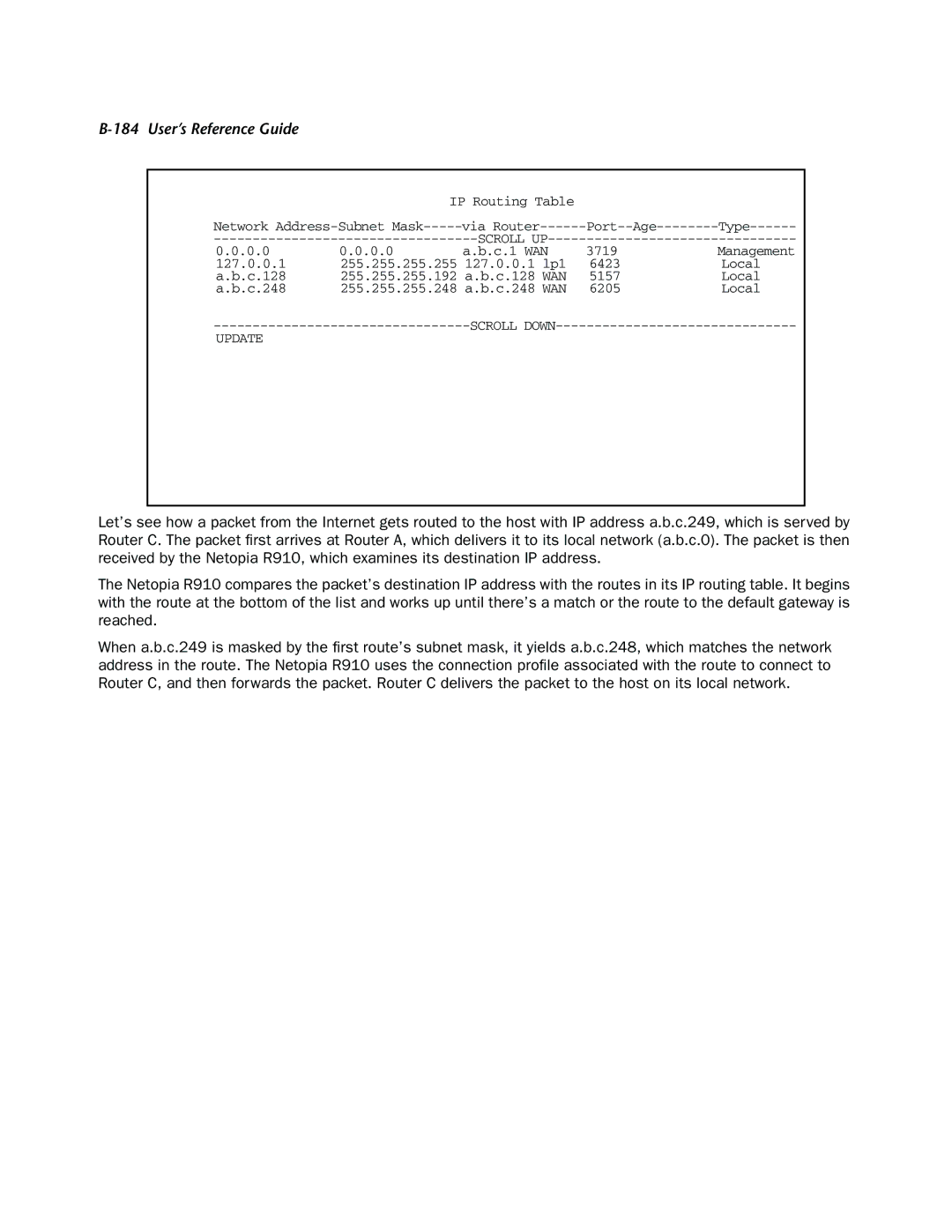
| IP Routing Table |
|
|
Network | via | |||
SCROLL |
| |||
0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | a.b.c.1 WAN | 3719 | Management |
127.0.0.1 | 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1 lp1 | 6423 | Local | |
a.b.c.128 | 255.255.255.192 a.b.c.128 WAN | 5157 | Local | |
a.b.c.248 | 255.255.255.248 a.b.c.248 WAN | 6205 | Local | |
UPDATE
Let’s see how a packet from the Internet gets routed to the host with IP address a.b.c.249, which is served by Router C. The packet first arrives at Router A, which delivers it to its local network (a.b.c.0). The packet is then received by the Netopia R910, which examines its destination IP address.
The Netopia R910 compares the packet’s destination IP address with the routes in its IP routing table. It begins with the route at the bottom of the list and works up until there’s a match or the route to the default gateway is reached.
When a.b.c.249 is masked by the first route’s subnet mask, it yields a.b.c.248, which matches the network address in the route. The Netopia R910 uses the connection profile associated with the route to connect to Router C, and then forwards the packet. Router C delivers the packet to the host on its local network.