MN1030 Series Cross Assembler User’s Manual
Page
Page
Reference Techniques
Manual Features
Heading
How to read
Program example
Usage note
Related Manuals
Chapter Writing Macro Control Statements
Purpose of This Chapter
Purpose of This Chapter Rules of Usage Usage Example
Chapter Types of Source Statements
Writing Assembler Control Statements
Readinig List Files
Error Correction Using Tag Jumps 306
Chapter
Purpose of This Chapter
Host machine Operating system Version of OS
Operating Environment
Solaris Or later
98/Me/2000/XP
As103 assembler
File Organization
Ld103 linker
Slib103 library manager
Installation
Setting command path
Setup
Start-up files
Keywordparameter
Start-up file format
Message
Keyword Description
Notation
Option
Ed-OPTION
En-OPTION
Stdlib
Libdir
File Conversion Utility
General command format
Options
Excv103 options EX format file name
Rules of output file name
Default specification
Example of specifying options
Program Development Flow
Program Development Flow
Main development flow
Program Development Flow
Assembler and compiler
Source code debugger
Programming with Assembler
Reference , Using Linker, for details
Required knowledge
Program format
Optimization
Programming style
Macros
Conditional assembly
Debugging
Program Development Flow Programming with Assembler
Introduction to Operation
Introduction to Operation
Files Used
Files Used by Assembler and Linker
Introduction to Operation
Create source files
Basic Operation of Assembler and Linker
Assemble
Contents of program2.asm are as follows
Generate final list files
Link
Contents of the final list file program1.lst are as follows
Contents of the final list file program2.lst are as follows
Assembling and Linking Multiple Sections
Assemble and generate list files
Contents of program4.asm are as follows
DATA, PUBLIC,4
Contents of the list file program4.lst are as follows
Parameter file during linking
Following command was input to link
CAE0 Data
Contents of the final list file program4.lst are as follows
Program Location
Program locations after linking
Create source file
Conditional Assembly and Linking
#ifdef
Assemble and link the program that you have created
Assemble and link
Select false condition, assemble, and link
Specify assembly conditions in the command
As103 -D Debug program5.asm
Introduction to Operation Conditional Assembly and Linking
Chapter Optimization
Has been optimized
Rules of Usage
Optimization is off by default
Optimization Instructions
Usage Example
Optimized Conditional Branch Instructions Type Branch Range
Instruction Type Branch Range
Abs, Dn
Abs, An
An, abs
Dn, abs Movhu abs, Dn Movhu Dn, abs
Instruction
Logical Instructions Subject To Optimization
Btst imm, Dn
Optimization processing
Assembler processing
Optimization processing of conditional branch instructions
Linker processing
BNE*+5
Optimization of function calls
BRA label
Optimization of branches
Label JMP label
Label JMP label Call label Calls label JSR label
Optimization
Optimization
Opt
Text
CA7F
Example subroutine call converted to a relative branch
Using Assembler
Using Asssembler
Starting Assembler
General format of commands
Specifying options
Summary of options
Command Options
Functional description
Output File Options
Rules of Use
Operation Example
As103 -l sample.asm
Output a list file
No list file will be output
As103 -Li -l sample.asm
Do not output files included by include to the list file
As103 -l -Li sampl.asm
As103 -l -Lm sampl.asm
