3.4 Flash-Write Algorithm
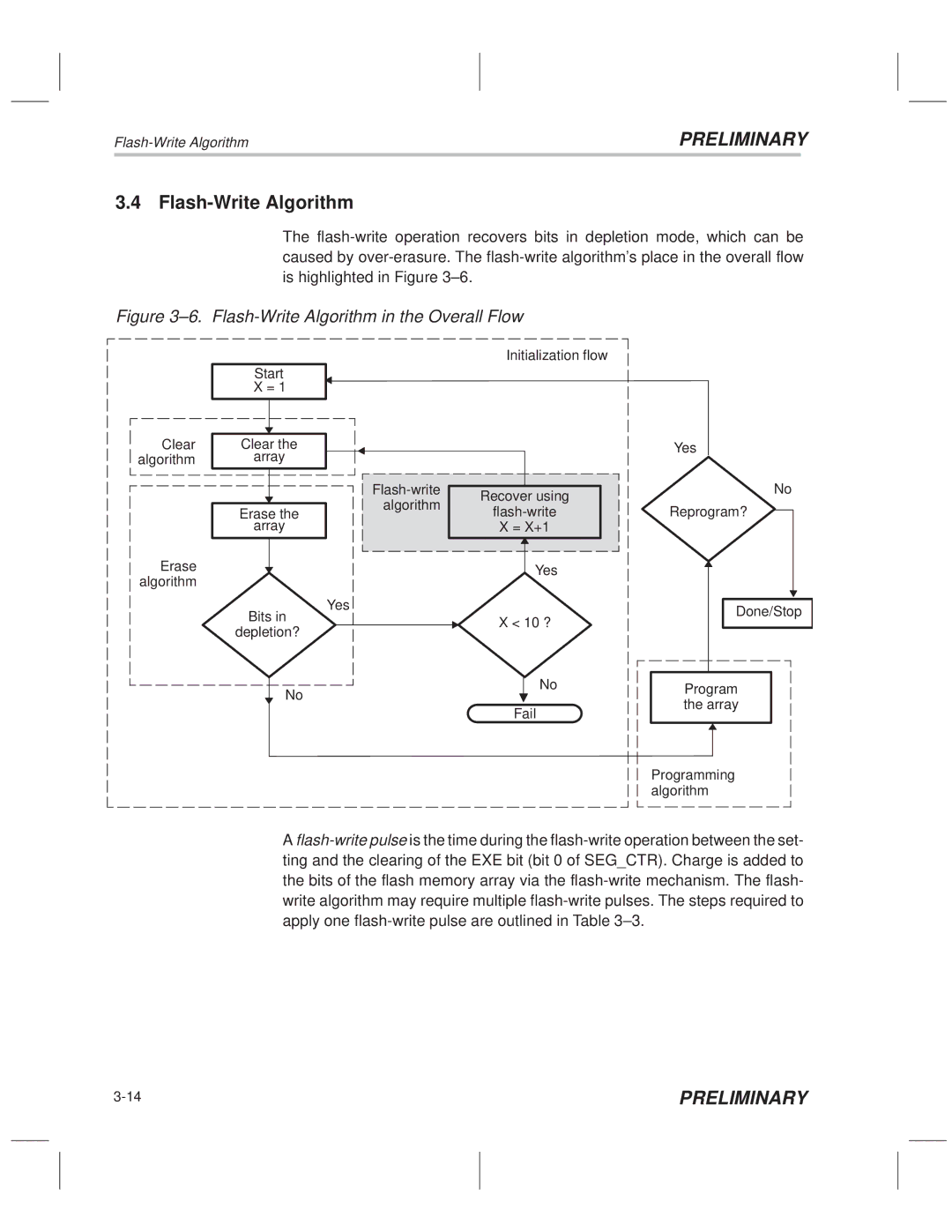
The flash-write operation recovers bits in depletion mode, which can be caused by over-erasure. The flash-write algorithm's place in the overall flow is highlighted in Figure 3±6.
Figure 3±6. Flash-Write Algorithm in the Overall Flow
Clear algorithm
Erase algorithm
Start
X = 1
Clear the
array
Erase the
array
Bits in
depletion?
No
Initialization flow
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | Flash-write | | | | |
| | | Recover using | |
| | algorithm | | |
| | | flash-write | |
| | | | |
| | | | X = X+1 | |
| | | | | | |
Yes | | | Yes |
| |
| | | |
| | | | X < 10 ? |
| | | |
No
Fail
Yes
No
Reprogram?
Done/Stop
Program the array
Programming algorithm
A flash-write pulse is the time during the flash-write operation between the set- ting and the clearing of the EXE bit (bit 0 of SEG_CTR). Charge is added to the bits of the flash memory array via the flash-write mechanism. The flash- write algorithm may require multiple flash-write pulses. The steps required to apply one flash-write pulse are outlined in Table 3±3.