The differences from example1 are that administrator and master switch IP are in the other IP domain (192.168.1.0).
Switch IP of master is 192.168.1.100. Set its management mode to “Agent Master”.
According to the basic rule 1, agent IP should be set in the same domain of slaves, that is, 192.168.223.100. The other procedures are the same as example 1.
Now administrator (192.168.1.30) can access the slaves in other domain (192.168.223.0).
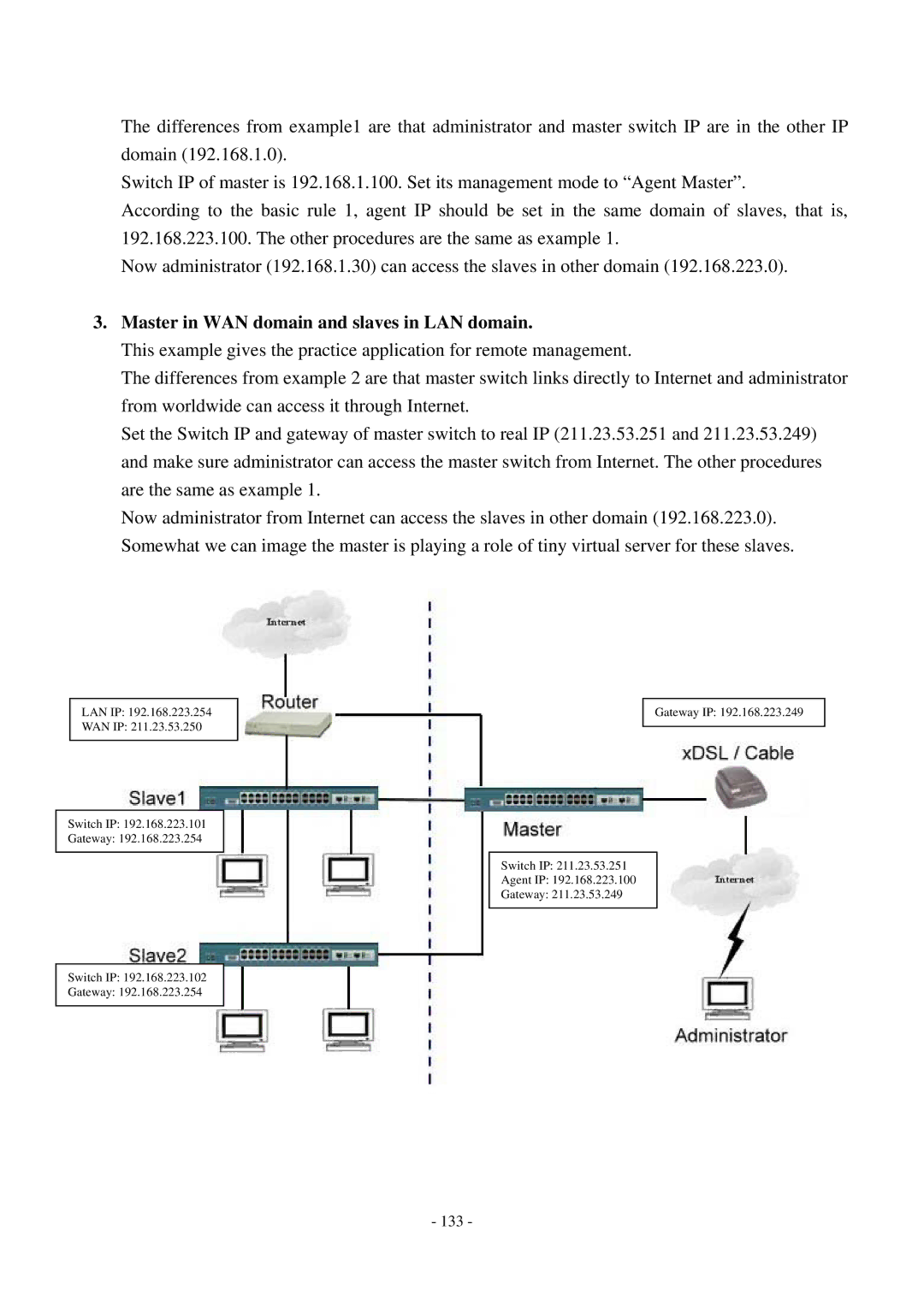
3.Master in WAN domain and slaves in LAN domain.
This example gives the practice application for remote management.
The differences from example 2 are that master switch links directly to Internet and administrator from worldwide can access it through Internet.
Set the Switch IP and gateway of master switch to real IP (211.23.53.251 and 211.23.53.249) and make sure administrator can access the master switch from Internet. The other procedures are the same as example 1.
Now administrator from Internet can access the slaves in other domain (192.168.223.0). Somewhat we can image the master is playing a role of tiny virtual server for these slaves.
LAN IP: 192.168.223.254
WAN IP: 211.23.53.250
Switch IP: 192.168.223.101
Gateway: 192.168.223.254
Gateway IP: 192.168.223.249
Switch IP: 211.23.53.251
Agent IP: 192.168.223.100
Gateway: 211.23.53.249
Switch IP: 192.168.223.102
Gateway: 192.168.223.254
- 133 -