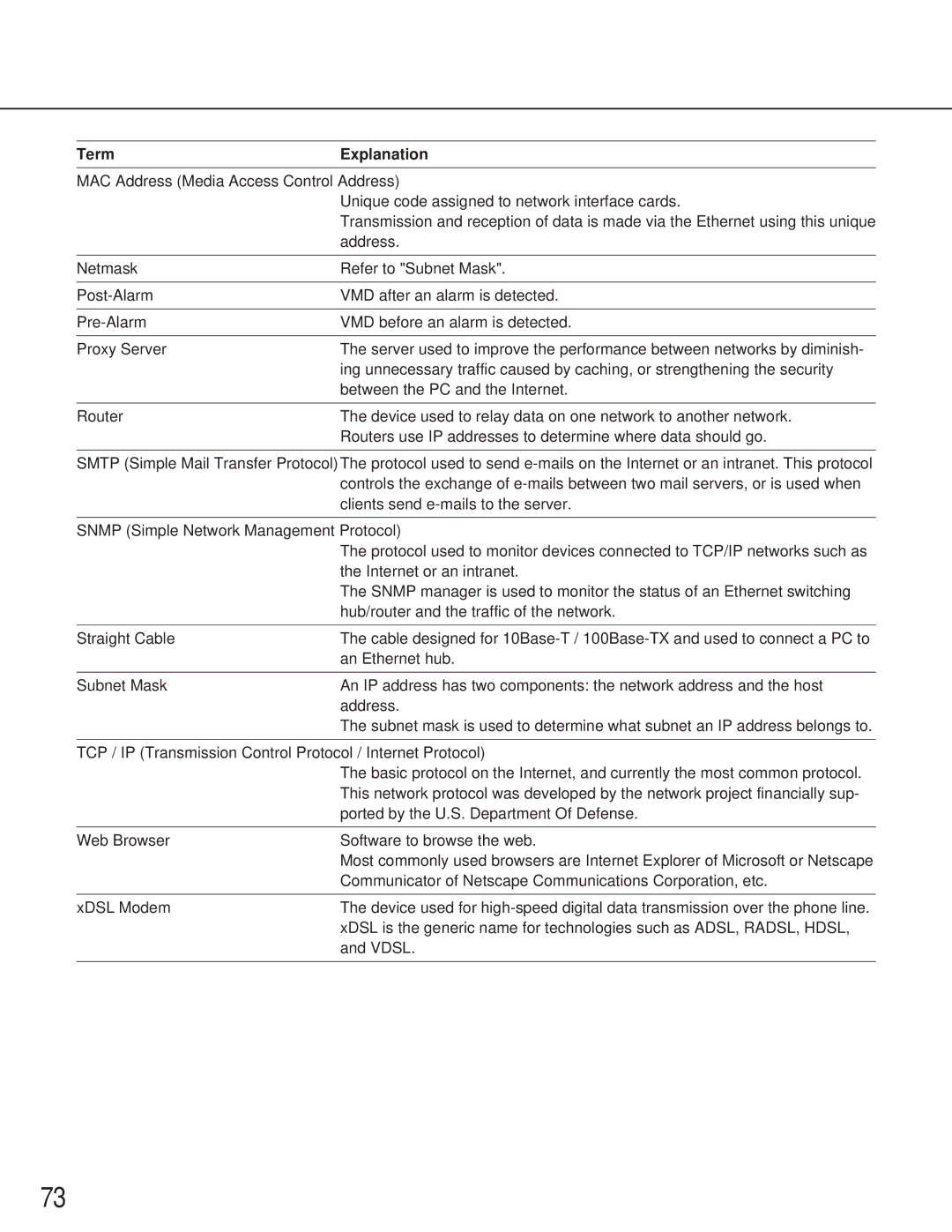
Term | Explanation |
MAC Address (Media Access Control Address)
Unique code assigned to network interface cards.
Transmission and reception of data is made via the Ethernet using this unique address.
Netmask | Refer to "Subnet Mask". |
VMD after an alarm is detected. | |
|
|
VMD before an alarm is detected. | |
|
|
Proxy Server | The server used to improve the performance between networks by diminish- |
| ing unnecessary traffic caused by caching, or strengthening the security |
| between the PC and the Internet. |
|
|
Router | The device used to relay data on one network to another network. |
| Routers use IP addresses to determine where data should go. |
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)The protocol used to send
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
The protocol used to monitor devices connected to TCP/IP networks such as the Internet or an intranet.
The SNMP manager is used to monitor the status of an Ethernet switching hub/router and the traffic of the network.
Straight Cable | The cable designed for |
| an Ethernet hub. |
|
|
Subnet Mask | An IP address has two components: the network address and the host |
| address. |
| The subnet mask is used to determine what subnet an IP address belongs to. |
TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol)
The basic protocol on the Internet, and currently the most common protocol. This network protocol was developed by the network project financially sup- ported by the U.S. Department Of Defense.
Web Browser | Software to browse the web. |
| Most commonly used browsers are Internet Explorer of Microsoft or Netscape |
| Communicator of Netscape Communications Corporation, etc. |
|
|
xDSL Modem | The device used for |
| xDSL is the generic name for technologies such as ADSL, RADSL, HDSL, |
| and VDSL. |
|
|
73