Version
PeditionSecurity Router
Page
Enterasys Networks, Inc Minuteman Road Andover, MA
Federal Communications Commission FCC Notice
Regulatory Compliance Information
Class a ITE Notice Clase A. Aviso de ITE
Product Safety
Industry Canada Notices
TTE Directive Declaration
Vcci Notice
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Compatibilidad Electromágnetica EMC
Elektro- magnetische Kompatibilität EMC
USA
Declaration of Conformity
Approved
Enterasys Networks, Inc Firmware License Agreement
Viii
Page
Page
Contents
Configuring an Interface Displaying Interface Attributes
Managing LAN/WAN Interfaces
Configuring T1/E1 & T3/E3 Interfaces
Configuring IP
How Triggered-on-Demand RIP Works
Configuration Considerations
Configuring the Border Gateway Protocol
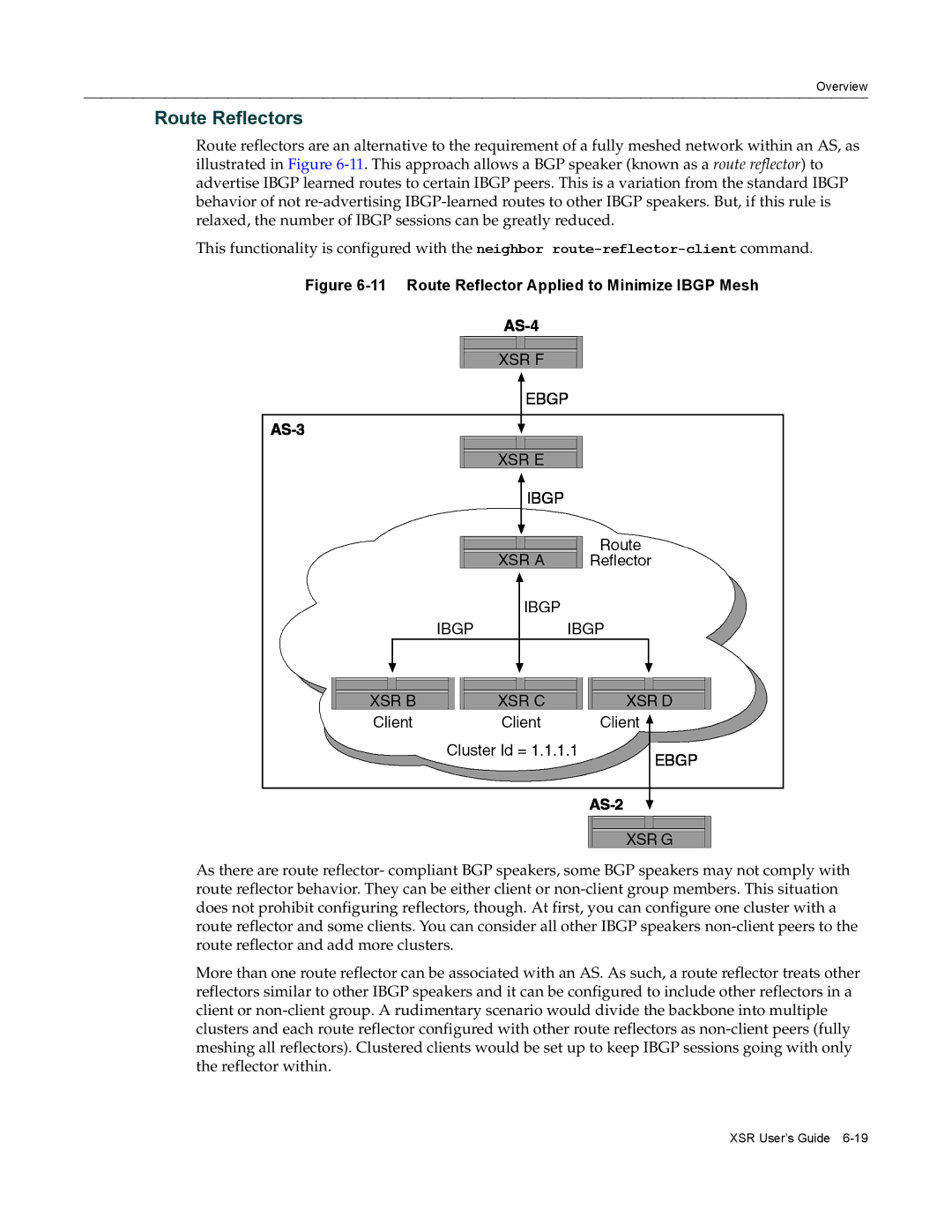
Route Reflectors Confederations
Configuring PIM-SM and Igmp
Configuring PPP
Configuring Dialer Services
Configuring Frame Relay
10-13
Configuring Quality of Service
Configuring Integrated Services Digital Network
Configuring Adsl
Configuring the Virtual Private Network
Configuring Dhcp
Configuring Security on the XSR
Appendix B XSR Snmp Proprietary and Associated Standard MIBs
DOS Attacks Blocked Counters DOS Attacks Blocked Table
Preface
Contents of the Guide
Following conventions are used in this guide
Conventions Used in This Guide
Bold/En negrilla
FTP
Getting Help
Overview
Overview
XSR User’s Guide
Overview
Connecting via the Console Port on XSR Series
Utilizing the Command Line Interface
Connecting a Serial Interface to a Modem
Using the Console Port to Remotely Control the XSR
Terminal Commands
Connecting via Telnet
Connecting via SSH
Synchronizing the Clock
Accessing the Initial Prompt
Managing the Session
Remote Auto Install
RAI Features and Requirements
Utilizing the Command Line Interface
Frame Relay Remote Router
RAI Requirements on the XSR
How RAI Components Work
Frame Relay Central Site
Bootp Client
Reverse DNS Client
Tftp Client
Dhcp over LAN RAI over Ethernet
PPP RAI over Adsl
PPP RAI over a Leased Line
PPP RAI over a Dial-in Line
CLI Editing Rules
CLI Shortcuts Command Description
Setting CLI Configuration Modes
Refer to -1for a graphic example of configuration modes
CLI Configuration Modes Function Access Method Prompt
Privileged Exec Mode
Global Configuration Mode
Exiting From the Current Mode
User Exec Mode
Following example
Mode Examples
Observing Command Syntax and Conventions
Supported Virtual Interfaces
CLI Command Limits
Describing Ports and Interfaces
Supported Physical Interfaces
Supported Ports
Setting Interface Type and Numbering
Setting Port Configuration Mode
Numbering XSR Slots, Cards, and Ports
Dialer Example
Configuration Examples
T1 Example
T1-PRI Isdn Example
Following interfaces are added
BRI-Dialer Idsn Example
You may type
Entering Commands that Control Tables
Adding Table Entries
Following sub-interfaces are added
Displaying Table Entries
Managing XSR Interfaces
Deleting Table Entries
Modifying Table Entries
Disabling an Interface
Configuring an Interface
Following command enables an interface
Enabling an Interface
Managing Message Logs
Performing Fault Management
Logging Commands
Capturing Fault Report Data
Fault Report Commands
RTC/Network Clock Options
Using the Real-Time Clock
Managing the System Configuration
RTC Commands
Using the Default Button XSR 1800/1200 Series Only
Resetting the Configuration to Factory Default
Downloading the Configuration
Configuration Save Options
Bulk Configuration Management
Using File System Commands
Full-config Backup
Uploading the Configuration/Crash Report