As103 -Lm -l sample.asm
As103 -l -Lc sampl.asm
As103 -Lc -l sample.asm
Symbol table will be output
Do not output a symbol table to the list file
As103 -Ls -l sample.asm
As103 -a sample.map -l sample.asm
As103 -j sample.asm
Error Message Options
This option is not available on DOS/V or PC/AT machines
As103 -Je sample.asm
As103 -Js sample.asm
As103 -Jj sample.asm
As103 -e sample.asm
Output error and warning messages in English
As103 -W 2001 sample.asm
Default is to display all warning messages
Wall Do not output any warning messages
As103 -Wall sample.asm
Pathname Specify the trace directory of the include file
Preprocessor Options
As103 -I/user/defs main.asm
As103 -D Version sample.asm
Output debug information to the relocatable object file
Program Generation Options
Executable format file .EX
As103 -g sample.asm
As103 -O sample.asm
Turn on optimization
Turn off optimization
As103 -Od sample.asm
As103 -h
Other Options
On the screen
Display the assemblers version number on the console
Operation Examples
Program assembly
As103 -g -D Version -o test.rf /user/source/main.asm
As103 -g -o test.rf -I /user/lib sample.asm
As103 -l -a main.map sub.asm
As103 -l -Lc -Lm -a main.map -D Mode prog1.asm
Chapter Using Linker
Link Model of Section Address Format
Ld103 options relocatableobjectfilename Libraryfilename
Starting Linker
Jmg
Main.ex -gm
@CODE=80000000 or -T @CODE=80000000
Path specifications on the relocatable object files
M103.map, respectively
Executable file
Linker options Option Type Symbol Description
Command Options
Ld103 -o /usr/tmp/test.ex main.rf sub.rf
Ld103 -m main.rf sub.rf
Output a map file
Ld103 -m -TTEXT=80000000 -TCONST=80005000 prog1.rf prog2.rf
Ld103 -j sample.rf
Ld103 -Je sample.rf
Ld103 -Js sample.rf
Ld103 -Jj sample.rf
Ld103 -e sample.rf
Ld103 -W3001 progr1.rf prog2.rf
Function description
Ld103 -Wall main.rf sub.rf
Ld103 -g main.rf sub.rf
Output debug information to the executable format file
Section =addresses Specify starting address for a section
Section layout rules
Ld103 main.rf sub.rf
Lowest section is referred to the section name
Ld103 -T @CODE=80000000 -T@DATA=0 main.rf sub.rf
Parameter file
Letter
Ld103 -r prog1.rf
Output an executable format file even if errors are detected
En option cannot be used in conjunction with the g option
Ld103 -En main.rf sub.rf
Output the Data section to the executable file
Ld103 -Ed main.rf sub.rf
Libraryfilename Specify a library file
Library File Options
Ld103 -l /usr/lib/sample.lib main.rf sub.rf
Message will be appeared
Library files specified by the l option will be read
Pathname Specify a directory containing library files
@filename Specify a parameter file
Operational example
Ld103 @pfile
Ld103
Ld103 -h
Instruction RAM Support
Structural Elements of an Iram Support Executable
Structure of Iram Support Executable File
Number field to
Layout Image for Instruction RAM and External Memory
These names for ordinary symbols
Using Linker
Same result
Iram Support Options
Starting address in instruction RAM is given in hexadecimal
Overlaytable Irammanage
PUT symbol=address Specify address for extra symbol
Address is in hexadecimal
Assigning to different addresses in instruction RAM
Operation Examples
Assignment to the same address in instruction RAM
Overlaps with actual code
Conflicts and suppresses executable file output
Using Linker Instruction RAM Support
Types of Source Statements
Type of Source Statements
Program Format
Equ 0x32
#include
