Chapter 10 Configuring Mobility Groups
Overview of Mobility
Overview of Mobility
Mobility, or roaming, is a wireless LAN client’s ability to maintain its association seamlessly from one access point to another securely and with as little latency as possible. This section explains how mobility works when controllers are included in a wireless network.
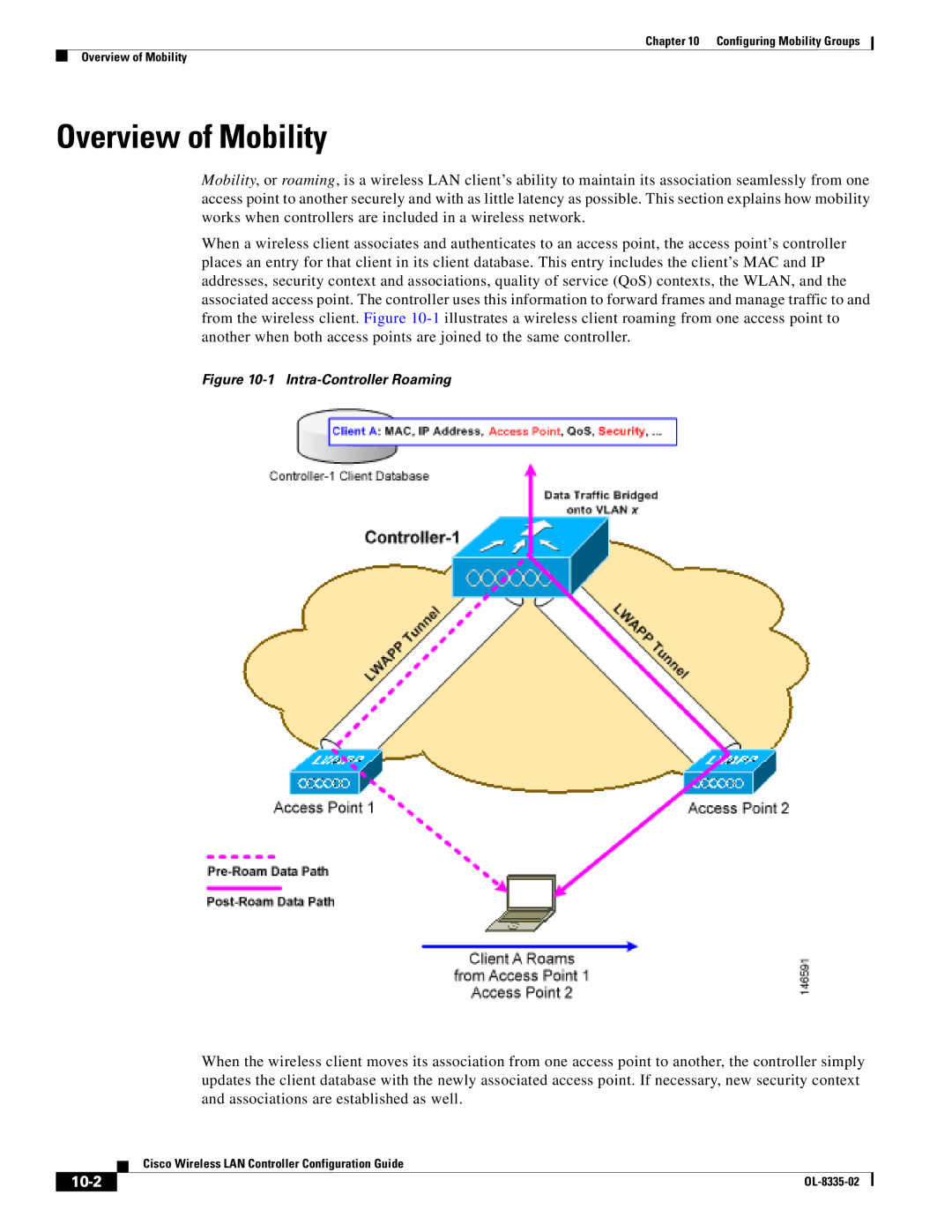
When a wireless client associates and authenticates to an access point, the access point’s controller places an entry for that client in its client database. This entry includes the client’s MAC and IP addresses, security context and associations, quality of service (QoS) contexts, the WLAN, and the associated access point. The controller uses this information to forward frames and manage traffic to and from the wireless client. Figure
Figure 10-1 Intra-Controller Roaming
When the wireless client moves its association from one access point to another, the controller simply updates the client database with the newly associated access point. If necessary, new security context and associations are established as well.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
|
|
|
|