Creating Alternate Configuration Files
Creating Alternate Software Image Files
BootRom Upgrade Choices
Pre-upgrade Procedures
Managing the Software Image
Using the Bootrom Update Utility
Using TFTP, transfer updateBootrom.fls from the network
Local Bootrom Upgrade
XSR1800 bU bootromuncmp.fls
Loading Software Images
Using EOS Fallback to Upgrade the Image
Configuring EOS Fallback via Snmp
Configuring EOS Fallback on the CLI
Set the operation to imageSetSelected
Software Image Commands
Configuration Change Hashing
Downloading with Fips Security
Creating Resources
Memory Management
Displaying System Status and Statistics
Network Management through Snmp
Statistics
Snmp Informs
Shaping Trap Traffic
Measuring Performance Metrics
Alarm Management Traps
Network Monitoring via Service Level Agreement Agent
Create a Measurement to Ping Via CLI
Create an Owner
Via CLI
Via Snmp
Schedule a measurement Via CLI
Following command schedules a measurement immediately
Cabletron CTdownload MIB
Full Configuration Backup/Restore
Using the SLA Agent in Snmp
Enterasys Configuration Management MIB
CLI Translator
Software Image Download using NetSight
Appending CLI Commands to Configuration Files via Snmp
Snmp Download with Auto-Reboot Option
Network Management Tools
Accessing the XSR Through the Web
NetSight Atlas Router Services Manager
Firmware Upgrade Procedures
Auto-discovery
Fault Reporting
Using the CLI for Downloads
Using Snmp for Downloads
Overview of LAN Interfaces
LAN Features
XSR supports the following LAN interface features
MIB Statistics
Configuring the LAN
Overview of WAN Interfaces
WAN Features
XSR supports the following WAN interface features
Configuring the WAN
Following example configures the XSR to dial-out async
Configuring the WAN Managing LAN/WAN Interfaces
T1/E1 Functionality
Features
T1/E1 Mode
Overview
E3 Mode
T3 Mode
T3/E3 Subsystem Configuration
T1/E1 Subsystem Configuration
T1 Drop & Insert One-to-One DS0 Bypassing
Drop and Insert Features
D&I NIM does not support channelized mode nor PRI
Specify the controllers framing type
Configuring Channelized T1/E1 Interfaces
Enter the no shutdown command to enable the line
Specify the clock source for the controller
Enable the Serial line
Configuring Un-channelized T3/E3 Interfaces
Enable the Controller line
Optionally, if you prefer to configure internal clocking
T1/E1 & T3/E3 Physical Layer Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting T1/E1 & T3/E3 Links
XSRconfig#controller t1 1/0 XSRconfig-controllerT1-1/0#
Restart the controller
T1/E1 & T3/E3 Alarm Analysis
Receive Alarm Indication Signal AIS Blue Alarm
Transmit Alarm Indication Signal AIS Blue Alarm
Receive Remote Alarm Indication RAI Yellow Alarm
Transmit Remote Alarm Indication RAI Yellow Alarm
Transmit Sending Remote Alarm Red Alarm
XSR
T1/E1 & T3/E3 Error Events Analysis
Controller
Slip Seconds Counter Increasing
Line Code Violations Increasing
Configuring the D&I NIM
Framing Loss Seconds Increasing
Page
General IP Features
Configuring IP
Secondary IP
Telnet
RIP
Troubleshooting Tools Ping Traceroute IP Routing
Proxy DNS
BOOTP/DHCP Relay
ARP and Proxy ARP
Local Broadcast
Broadcast
Directed Broadcast
Telnet
TCP
Interface & Secondary IP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol Tftp
IP Interface
Secondary IP
Icmp & Secondary IP
ARP & Secondary IP
Unnumbered Interface & Secondary IP
Routing Table Manager & Secondary IP
Ospf & Secondary IP
RIP & Secondary IP
Traceroute
IP Routing Protocols
Maximum Transmission Unit MTU
Ping
RIPv1
How Triggered-on-Demand RIP Works