Dataset Macro
Movw Data, A0 0x12 D0, A0 Endm
Directive statements
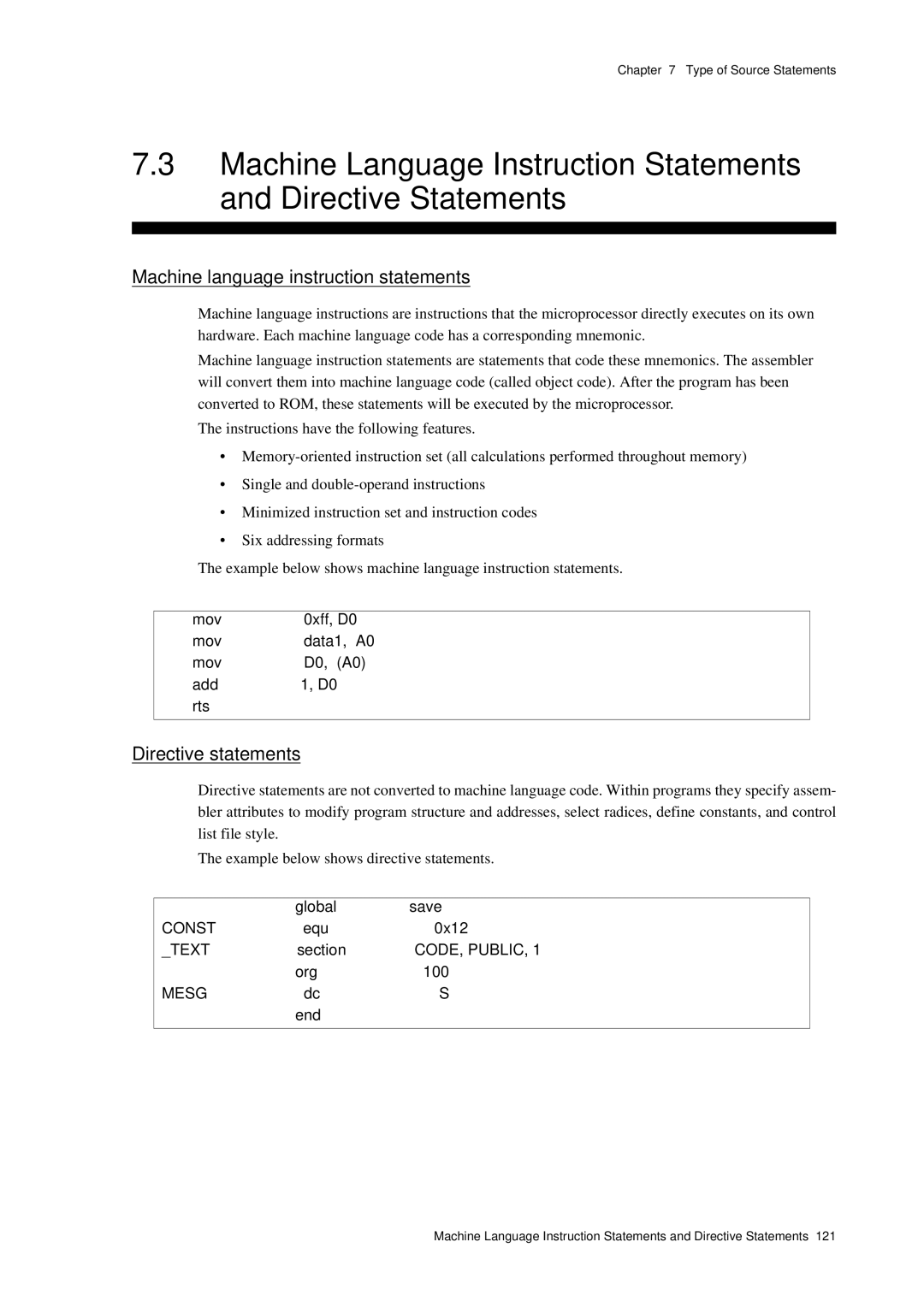
Machine language instruction statements
#else Mov 0x22, D0
Assembler Control Statements
Mov 0x11, D0
Adrset Macro data, reg Mov Reg, A0 Data, D0 D0, A0 Endm
Macro Control Statements
Adrset Data1, reg1 Data2, reg2
Comment Statements
Conditional assembly definition
Program Start main
Blank Statements
Type of Source Statements Blank Statements
Writing Source Statements
Writing Source Statements
Digits
Permitted Characters
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Letters
Radices and allowed digits
Numbers
C D E F or
Re hexadecimal digits that correspond to decimal
Intel format
Extended C language format
Coding rules
’101’
Matsushita format
’567’
’789’
Character constants
Character Constants
Specifies the string Abcdefg as Ascii code
String constants
+-&%$#@ Specifies the string +-&%$#@!,. as Ascii code
Specified
Example
Address Constants
Location Counter
Assembler or linker
Expressions
Section CODE,PUBLIC,1
Sec
Arithmetic operators
Operators
Shift operators
Operator Meaning
Logical operators perform calculation in bit units
Logical operators
Formats Example Operand1 Operand2
Precedence Operator Description
Expression Evaluation
Equ 0b01101110
Mov 10+5, d0
Expression Syntax
Mov +10+5, d0
Mov 10+5+2, d0
Operation result attributes
Expression Attributes
For ~, +, unary operators
Attribute of Operand Attribute of Result
For subtraction operator
For + addition operator
For *, /, %, , , &, , operators
D0, d1, d2, d3, a0, a1,a2, a3, PSW, mdr, sp
Reserved Words
Define, if Ifb, ifdef, ifeq, ifge, ifgt, ifle
Iflt, ifn, ifnb, ifndef, ifneq, include, undef
Page
Purpose of This Chapter
Coding rules
Instruction Statement Fields
Coding examples
Writing Label Field
Label Longlabellonglabellonglabellonglab main Startcont
Equ
Writing Operation Field
Start Mov
One operand
Writing Operand Field
Operands are register and expression
Jsr
Mov 0x10, D0
Writing Comment Field
Set count value
Writing Machine Language Instruction Statements
List of directives
Writing Directive Statements
Document conventions
Below is a list of directives
Section
Default settings
Syntax
Section linking rules
Directive coding rules
Operand coding rules
Usage example
Main Jsr
Label Operation Operand Align Expression
Align
Current location counter value will be inherited
00000000
Below is an example use of the align directive
0x01
Label
3 end
Name end
Below is an example use of the end directive
Label operation operand Name listoff Name liston
Listoff, liston
Listoff and liston directives themselves are output
These directives take no operands
Label Operation Operand Notation
Notation
Clang will be selected
Operand Format
Notation
Below is an example use of the notation directive
Secadr
6 org
Secfnc Org 0x20
Org 0x100 End
Opt on Opt off
7 opt
Number of lines = Number of columns =
Label Operation Operand Linesexpression ,columnsexpression
Below is an example use of the page directive
Label Operation Operand Radix Expression
Radix
Another radix
Below is an example use of the radix directive
10 dc
11 ds
When expression2 is omitted, expression3 cannot be specified
PanaX Series MN1030 Cross Assembler Loc Object Line Source
Below is an example use of the ds directive
Ds0
1122
Section DATA, Public
12 dw
3930 Dw0 dw 12345
34127856 Dw1 dw 0x1234
Label Operation Operand Name Expression, expression
13 dd
78563412 Dd0 0x12345678
00000000 Dd0
