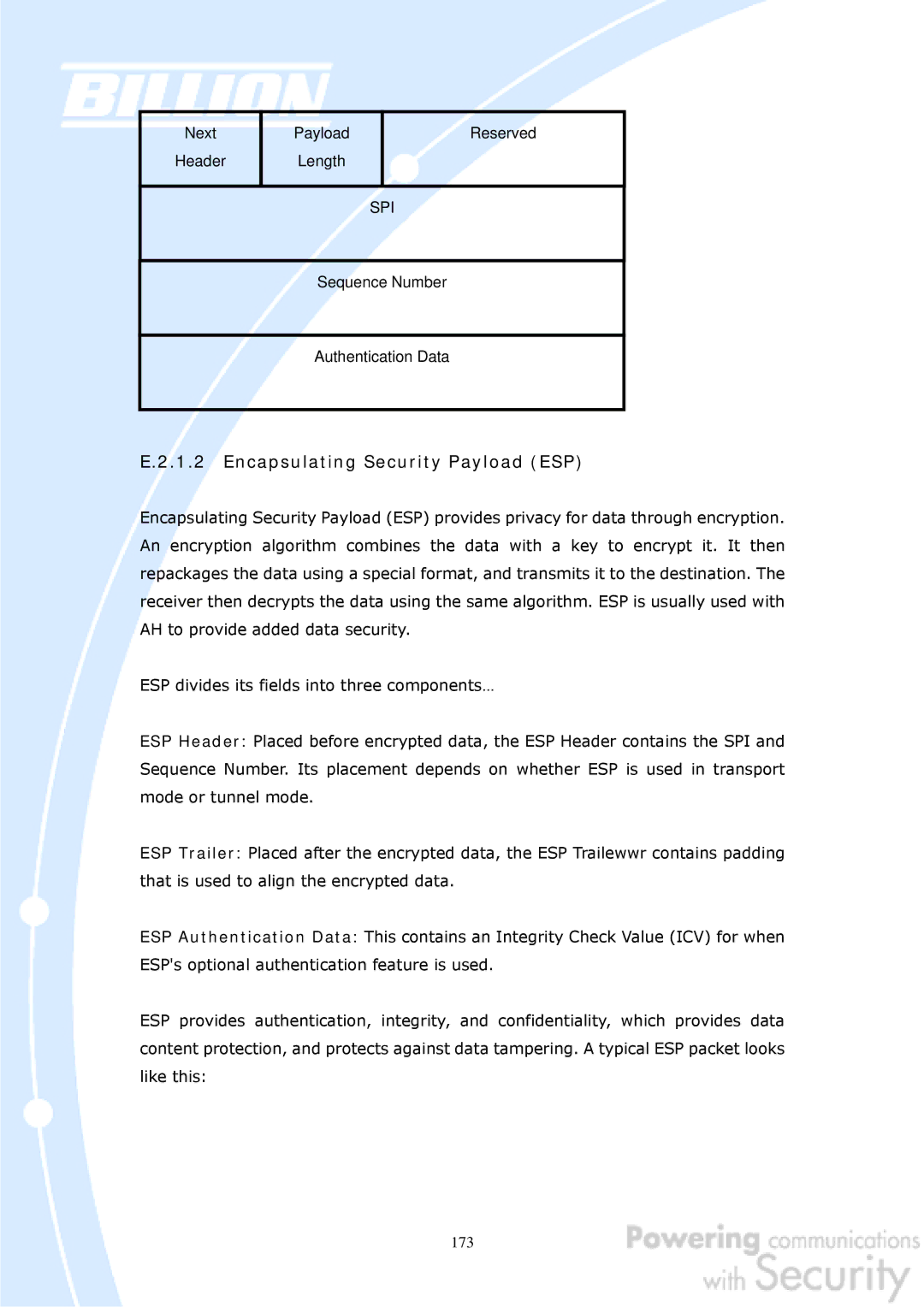
Next
Header
Payload
Length
Reserved
SPI
Sequence Number
Authentication Data
E.2.1.2 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) provides privacy for data through encryption. An encryption algorithm combines the data with a key to encrypt it. It then repackages the data using a special format, and transmits it to the destination. The receiver then decrypts the data using the same algorithm. ESP is usually used with AH to provide added data security.
ESP divides its fields into three components…
ESP Header: Placed before encrypted data, the ESP Header contains the SPI and Sequence Number. Its placement depends on whether ESP is used in transport mode or tunnel mode.
ESP Trailer: Placed after the encrypted data, the ESP Trailewwr contains padding that is used to align the encrypted data.
ESP Authentication Data: This contains an Integrity Check Value (ICV) for when ESP's optional authentication feature is used.
ESP provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality, which provides data content protection, and protects against data tampering. A typical ESP packet looks like this:
173