Triggered-on-Demand RIP
IP Routing Protocols
Ospf
Ospf Database Overflow
LSA Type 3 and 5 Summarization
Following is a high priority Overflow Exited log report
Ospf Passive Interfaces
Following is a high priority Overflow Entered log report
Route Preference
Ospf Troubleshooting
Null Interface
Vlan Routing
Static Routes
802.1Q Vlan Tag
Forwarding VLAN, PPPoE over Vlan
IP Routing Table
Vlan Processing Over the XSR’s Ethernet Interfaces
Vlan Ethernet to Fast/GigabitEthernet Topology
Vlan Processing VLAN-enabled Ethernet to WAN Interfaces
QoS with Vlan
Accessing the Global Routing Policy Table
Policy Based Routing
PBR Cache
Match Clauses
Set Clauses
Router ID
Default Network
Classless Inter-Domain Routing Cidr
Real Time Protocol RTP Header Compression
Network Address Translation
Features
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
XSR1 XSR2
Vrrp Definitions
Different States of a Vrrp Router
How the Vrrp Works
Multiple VRs Per Router
Vrrp Features
Authentication
Multiple Virtual IP Addresses per VR
Proxy ARP
Load Balancing
ARP Process on a Vrrp Router
Host ARP
Interface Monitoring
Icmp Ping
Watch Group Monitoring
Equal-Cost Multi-Path Ecmp
Configuration Considerations
Central XSR
Configuring RIP Examples
Configuring RIP Examples
Configuring Ospf Example
Configuring Unnumbered IP Serial Interface Example
Basic One-to-One Static NAT
Configuring NAT Examples
Configuring Static Translation
Register the global NAT pool
Dynamic Pool Configuration
Configuring Dynamic Pool Translation
Bind the interface and optional ACL to the NAT pool
Configuring Napt
Enable an interface F1, for example
Network Address and Port Translation
14 Multiple NAT Pools within Interface
Multiple NAT Pools within an Interface
Static NAT within an Interface
15 Static NAT within Interface
Inside Outside
NAT Port Forwarding
Configuring Policy Based Routing Example
Enter the following commands to enable NAT Port Forwarding
Router XSRb
Configuring Vrrp Example
Router XSRa
For a QoS with Vlan example, refer to QoS with Vlan on
Configuring Vlan Examples
Following example configures a Vlan interface for PPPoE
Configuring the Border Gateway Protocol
Open
Describing BGP Messages
Notification
Update
Defining BGP Path Attributes
Keepalive
Origin
AS Path
Local Preference
Next Hop
Local Preference Applied to Direct Egress Traffic from AS
Atomic Aggregate
Weight
Multi-Exit Discriminator
Aggregator
Aspath Communities
Community
Application of Community Attribute
BGP Routing Policy
BGP Path Selection Process
Route Maps
Access Control Lists
Filter Lists
Community Lists
Regular Expression Examples
Regular Expressions
Regular Expression Characters
Display all routes with any AS path
Peer Groups
Creating a Peer Group
Assigning Peer Group Options
Adding BGP Neighbors
Initial BGP Configuration
Resetting BGP Connections
For an example, refer to Configuring BGP Neighbors on
Route Flap Dampening
Synchronization
Address Aggregation
Recommendations for Route Flap Dampening
Capability Advertisement
Route Refresh
10 Fully Meshed BGP
Scaling BGP
11 Route Reflector Applied to Minimize Ibgp Mesh
Route Reflectors
Confederations
12 Use of Confederations to Reduce Ibgp Mesh Sub AS-302
Displaying System and Network Statistics
Configuring BGP Route Maps
BGP Path Filtering by Neighbor Example
Configuring BGP Neighbors
BGP Aggregate Route Examples
Configuring BGP Confederations
This section details Ibgp and an Ebgp peer group examples
Configuring BGP Peer Groups
TCP MD5 Authentication for BGP Example
Ibgp Peer Group Example
BGP Community with Route Maps Examples
Ebgp Peer Group Example