Label Operation Operand Name Equ Expression
14 equ
Memory equ Motor equ Stop equ 0b00001000 Base equ
Equ 0b00001000
Equ 0x20
Equ 0x1000
8020 Mov
Label Operation Operand Name Global Name, name
Global
External declaration
Below is an example use of the global directive
External reference
Mov 0x11, D0 Rts End
Label operation operand Titstring
16 tit
Below is an example use of the tit directive
Loc Object Line Source Tit
Name Xlistoff Xliston
Xlistoff, xliston
Xlistoff and xliston directives themselves are not output
These directives take no operand
Funcinfo
Directive Specification Rules
Usage Examples, Optimization of function calls
Call 0func Global 0func, func
Global 0func
Func Movm D2, SP Add 0func Funcinfo Func, 8, D2 Ret
Stack
Usage examples
Assign
Assign 0x01 00000000 8001 Mov
Assign 0x02 00000002 8002 Mov
Page
Writing Assembler Control Statements
Contents of brackets may be omitted
Symbols used in this chapter have the following meanings
Common coding rules
File Inclusion
#include filename
10.2.1 #include
Path name is coded within filename
File to be assembled consists of the following statements
Data equ
#include Inc.h
Main Mov Data, A0 0x34, D0 D0, A0 End
Identifier Definement
10.3.1 #define
#define Replacementstring comment
#define Data Load Mov Data, D0
Main Mov Data, D0 Load End
#undef identifier
10.3.2 #undef
Source file that uses #undef is shown below
#define Data1 0x11 Data2 0x22
Contents of brackets from #else on can be omitted
Conditional Assembly
#if
These directives can be used only within macro definitions
Table below lists the conditional assembly directives
Syntax for #ifdef Syntax for #ifndef
10.4.1 #ifdef, #ifndef
#ifdef Identifier #ifndef Block1 #else Block2 #endif
#ifndef
#else Mov 0x03, D1 0x04, D1 #endif
#else Mov 0x01, D0 0x02, D0 #endif #ifndef
8001 Mov 0x01, D0 #else 0x02, D0 #endif #ifndef
10X Mov 0x03, D1 #else
Syntax for #if Syntax for #ifn
10.4.2 #if, #ifn
#ifn
#if
#else Mov 0x03, D0 0x04, D0 #endif
#else Mov 0x01, D0 0x02, D0 #endif #ifn
Mov 0x01, D0 #else
8002 Mov 0x02, D0 #endif #ifn
#ifeq
10.4.3 #ifeq, #ifneq
#ifneq
Compare Abc, abc Abc, acb
8002 11+ Mov 0x02, D0 #endif
M10 Compare Abc, abc 10+ #ifeq
#iflt
10.4.4 #iflt, #ifle
#ifle
12+ #iflt
M12 Dsize
12X Mov 0x01, D0 12+ #else
8002 12+ Mov 0x02, D0 #endif
#ifgt
10.4.5 #ifgt, #ifge
#ifge
#else Mov 0x01, D0 0x02, D0 #endif #ifge
8002 Mov 0x02, D0 #endif #ifge
#ifb
10.4.6 #ifb, #ifnb
#ifnb
Debugon
14+ #ifb Debugon 14X Jsr Check Proc #else 00000000
M14 Debug
+14+ Jsr Proc 00000008 00F8FE04 #endif #undef
M17 Debug
Writing Macro Control Statements
#include directive Macro definitions
Macroname
Macro Definitions macro, endm
Dummyparameter , dummyparameter
Macrobody
An example macro definition is shown below
Macroname Parameter , parameter
Macro Calls and Expansion
Up to10 dummy parameters can be specified
Var1 Equ 0x10 Var2 Var1+2 Addadr Macro Adr Adr, A0 Endm
Operator Description
Macro Operators
Text Section CODE,PUBLIC,1
Macroname macro parameter Local symbol , symbol Symbol
Local Symbol Declaration local
Up to 30 symbols can be specified
An example using the local directive is shown below
Parameter
Forced Termination of Macro Expansion exitm
#endif Exitm Endm
Test
Purge macroname , macroname
Purging Macro Definitions purge
Reptexpression block
Rept
Assembled list file is shown below
Irp
11.9 irp
Dummyparameter, parameter , parameter
Block
Irp
Irpc
Irpc
Dummyparameter, string
Following example uses the irpc directive
