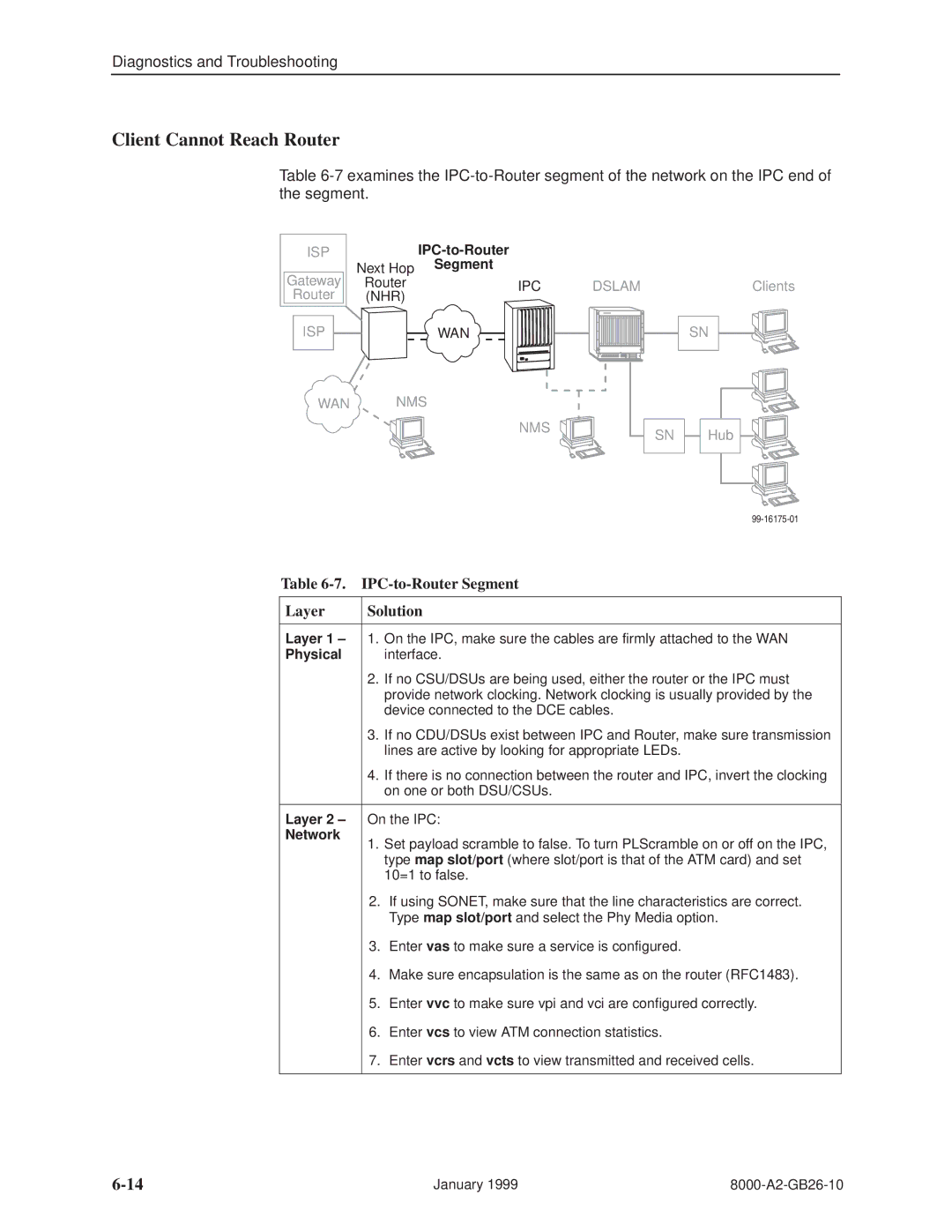
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Client Cannot Reach Router
Table
ISP |
|
| ||
| Next Hop | Segment |
|
|
Gateway |
|
|
| |
Router |
| IPC | DSLAM | |
Router | (NHR) |
|
|
|
ISP |
| WAN |
|
|
WAN | NMS |
|
|
|
|
|
| NMS | SN |
|
|
|
| |
Clients
SN
Hub ![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 6-7. IPC-to-Router Segment
Layer Solution
Layer 1 ± 1. On the IPC, make sure the cables are firmly attached to the WAN
Physical interface.
2.If no CSU/DSUs are being used, either the router or the IPC must provide network clocking. Network clocking is usually provided by the device connected to the DCE cables.
3.If no CDU/DSUs exist between IPC and Router, make sure transmission lines are active by looking for appropriate LEDs.
4.If there is no connection between the router and IPC, invert the clocking on one or both DSU/CSUs.
Layer 2 ± On the IPC: | |
Network |
|
1. Set payload scramble to false. To turn PLScramble on or off on the IPC, | |
| type map slot/port (where slot/port is that of the ATM card) and set |
| 10=1 to false. |
2. | If using SONET, make sure that the line characteristics are correct. |
| Type map slot/port and select the Phy Media option. |
3. | Enter vas to make sure a service is configured. |
4. | Make sure encapsulation is the same as on the router (RFC1483). |
5. | Enter vvc to make sure vpi and vci are configured correctly. |
6. | Enter vcs to view ATM connection statistics. |
7. | Enter vcrs and vcts to view transmitted and received cells. |
January 1999 |