XSRconfig#router bgp XSRconfig-router#network 1.0.0.0 mask
Configuring BGP Peer Groups
Differences with Industry-Standard Approach
Configuring PIM-SM and Igmp
Defining Multicast Group Addressing
IP Multicast Overview
Comparing Multicast Distribution Trees
Outlining Igmp Versions
Forwarding Multicast Traffic
Describing the XSR’s IP Multicast Features
Sending a Query
Group Membership Actions
Sending and Receiving Queries and Reports
Interoperating with Older Igmp Versions
Behavior of Multicast Routers Among Older Version Queriers
Describing the XSR’s PIM-SM v2 Features
Behavior of Group Members Among Older Version Group Members
Phase 2 Building Shortest Path Tree Between Sender & RP
Phase 1 Building a Shared Tree
Phase 2 Topology Shortest Path Tree Between Sender and RP
Neighbor Discovery and DR Election
Assert Processing
Bootstrap & Rendezvous Point
PIM Register Message
PIM Join/Prune Message
PIM SM over Frame Relay
Source-Specific Multicast
PIM Configuration Examples
PIM Configuration Examples Configuring PIM-SM and Igmp
PPP Features
Configuring PPP
Network Control Protocol NCP
Link Control Protocol LCP
Microsoft Challenge Handshake Protocol MS-CHAP
Authentication
Password Authentication Protocol PAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol Chap
Multilink PPP Mlppp
Link Quality Monitoring LQM
Multi-Class Mlppp
Multilink Header Option Format
Multilink Head Format Negotiation
Fragment Interleaving Over the Link
Multi-Class Receiving Packet
Events and Alarms
IP Control Protocol Ipcp
Multi-Class Option Negotiation
IP Address Assignment
PPP Bandwidth Allocation/Control Protocols BAP/BAPC
Enter encapsulation ppp to enable PPP encapsulation
Configuring PPP with a Dialed Backup Line
Configuring a Synchronous Serial Interface
Enter the media-type for the interface default RS232
Enter no shutdown to enable this interface
Configuring a Dialed Backup Line
Configuring the Dialer Interface
Configuring the Physical Interface for the Dialer Interface
Configure interface dialer 1 to use dial pool
Configuring the Interface as the Backup Dialer Interface
Dialer Example
Configuring Mlppp on a Multilink/Dialer interface
Multilink Example
XSR1 Configuration
Configuring BAP
Dual XSRs One Router Using DoD with Call Request
Configure the dialer list and ACL for DoD
XSR2 Configuration
Configure the Dialer 1 interface with a dialer pool
Dual XSRs BAP Using Call/Callback Request
Configuring BAP
Configuring BAP Configuring PPP
DLCIs
Virtual Circuits
DCEs
DTEs
Multi-Protocol Encapsulation
Frame Relay Features
Rate Enforcement CIR Generic Traffic Shaping
Address Resolution
Dynamic Resolution Using Inverse ARP
Controlling Congestion in Frame Relay Networks
Backward Explicit Congestion Notification Becn
Discard Eligibility DE Bit
Forward Explicit Congestion Notification Fecn
Controlling Congestion in Frame Relay Networks
Sub-interfaces
Link Management Information LMI
End-to-End Fragmentation
User Configuration Commands
FRF.12 Fragmentation
Clear Statistics
Reports and Alarms
Map-Class Configuration
Show Running Configuration
Minneapolis Houston Memphis
Interconnecting via Frame Relay Network
Multi-point to Point-to-Point Example
Configuring Frame Relay
Configuring Frame Relay
Configuring Frame Relay
Configuring Frame Relay
Dial Services Features
Overview of Dial Services
25bis over Synchronous Interfaces
AT Commands on Asynchronous Ports
Asynchronous and Synchronous Support
DTR Dialing for Synchronous Interfaces
Time of Day feature
Typical Use for Dial Services
Ethernet Backup
Dialer Profiles
Implementing Dial Services
