Corporate Headquarters
Text Part Number OL-3141-01
Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc All rights reserved
N T E N T S
Iii
What You Need
DNS1IP DNS2IP
Recommended Values
Syntax
Vii
Cisco ATA Style Conference Calling Procedure A-7
Viii
Audience
Preface
Overview
Organization
Conventions
Preface Conventions
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco IOS Telephony Service documentation
Related Documentation
Cisco.com
Ordering Documentation
International Cisco web sites can be accessed from this URL
Documentation CD-ROM
Documentation Feedback
Cisco TAC Website
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Technical Assistance Center
Xiv
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Cisco TAC Escalation Center
Xvi
Cisco Analog Telephone Adaptor Overview
A P T E R
Overview of the Skinny Client Control Protocol
4illustrates the architecture of an Sccp network
Hardware Overview
Link LED
Function Button
Voice Codecs Supported
Software Features
Sccp Version
Other Supported Protocols
Additional Supported Signaling Protocols
Basic Services
Pre-call Services
Fax Services
Pre-call and Mid-call Services
Pre-call Services, Mid-call Services,
Cisco ATA style services Cisco ATA Style, page A-6
Mid-call Services
Style and Related Services Procedure Reference
Bellcore Style, page A-4
Installation and Configuration Overview
Action Reference
OL-3141-01
Installing the Cisco ATA
What the Cisco ATA Package Includes
Safety Recommendations
Network Requirements
What You Need
Installation Procedure
5V power adaptor Power cord
Procedure
Cisco ATA 186 Rear Panel Connections
Installing the Cisco ATA Installation Procedure
Power-Down Procedure
Configuring the Cisco ATA for Sccp
Default Boot Load Behavior
Page
Parameter and Bits Reference
VLANSetting
Feature
Bits
Hexadecimal format, this value is 0x01cc002b
Steps Needed to Configure the Cisco ATA
Action Reference
Action
Configuring the Cisco ATA Using a Tftp Server
Basic Configuration Steps in a Non-TFTP Server Environment
Setting Up the Tftp Server with Cisco ATA Software
Configurable Features and Related Parameters
Configurable Features Related Parameters
Creating a Cisco ATA Default Configuration File
Parameters Not Used for Sccp
Syntax of the cfgfmt program follows
Syntax
Save your changes
Creating a Configuration File for a Specific Cisco ATA
You could change the values as follows
Using atapname.exe Tool to Obtain MAC Address
Cfgfmt -tmgcpptag.dat ata0a141e28323c.txt ata0a141e28323c
Command Output
Using the EncryptKey Parameter and cfgfmt Tool
Command Example
Syntax examples
Without Using a Dhcp Server,
Using a Dhcp Server
Using a Dhcp Server,
Procedure
Without Using a Dhcp Server
Other Dhcp Options You Can Set
Voice Configuration Menu
Using the Voice Configuration Menu
Voice Menu Number Features
Key Alphanumeric Characters
Resetting the Cisco ATA to Factory Default Values
Entering Alphanumeric Values
Cisco ATA Web Configuration
DNS1IP
Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager
Upgrading the Sccp Signaling Image
Confirmation box appears. Click OK
Adding the Cisco ATA to the Cisco CallManager
Time
Default value of None
Adding Cisco ATAs Manually
Click OK
Using the Cisco Bulk Administration Tool BAT
Using Auto-Registration
Parameters and Defaults
Configuration Text File Template
