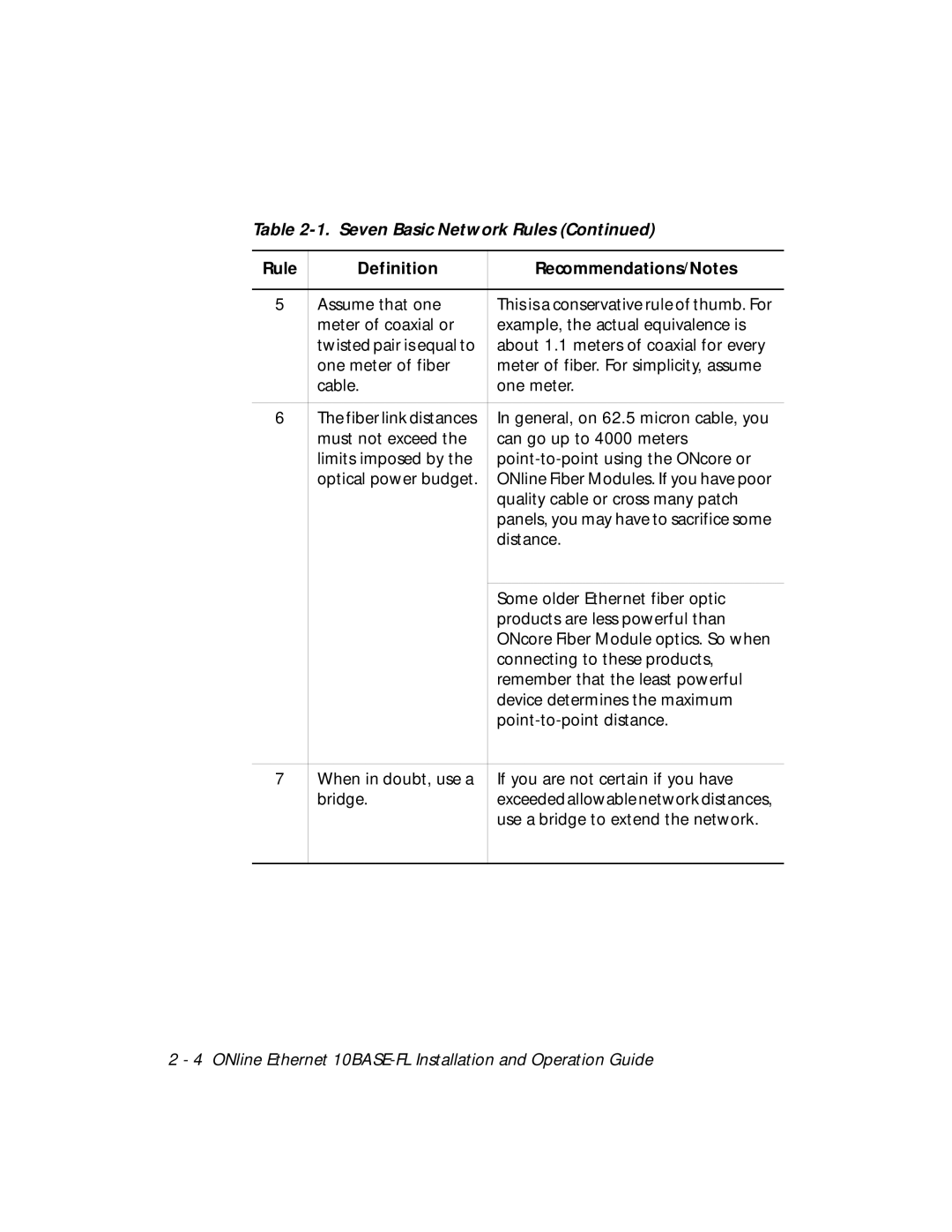
Table 2-1. Seven Basic Network Rules (Continued)
Rule | Definition | Recommendations/Notes |
|
|
|
5 | Assume that one | This is a conservative rule of thumb. For |
| meter of coaxial or | example, the actual equivalence is |
| twisted pair is equal to | about 1.1 meters of coaxial for every |
| one meter of fiber | meter of fiber. For simplicity, assume |
| cable. | one meter. |
|
|
|
6 | The fiber link distances | In general, on 62.5 micron cable, you |
| must not exceed the | can go up to 4000 meters |
| limits imposed by the | |
| optical power budget. | ONline Fiber Modules. If you have poor |
|
| quality cable or cross many patch |
|
| panels, you may have to sacrifice some |
|
| distance. |
|
|
|
|
| Some older Ethernet fiber optic |
|
| products are less powerful than |
|
| ONcore Fiber Module optics. So when |
|
| connecting to these products, |
|
| remember that the least powerful |
|
| device determines the maximum |
|
| |
|
|
|
7 | When in doubt, use a | If you are not certain if you have |
| bridge. | exceeded allowable network distances, |
|
| use a bridge to extend the network. |
|
|
|
2 - 4 ONline Ethernet