Addressing Dialer Resources
Dialer Interface
Dialer Strings
Dialer Pool
Isdn Callback
Configuring Encapsulation
Logical View of Dialer Profiles
Sample Dialer Topology
Dialer Profile of Destination 416
Dialer Profile of Destination 987
Creating and Configuring the Dialer Interface
Configure a backup link for dial purposes with priority
Sample Dialer Configuration
Configuring the Map Class
Configuring the Physical Interface for the Dialer Interface
Point-to-Multipoint with One Neighbor
Configuring Isdn Callback
Point-to-Point with Matched Calling/Called Numbers
Point-to-Point with Different Calling/Called Numbers
Dial Backup Features
Overview of Dial Backup
Sequence of Backup Events
Backup Link Failure Example
Link Failure Backup Example
Configure backup serial port for dialing purposes
Configuring Interface as the Backup Dialer Interface
Dialer
Sample Configuration
Configure interface dialer 2 to use dial pool
Overview of Dial on Demand/Bandwidth on Demand
Dialer Watch
Dialer Interface Spoofing
Dialer Watch Topology
Dialer Watch Behavior
Caveat
Answering Incoming Isdn Calls
Incoming Call Mapping Example
Node a Calling Node Configuration
Following command maps ACL 101 to dialer group
Node D Calling Node Configuration
Node B Called Node Configuration
Following command maps ACL 1061 to dialer group
Configuring DoD/BoD
11 Dial on Demand Topology
PPP Point-to-Multipoint Configuration
Node a Configuration
PPP Multipoint-to-Multipoint Configuration
Following command maps ACL 105 to dialer group
PPP Point-to-Point Configurations
Node B Configuration
Dial-out Routing for Dial on Demand Example
Following commands configure dialer interface
Dial-in Routing for Dial on Demand Example
13 PPP Point-to-Multipoint Topology
PPP Point-to-Multipoint Configurations
Dial-in Router Example
Dial-out Router Example
Following command sets remote user authentication
Mlppp Point-to-Multipoint Configuration
14 Mlppp Point-to-Point Topology
Mlppp Point-to-Point Configurations
Mlppp Point-to-Multipoint Configurations
15 Mlppp Point-to-Multipoint Topology
Mlppp Multipoint-to-Multipoint Configuration
Bandwidth-on-Demand
Switched PPP Multilink Configuration
Following command maps ACL 106 to dialer group
Node C Called Node Configuration
Node a Backed-up Node Configuration
Backup Configuration
Backup Using Isdn
XSRconfig#username toronto privilege 0 password cleartext z
Following command configures Serial sub-interface 2/01
Configuration for Backup with Mlppp Bundle
Following command configures Serial sub-interface 2/00
Following commands configure Serial sub-interface 2/00
Configuration for Ethernet Failover
Configuration for Frame Relay Encapsulation
Backup Configuration Configuring Dialer Services
Leased line Isdn configuration examples T1 PRI E1 PRI
Isdn Features
Understanding Isdn
BRI Features
PRI Features
Channel
Basic Rate Interface
Primary Rate Interface
Channels
Channel Standards
Channel Signaling and Carrier Networks
Isdn Equipment Configurations
Security
Bandwidth Optimization
Q921 Decoding
Call Monitoring
Isdn Trace
Trace Decoding
Reference Parameters
Q931 Decoding
Status
+ Next line 04 Bearer capability
BRI NI-1, DMS100 & 5ESS Spid Registration
Isdn Configuration
Terminal Endpoint Identifier TEI Management Procedures
Decoded IEs
BRI Switched Configuration Model
Switched BRI Configuration Model
PRI Configuration Model
PRI Configuration Model
Interface BRI 0/1/21
Leased-Line Configuration Model
Following example configures a switched line BRI connection
More Configuration Examples
Following example configures a PRI connection on a T1 card