CA0UID0 CA1UID0
UIPassword
User Interface UI Parameter
Range Default Voice Configuration Menu Access Code
Parameters for Configuration Method and Encryption
Settings
UseTFTP
905
EncryptKey
Maximum 31 characters
UseTFTP, Domain,
UseTFTP, TftpURL,
Network Parameters
320
DHCP, StaticIp, StaticRoute, StaticNetMask,
StaticRoute
Voice Configuration Menu Access Code Related Parameters
StaticIp
DHCP, StaticRoute, StaticNetMask,
EPID0orSID0 and EPID1orSID1
Account Information Parameters
StaticNetMask
Value Types
Examples
Voice Configuration Menu Access Codes
CA0orCM0 and CA1orCM1
UseMGCP
Sccp Mode Parameter
Operating Parameters
Other Parameters
LBRCodec
Integer
ConnectMode, page 5-13bit AudioMode, page 5-12bits 1
PrfCodec
AudioMode
LBRCodec, ConnectMode,
0x90000400
ConnectMode
Bit Number Definition
311
To Use Pre-call and Mid-call Services
CallerIdMethod
916
0x00019e60
316
DHCP,
Domain
917
TftpURL, CA0orCM0 and CA1orCM1,
NumTxFrames
OpFlags
See the VLANSetting section on
VLANSetting
TftpURL, DHCP, VLANSetting,
CallWaitTone,
Optional Feature Parameters
SigTimer
Default Recommended Values
RingCadence
Tone Parameter Syntax
Call-Progress Tone Parameters
List of Call-Progress Tone Parameters
Each tone is specified by nine integers, as follows
Use the following formula to calculate the scaling factor a
How to Calculate Scaling Factors
Recommended Values
DialTone
Default values for the nine-integer array
Specific Call-Progress Tone Parameter Information
920
ReorderTone
Cisco ATA plays the busy tone when the callee is busy
BusyTone
921
923
RingbackTone
CallWaitTone
924
925
NPrintf
ConfirmTone
Extended IP address
TraceFlags
Range Default
UDPTOS, VLANSetting,
MediaPort
Page
Configuring and Debugging Fax Services
Using Fax Pass-through Mode
AudioMode
Configuring the Cisco ATA for Fax Pass-through mode
This setting translates to the following bitmap
AudioMode, ConnectMode,
This setting translates to the bitmap
Configuring Cisco IOS Gateways to Enable Fax Pass-through
Recommended Setting
Enable Fax Pass-through Mode, Disable Fax Relay Feature,
Run the following command
Enable Fax Pass-through Mode
System Level commands
Perform the command
Disable Fax Relay Feature
Dial-Peer Level Commands
Using FAX Mode
Configuring the Cisco ATA for Fax Mode
Common Problems When Using IOS Gateways
Debugging the Cisco ATA 186/188 Fax Services
Configuring the Cisco IOS Gateway for Fax Mode
Run the command
Prserv Overview, Analyzing prserv Output for Fax Sessions,
Using prserv for Diagnosing Fax Problems
Prserv Overview
Decoding timestamp was set to timestamp2
Analyzing prserv Output for Fax Sessions
Log event Description
That the first RTP packet that the Cisco ATA received was
Terminating-Gateway Example
Debugging FAX Pass-through Mode
100
Possible Reasons for Failure
Debugging FAX Mode
Originating-Gateway Example
Rtpcatch Overview
Using rtpcatch for Diagnosing Fax Problems
How to Use
Major functions
Output
Example of rtpcatch
Options
Explanation
CED tone Detected
1032.116=2.213
Analysis
Fax relay mode Cisco fax relay mode
Analyzing rtpcatch Output for Fax Sessions
Both sides use G.711 for the entire fax session
Using rtpcatch to Analyze Common Causes of Failure
Possible Causes for Failure
Cisco fax relay option is not disabled on the gateway
Possible Cause for Failure