DATA, Public
Writing Macro Control Statements Irpc
List of Machine Language Instructions
List of Machine Language Instructions
Register indirect addressing
Addressing Modes
Register relative indirect addressing
Absolute addressing
Index addressing
List of Machine Language Instructions
Move source to destination
12.3.1 Data Move Instructions
Mnemonic Description of operation
Movhu
Index
Absolute
Extend Sign
ADD with Carry
Arithmetic Instructions
Subtract with Borrow
Compare source with destination
Source with destination
Logical Instructions
Or source with destination
EXCLUSIVE-OR source with destination
ASR imm8, Dn
Mnemonic Description of operation ASR Dm, Dn
ASR Dn
Mnemonic Description of operation LSR Dm, Dn
Bit operations
Bit Manipulation Instructions
Bclr imm8,abs32
Call Subroutine
Branching Instructions
Mnemonic Description of operation JMP An
Unconditional Branch
JMP label
Mnemonic Meaning Description of operation
Conditional Branch
ZF=1 If ZF = 0, execute next instruction
Conditional Branch for Loop
ZF=0 If ZF = 1, execute next instruction
If ZF = 1 or NF != VF, execute next instruction
User Defined Function
User-Defined Instructions
UDFnn Dm, Dn
UDFnn imm, Dn
Do nothing
Other Instructions
Error Messages
Error Messages
Assembler Errors
Define symbol multiple defined
Operand error
Define symbol not defined
Illegal operand value
Symbol name too long
Not guaranteed operand by the instruction allocation
Line of the source file exceed 65535 lines
Error Messages
Macro symbol is used recursively
Debug operand error
Illegal section name
Illegal operand expression
Too many arguments
Error in configure file
Can’t find Funcinfo directive
No optimizing information
Fatal Error Messages
Linker Errors
Filename Section not found. This file ignored
Extra symbolname address aligned. address
Filename Illegal sectionname attribute or align value
Address overlay with Iram manager
Multiply defined symbol
Bad option switch.string
Undefined symbol
Filename Symbolname not defined with FUNCINFO. line lineno
3313
Extra symbolname used as normal symbol
No memory space
Filename Invalid symbol detail information type.type
Fileneme Cannot open file
Filename Cannot read file
Internal Error.string
Filename Referring to symbolname defined in a programID=id
Filename Illegal relocation information.line lineno
Filename Illegal optimize information.line lineno
Error Messages Linker Errors
Readinig List Files
Reading List Files
Reading List Files
Location Loc
Output Format of Machine Language Code
Machine language code Object
Machine language code supplemental information
Supplemental information
Version
Source statement Source
Symbol Value
Symbol Table
Symbol Type
Symbols value is shown as eight hexadecimal digits
Symbol Name
Using Library Manager
Using Library Manager
Starting Library Manager
Slib103 test.lib -f -j test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -f -Je test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -f -Js test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slig103 test.lib -f -Jj test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Rules os use
Slib103 test.lib -f -e test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -Wall -c test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -W4001 -o test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -c test1.rf
Create a new library file
Slib103 test.lib -c test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf test4.rf
