Chapter 10 Configuring Mobility Groups
Overview of Mobility
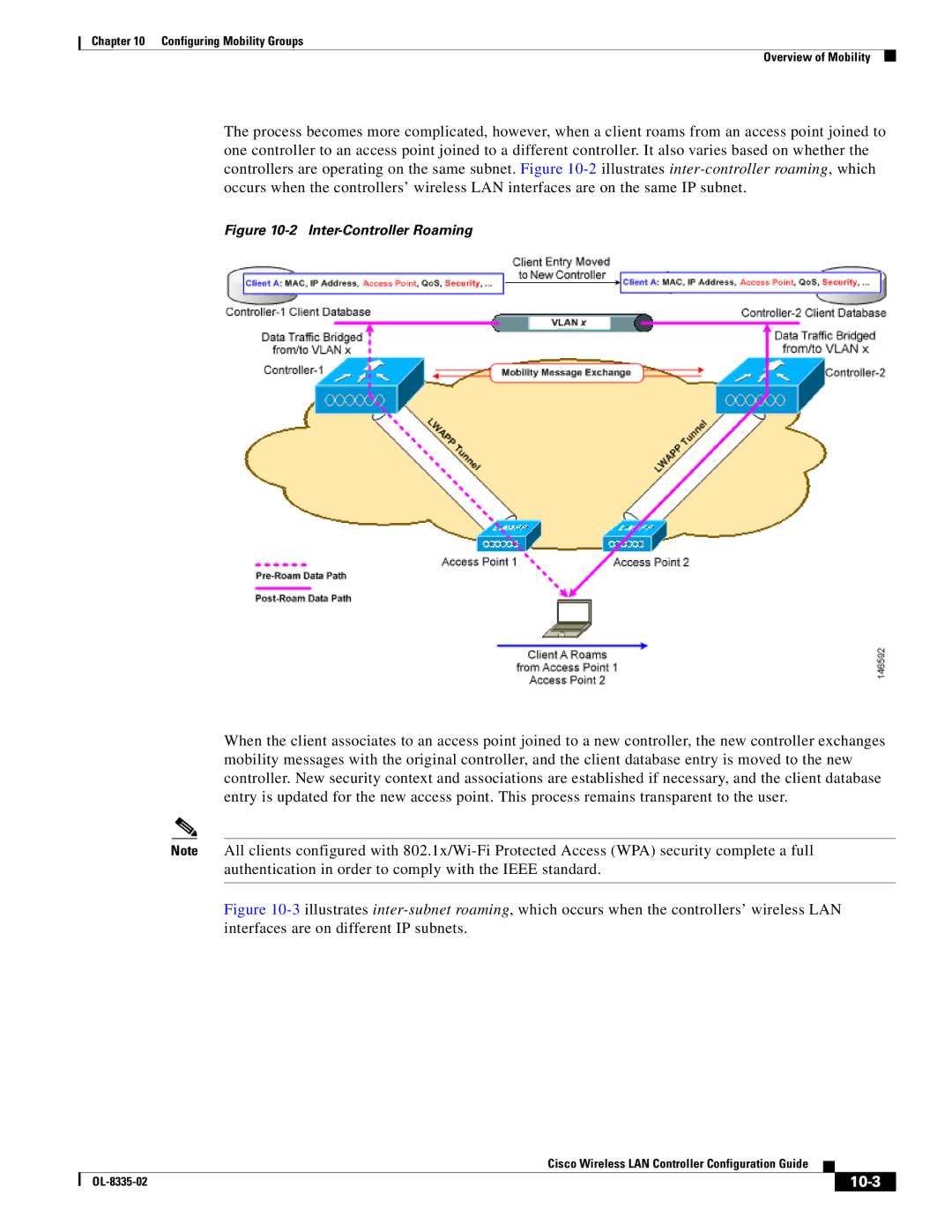
The process becomes more complicated, however, when a client roams from an access point joined to one controller to an access point joined to a different controller. It also varies based on whether the controllers are operating on the same subnet. Figure
Figure 10-2 Inter-Controller Roaming
When the client associates to an access point joined to a new controller, the new controller exchanges mobility messages with the original controller, and the client database entry is moved to the new controller. New security context and associations are established if necessary, and the client database entry is updated for the new access point. This process remains transparent to the user.
Note All clients configured with
Figure 10-3 illustrates inter-subnet roaming, which occurs when the controllers’ wireless LAN interfaces are on different IP subnets.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
|
|
| |
|
|