Example 6-10 Fax Pass-through Mode Failure
Rtpcatch Limitations
Page
Upgrading the Cisco ATA Signaling Image
Upgrading the Signaling Image Via Cisco CallManager
Procedure for Upgrading all Cisco ATAs at Once
Upgradecode Definitions
ProcedureforUpgradingOneCiscoATA
Upgradecode Syntax
Running the Executable
Running the Executable File
Upgrading the Signaling Image Manually
Preliminary Steps
Preliminary Steps, Running the Executable File,
Syntax
Upgrade Requirements
Upgrade Procedure
Definitions
Using the telephone keypad, enter the following
Confirming a Successful Signaling Image Upgrade
Using a Web Browser
Using a Web Browser, Using the Voice Configuration Menu,
Using the Voice Configuration Menu
OL-3141-01
Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Tips
Symptoms and Actions
Installation and Upgrade Issues
Restarting the Cisco CallManager
You should also have access to a sniffer or LAN analyzer
Debugging
Frequently Asked Questions
Ring Load per RJ-11 FXS Port Maximum Distance
Procedure
Contacting TAC
Access Voicemail
How to Use Pre-call and Mid-call Services
Procedures for Using Pre-call Services
Redial
Cancel Call-Forward-All
Activate Call-Forward-All
Speed Dial
Group Call Pickup
To use this feature, follow these steps
Call Pickup
MeetMe Conference
Bellcore Style Conference Call Procedure
Procedures for Using Mid-call Services
Bellcore Style Call Transfer Procedure
Bellcore Style
Cisco VG248 Style
Cisco VG248 Style Three-way Calling Procedure
Cisco VG248 Call Transfer Procedure
Cisco ATA Style Call Transfer Procedure
Cisco VG248 Conference Call Procedure
Cisco ATA Style Call Hold/Resume Procedure
Cisco ATA Style
Cisco ATA Style Conference Calling Procedure
OL-3141-01
Voice Menu Option Code Description
Voice Menu Codes
Table B-1lists codes to return basic Cisco ATA information
916 IP address of the primary DNS server
DNS 2 IP
Table B-3 Cisco ATA Voice Menu Codes-Software Upgrade
OL-3141-01
Specification
Cisco ATA Specifications
Physical Specifications
Immunity Specifications
Electrical Specifications for Cisco ATA
Environmental Specifications
Description Specification
Physical Interfaces
Ringing Characteristics
Software Specifications
Tip/ring interfaces for each RJ-11 FXS port Slic
Appendix C Cisco ATA Specifications Software Specifications
Sccp
OL-3141-01
This section describes basic call flows for the Cisco ATA
Sccp Call Flows
Supported Sccp Message Set
Appendix D Sccp Call Flows Supported Sccp Message Set
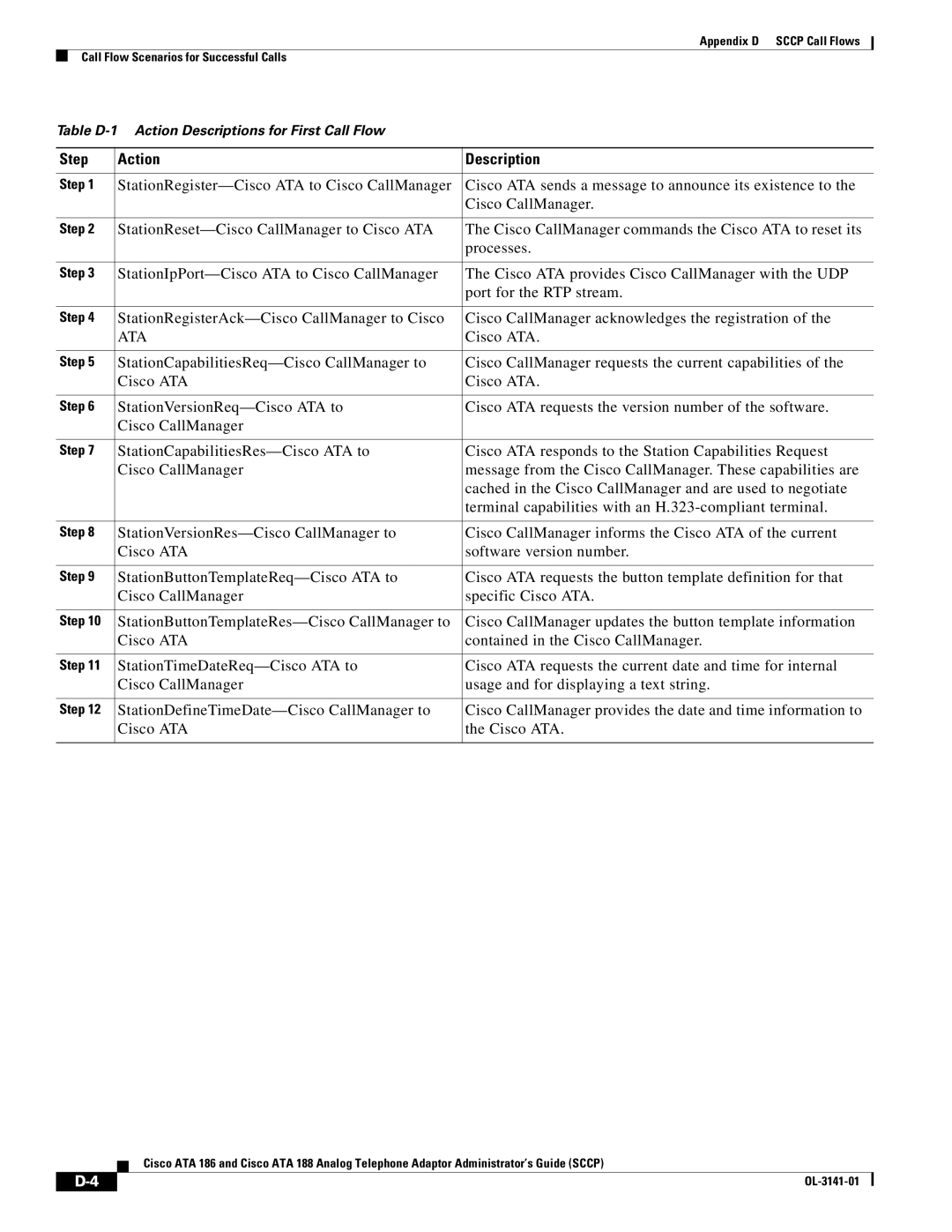
Call Flow Scenarios for Successful Calls
Cisco ATA-to-Cisco CallManager
Step Action Description
ATA
Cisco ATA-to-Cisco CallManager-to-Cisco ATA
Step Station Call Info Description
Step Station Call Info Description
Step Station Call Info Description
OL-3141-01
Process
Performing a Cross-Protocol Upgrade
Syntax of upgradecode Parameter
Upgradecode parameter value could be
GL-1
GL-2
GL-3
GL-4
GL-5
Signaling connection control part
Messages can be part of Sgcp and Mgcp messages
GL-6
Allow you to define your own customized markup language
Business-class services for Internet telephony
Traffic
GL-7
GL-8
IN-1
Enabling use
CallerIdMethod ConnectMode Dhcp
EncryptKey
IN-2
IN-3
RTP frames RTP media port configuration
IN-4
Safety recommendations Scaling factor calculation
IN-5
IP encapsulation
IN-6