Name
Slib103 test.lib -f test1.rf
Force creation of a library file
Slib103 test.lib -f test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf test4.rf
Files with the same name
Slib103 test.lib -a test.1.rf
Functional Options
Slib103 test.lib -a test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Path name will be added in the library file
Slib103 test.lib -d test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -d test1.rf
Slib103 test.lib -p test1.rf slib103 test.lib -p
Slib103 test.lib -p
Slib103 Test.lib -r test1.rf test2.rf test3.rf
Slib103 test.lib -r test1.rf
File
Slib103 test.lib -t test1.rf slib103 test.lib -t
Slib103 test.lib -t test1.rf
Slib103 test.lib -x test1.rf slib103 test.lib
Slib103 test.lib -x test1.rf
Existing in the current directory
Slib103 @pfile
There is no default specification
Assume that the file pfile contains the following line
Slib103 -h
Default is not to display the version number
Display the library manager’s version number on the console
Slib103
Errornumber Displayedmessage
Error Messages
Cause Solutions
4001 Filename not found
4002 This file has no public symbol information.filename
4003 Filename not found. In addition to library
4312 Symbol name length over. max 66. symbol
4310 This file has redefined public symbol. filename
4301 Multiply specified object file name.filename
4302 Premature EOF. filename
4314 Cannot read parameter-file. filename
4313 Parameter-file already specified. filename
4315 Not warning message number
4501 Illegal option. string
4504 Memory allocation error
4502 Library file name not found
4503 Multiply specified library file name. filename
Page
Purpose of This Chapter
Personal Computer Versions
PC/ATWindows98/2000/Me/XP DOS/VWindows98/2000/Me/XP
Operating Environment
AS103.EXE Assembler
Files
LD103.EXE linker
SLIB103.EXE library manager
Installation
SET PATH=A\usr\local\bin
Environment Settings
New setting will then automatically take effect
Differences From Workstation Versions
Command line differences
Generate error file
Error Correction Using Tag Jumps
Contents of the generated error file Error are as follows
Contents of the file Error will be displayed on the screen
Fix errors
First error message matches this display on the screen
Tag jumps
MAIN.ASM7 Error 2306 Multiple define symbol
Return to error file
Appendix
Numeric Restrictions
List of Command Options
Assembler command general format
List of Assembler Command Options
Output file options
Preprocessor options
Error message options
Program generation options
Display the assembler’s version number on the console
Others
Linker command general format
List of Linker Command Options
Instruction RAM options
Library file options
Display help information on the console
Ld103 @ pfile
Display the linker’s version number on the console
List of Assembler Directives
Directives for symbols
Directives for program control
Syntax Function & Notes
Directives for list control
Directives for data area allocation
Other directives
Clang Extended C language format default
Intel Intel format
Pana Matsushita format
This section provides a list of assembler control statements
List of Assembler Control Statements
Syntax Function & Notes
Symbols
Machine language code supplemental information
Libraryfilename 103 Pathname 104 Label Field 148
Macro 207
Macroname 207
Undefined 142 173 Number Wall 313 289 Xlistoff 176 Xliston
Index
MN1030 Series Cross Assembler User’s Manual
Sales Offices