Following example configures a PRI connection on an E1 card
BRI Leased PPP
Following example configures a leased-line BRI connection
Isdn ITU Standard Q.931 Call Status Cause Codes
BRI Leased Line
Call Status Cause Codes Code Cause
Incoming calls barred
Configuring Quality of Service
Traffic Classification
Mechanisms Providing QoS
Describing the Policy Map
Describing the Class Map
Describing Class-Based Weight Fair Queuing
Queuing and Services
Describing Priority Queues
Configuring Cbwfq
Configuring Priority Queues
Measuring Bandwidth Utilization
Assign the class frost to the priority queue
Configuring Traffic Policing
Describing Traffic Policing
Class-based Traffic Shaping
Traffic Shaping per Policy-Map
Traffic Shaping and Queue Limit
Differences Between Traffic Policing and Traffic Shaping
Describing Random Early Detection
Congestion Control & Avoidance
Describing Queue Size Control Drop Tail
RED Drop Probability Calculation
Describing Weighted Random Early Detection
VPN
Configuration per Interface
QoS and Link Fragmentation and Interleaving LFI
Suggestions for Using QoS on the XSR
Configuring QoS with Mlppp Multi-Class
QoS with Vlan
Configuring QoS with FRF.12
Vlan Packet with Priority Routed out a Serial Interface
Describing Vlan QoS Packet Flow
LAN/QoS Serial Scenario
QoS with Vlan Configuration Process
QoS on VPN
QoS on Input
Configuring QoS on a Virtual Tunnel Interface
QoS over VPN Features
Configuring QoS on a Physical Interface
QoS on a Virtual Interface Example
Configure the output policy map Ser classes RTP1 and FTP1
Configure the input policy map Vpn classes RTP and FTP
Configure the IPSec SA
Configure ACLs
Configure the IKE policy foo for pre-share keys
Route
QoS and VPN Interaction
AH Hmac ESP+3DES
Configuring the Shaper on the VPN Interface
Create the policy map
QoS Policy Configuration Examples
Simple QoS on Physical Interface Policy
QoS for Frame Relay Policy
Apply the configuration to the interface
QoS with Mlppp Multi-Class Policy
QoS with FRF.12 Policy
Input and Output QoS Policy
QoS with Vlan Policy
Input QoS on Ingress to the Diffserv Domain Policy
QoS Policy Configuration Examples
Configuring Adsl
PPP over ATM
PDU Encapsulation Choices
PPP over Ethernet over ATM Routed
PPPoA Network Diagram
Routed IP over ATM
PPPoE Network Diagram
NIM Card
Adsl Limitations
Adsl Hardware
DSP Firmware
Adsl Data Framing
ATM Support
Adsl on the Motherboard
OAM Cells
Access Concentrator Restrictions
Class of Service
Dslam Compatibility
PPPoE
Configuration Examples
Inverse ARP
QoS
PPPoA
Following optional commands configure two default routes
Following optional commands configure NAT
IPoA
Enter the following commands to configure a IPoA topology
VPN Overview
Internet Security Issues
How a Virtual Private Network Works
Ensuring VPN Security with IPSec/IKE/GRE
Transport Mode Processing
GRE over IPSec
Tunnel Mode Processing
Digital Signatures
Describing Public-Key Infrastructure PKI
Defining VPN Encryption
Machine Certificates for the XSR
Certificates
Certificate Chains
CA Hierarchies
Certificate Chain Example
RA Mode
CRL Retrieval
Pending Mode
Enroll Password
DF Bit Functionality
VPN Applications
NAT Traversal
Site-to-Site Networks
Site-to-Central-Site Networks
Internet
Client Mode
Network Extension Mode NEM
Remote Access Networks
Configuring Ospf Over Site-to-Central Site in Client Mode
Using Ospf Over a VPN Network
Ospf Commands
Server
Client
Server
Client
Internet
Interfaces Fast/GigabitEthernet 1 and VPN
Configuring Ospf with Fail Over Redundancy
Server
Client
Interfaces Fast/GigabitEthernet 1, VPN 1 and VPN
