Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Network Problems
To provide a practical aid in the isolation and resolution of Layer 2 network difficulties, the guidelines in this section provide information on troubleshooting a generic network containing the devices found in most networks.
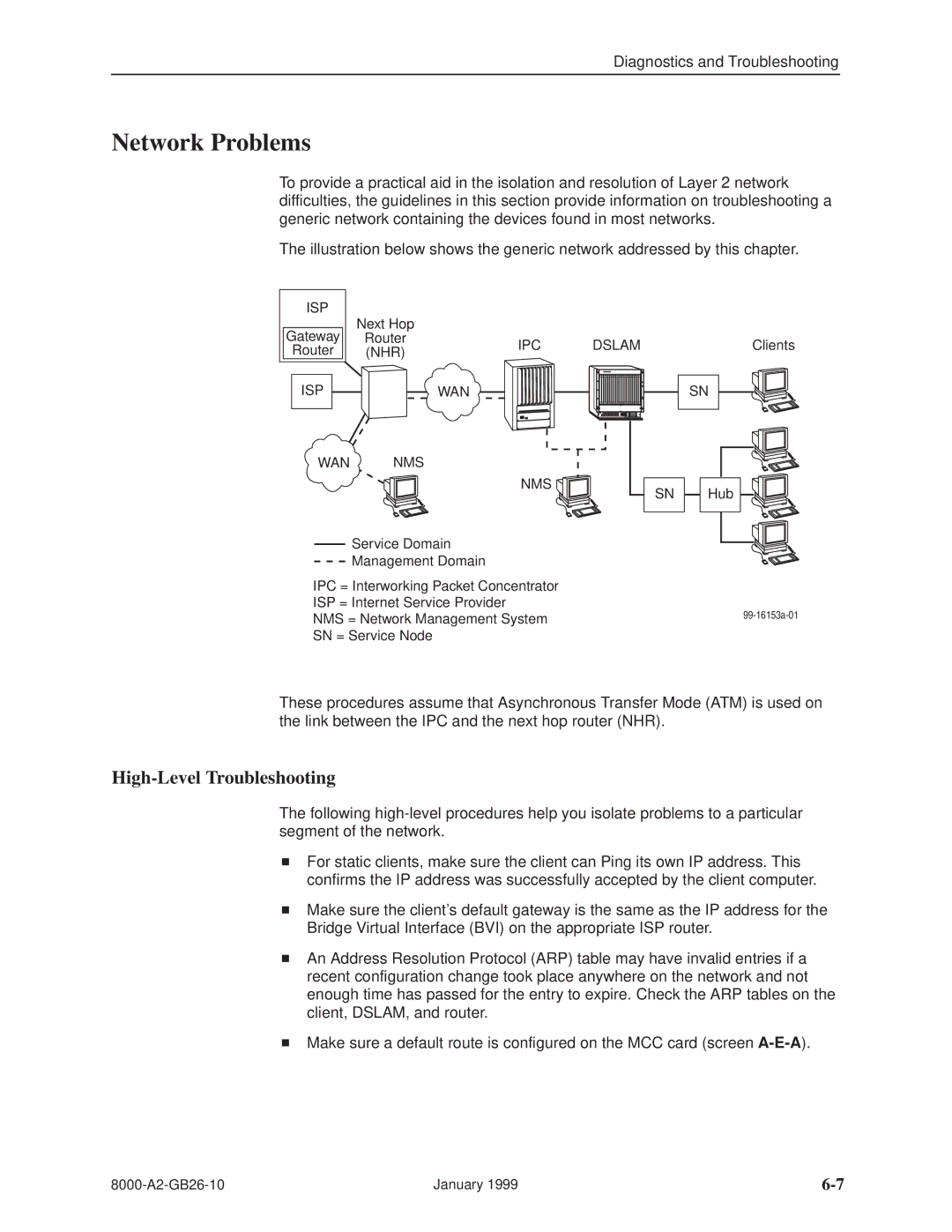
The illustration below shows the generic network addressed by this chapter.
ISP | Next Hop |
|
| |
Gateway |
|
| ||
Router | IPC | DSLAM | ||
Router | (NHR) | |||
|
| |||
ISP |
| WAN |
| |
WAN | NMS |
|
| |
|
| NMS | SN | |
|
|
|
Service Domain
Management Domain
IPC = Interworking Packet Concentrator
ISP = Internet Service Provider
NMS = Network Management System
SN = Service Node
Clients
SN
Hub ![]()
![]()
![]()
These procedures assume that Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is used on the link between the IPC and the next hop router (NHR).
High-Level Troubleshooting
The following
HFor static clients, make sure the client can Ping its own IP address. This confirms the IP address was successfully accepted by the client computer.
HMake sure the client's default gateway is the same as the IP address for the Bridge Virtual Interface (BVI) on the appropriate ISP router.
HAn Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table may have invalid entries if a recent configuration change took place anywhere on the network and not enough time has passed for the entry to expire. Check the ARP tables on the client, DSLAM, and router.
HMake sure a default route is configured on the MCC card (screen
January 1999 |