XSR VPN Features
Limitations
Napt
Master Encryption Key Generation
VPN Configuration Overview
Configuring ACLs
ACL Configuration Rules
SA lifetimes
Selecting Policies IKE/IPSec Transform-Sets
Security Policy Considerations
Configuring Policy
Creating Crypto Maps
Configuring Crypto Maps
User-Name
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting Configuration
Configuring AAA
AAA Commands
PKI Configuration Options
PKI Certificate Enrollment Example
Configuring PKI
CA-AUTHENTICATED
XSRconfig#ip domain acme.com
Interface VPN Options
Following sub-commands are available at VPN Interface mode
Configuring a Simple VPN Site-to-Site Application
VPN Interface Sub-Commands
XSRconfig#crypto isakmp proposal Test
XSRconfig-crypto-m#description external interface
Configuring the VPN Using EZ-IPSec
XSRconfig#interface vpn 1 point-to-point
EZ-IPSec Configuration
XSR with VPN Central Gateway
Add ACLs to permit IP and UDP traffic
Configure IKE policy for the remote peer
Configure the following four IPSec SAs
Add a default route to the next hop Internet gateway
Configure and enable the FastEthernet 1 interface
Clear the DF bit globally
Create a group for NEM and Client mode users
Tunnel a XSR-3250 VPN GRE Site-to-Site Tunnel
GRE Tunnel for Ospf
XSRconfig-isakmp-peer#proposal shared
Tunnel B XSR-1805 VPN GRE Site-to-Site Tunnel
Enable Ospf on the trusted and VPN interfaces
Enable Ospf on the trusted and VPN interfaces
XSR/Cisco Site-to-Site Example
Cisco Configuration
XSR Configuration
Scenario 1 Gateway-to-Gateway with Pre-Shared Secrets
Interoperability Profile for the XSR
Configure IKE Phase 1 policy
Configure the Gateway a external LAN network AW
Configure a default route
Interoperability Profile for the XSR
14 Gateway-to Gateway with Certificates Topology
Scenario 2 Gateway-to-Gateway with Certificates
XSR#clock timezone -7
State
CA-AUTHENTICATED
Overview of Dhcp
Configuring Dhcp
Dhcp Server Standards
How Dhcp Works
Temporary or Permanent Network Address Allocation
Dhcp Services
Assigned Network Configuration Values to Clients Options
Persistent Storage of Network Parameters for Clients
Pool subnet
Bootp Legacy Support
Provisioning Differentiated Network Values by Client Class
Nested Scopes IP Pool Subsets
Manual Bindings
Scope Caveat
Dhcp Client Interaction
Dhcp Client Services
Router Option
Parameter Request List Option
Interaction with Remote Auto Install RAI
Dhcp Client Timeouts
Dhcp CLI Commands
Configuring Dhcp Network Configuration Parameters
Dhcp Set Up Overview
Configuration Steps
Configuring Dhcp Address Pools
Optional Configure a Dhcp Manual Binding
Configure Dhcp Network Parameters
Enable the Dhcp Server
Optional Set Up a Dhcp Nested Scope
Manual Binding with Class Example
Dhcp Server Configuration Examples
Pool with Hybrid Servers Example
Manual Binding Example
Dhcp Option Examples
Bootp Client Support Example
Access Control Lists
Configuring Security on the XSR
LANd Attack
ACL Violations Alarm Example
First alarms logged will display as follows
Packet Filtering
Spoofed Address Check
Smurf Attack
Fraggle Attack
IP Packet with Multicast/Broadcast Source Address
Ping of Death Attack
General Security Precautions
Spurious State Transition
Large Icmp Packets
AAA Services
Connecting Remotely via SSH or Telnet with AAA Service
PuTTY Exit Option
PuTTY Alert Message
Reasons for Installing a Firewall
Firewall Feature Set Overview
ACL and Packet Filter Firewalls
Types of Firewalls
ALG and Proxy Firewalls
Filtering non-TCP/UDP Packets
XSR Firewall Feature Set Functionality
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
Stateful Firewall Inspection SFI
Application Level Gateway
Application Level Commands
Enabling URL Filtering in Firewall Policy
On Board URL Filtering
Importing URL Lists from an Ascii File
Writing URL List Entries
Configuring URL Redirection
Denial of Service DoS Attack Protection
Alarms
Alarm Logging
12 Authentication Process
Authentication
ACLs and Firewall
Dynamic Reconfiguration
Firewall and NAT
Firewall and VPN
Firewall CLI Commands
Firewall CLI Commands
13 Sample Telnet Screen
Firewall Limitations
Steps to Configure the Firewall
Pre-configuring the Firewall
XSR with Firewall
Log only critical events
Complete LAN and WAN interface configuration
15 XSR Firewall with PPPoE DSL and Dhcp
XSR with Firewall, PPPoE and Dhcp
XSR with Firewall and VPN
Configure the Dhcp pool, DNS server and related settings
Add four ACLs to permit IP pool, L2TP and NEM traffic
XP PC NEM
Configure the following IPSec SAs
XSRconfig#ip local pool test 10.120.70.0
Define the local pool network used for tunnel IP addresses
Define the Internet as all possible IP addresses
Define the public VPN interface crypto map
Define three trusted networks in the enterprise
Define service for Radius accounting
Define service for Isakmp
Define service for L2TP tunnels
Define service for Radius authentication
Configure Radius network objects
Firewall Configuration for Vrrp
Load the firewall configuration
Configuring Simple Security
RPC Policy Configuration
Configuration Examples Configuring Security on the XSR
Recommended System Limits
Alarms/Events, System Limits Standard Ascii Table
Snmp views
Table A-5 Alarm Behavior
System Alarms and Events
Driv
ETH1
ETH0
Table A-6 High Severity Alarms/Events
Table A-7 Medium Severity Alarms/Events
Sntp
PPP MS-CHAP authentication failed while
Shutdown command
Portchannel
Corrected the problem by resetting itself
Table A-9 Firewall and NAT Alarms
Firewall and NAT Alarms and Reports
NAT TCP reset, NAT port %d, %IPP2
UDP Detected UDP Flood attack %IPP2
Deny Icmp unsupported packet %IP2ICMP
UDP Request Entry pool is empty
Space
Standard Ascii Character Table
Standard Ascii Character Table
VPN MIB Tables on page B-12
Service Level Reporting MIB Tables
EtsysSrvcLvlMetricTable
EtsysSrvcLvlHistoryTable
EtsysSrvcLvlOwnerTable
EtsysSrvcLvlNetMeasureTable
Field Example CLI command
Rtr schedule aliased to
EtsysSrvcLvlAggrMeasureTable
BGP v4 Peer Table
BGP v4 MIB Tables
General Variables Table
BgpPeerAdminStatus
Bgp4PathAttrIpAddrPrefix
BGP-4 Received Path Attribute Table
BGP-4 Traps
Global Interface Operations
Firewall MIB Tables
Session Totals Counters
Monitoring Objects
Policy Rule Table Totals Counters
Policy Rule True Table
IP Session Table
Authenticated Address Counters
Authenticated Addresses Table
IP Session Counters
DOS Attacks Blocked Table
VPN MIB Tables
DOS Attacks Blocked Counters
EtsysVpnIkePeerProposals Table
EtsysVpnIkePeer Table
EtsysVpnIntfPolicy Table
EtsysVpnIkeProposal Table
EtsysVpnIpsecPolicy Table
EtsysVpnIpsecPolProposals Table
EtsysVpnIpsecPolicyRule Table
EtsysVpnAhTransform Table
EtsysVpnIpsecProposal Table
EtsysVpnIpsecPropTransforms Table
EtsysVpnIpcompTransform Table
EtsysVpnEspTransform Table
Host Resources MIB Objects
IpCidrRouteTable for Static Routes
Field Description ConfigMgmtOperations
Enterasys Configuration Management MIB
Field Description EtsysConfigChangeNonVolatile Group
Enterasys Configuration Change MIB
Enterasys Snmp Persistence MIB
Field Description EtsysSyslogClient Group
Enterasys Syslog Client MIB
Table B-46 Enterasys Syslog Client MIB
Compliance Statements