Application Manual
Page
Limited Warranty and Imitation of Liability
Page
Safety Precautions
Required
Prohibited
Page
Table of Contents
High-Speed Counter Single-Phase
Input/Output Setting
High-Speed Counter Two-Phase Counter
Memory Size and Memory Assignment
Syntax and Assembler Error Codes
Connecting to the Ports
Operation Error Codes
Error Display and Actions
Memo
Easily adjustable potentiometer
Remote maintenance through modem connection
Maintaining programs without a battery
Compliant with overseas specifications as standard
Memo
System Overview
Device name Description
23,28-point type system configuration diagram
General Specifications
Chapter Function and Performance Specifications
Timer counter is provided internally
Function Specifications
Device that has been connected
WR, DR
Is running, operation stops and the outputs are aborted OFF
Off to stop operation
R7EC
General purpose port
Interrupt input
Calculation Specifications
Performance Specifications
Circuit diagram
Input Specifications
Specification
OFF → on
Y100 of EH-*23DRP/A23DRT/*28DRP/*28DRT
Output Specifications
Ms max 24 V DC 0.2A
Output specification
Ms max 24 V DC 0.2A Response time
Load current Common Output
Number of output points See Chapter Number of common
Maximum Circuit Load current Common Output
Ms max
Externally supplied power
Maximum Circuit A 240 V AC Load current Common
At 1 cycle or less/common
PWM Output/Pulse Train Output Specifications
High-Speed Counter Specifications
Analogue Input Specifications
Point and 28-point type 10/14/28-point Relay Output
Circuit diagram 23 points type
Analogue Output Specifications
Circuit diagram Analog expansion unit
Module type Points type module Analog exp. unit
Interrupt Input Specifications
Potentiometer Analogue Input Specifications
Backup
Expansion
Clock Function
Power Supply for Sensor
Product lineup
Others Model
Detailed explanation Remarks
10-Point Basic Unit
Name and function of each part Type
EH-*14
14-Point Basic Unit
To the right
23-Point and 28-Point Basic Unit
EH-*23 EH-*28
Name and function of each part
Expansion Unit
RUN
Terminal Layout and Wiring
Power supply 24V DC Load power supply 24V DC 100-240V AC
DC power supply 24V DC
AC power supply 100-240V AC Load power supply 24V DC
AC power supply
Input
Power supply 24V DC Output Load power supply 12/24V DC
Power supply 24V DC 12/24V DC
Output Load power supply 12/24V DC
Power supply 24V DC
WRF06E
Power supply 24V DC Output
Output Power supply 100-240V AC
Output Power supply 24V DC
24V DC 12/24V DC
Output Power supply
100-240V AC Input Output
Load power supply 24V DC, 100-240V AC Output
Input Output Power supply 100-240V AC
Current input ⋅
EH-D6EAN Example of current input and current output
IO6 OC7 VO7
OC6 VO6 IO7
100V AC 264V AC 24V DC Normal Rush
Weights and Power Consumption
Type Weight
140 150
Exterior Dimensions
Memo
Instruction classification table Description Type
Instruction Classifications
List of Instructions
Nand
TD, SS, CU, CT
TD, SS, CU CTU, CTD, CL
RES
Basic instructions timer, counter
DX, DY, DR
Basic instructions relational box
WX, WY, WR
Item number Ladder symbol Instruction symbol
WR, WM
BCD
DR, DM
Number
Instruction symbol Process descriptions
WY, WR, WM
Instruction symbol Process descriptions Name
WM, TC
Processing time when n=1
BCD →
FUN instructions
BOX
PWM
Instruction Specification Details
Ladder format Condition code
Item number
Remark
Bit Word Double word Constant Usable I/O
ANI
Basic instructions-3
Contact serial connection AND, ANI
Contact parallel connection OR, ORI
Basic instructions-5
Condition
ORI
Negation not
Basic instructions-7
Instruction format
Not
Leading edge detection and DIF, or DIF
Basic instructions-8
DIF n
Number To 511 Decimal
DFN n
Basic instructions-9
Trailing edge detection and DFN, or DFN
Usable I/O Other
Bit Word Double word
WX WY WM DX DY TD, SS
Usable I/O Bit
Word Double word Constant Other
Basic instructions-13
Set start/reset cancel master control MCS, MCR
Remark
Upper case MCS
MPS
Ladder format
MRD
MPP
See Function column
Basic instructions-18
Logical block serial connection ANB
Logical block parallel connection ORB
Basic instructions-19
Processing box start and end Processing BOX
Basic instructions-20
Bit Word
Indicates the start and end of the processing box
Function Indicates the start and end of the relational box
Basic instructions-21
Relational box start and end Relational BOX
OUT TD n t s
On delay timer on Delay Timer
Basic instructions-22
Time chart
Single shot Single Shot
Basic instructions-23
OUT SS n t s
TMR, CU
Progress value is updated
SS11 turns off when set value ≥ progress value
Conditions are ignored because it uses edge trigger
SS11 is turned on at the leading edge of X00001 again,
Counter Counter
Basic instructions-24
OUT CU n s
Counter number To 255 Decimal Set value To 65535 Decimal
Ignored X00005 CL15 CU15 Set value Progress Value CU15 TC15
UP/DOWN Counter
CTU17
Counter clear Counter Clear
Basic instructions-27
OUT CL n s
Counter number To 255 Decimal
Word Double word
Double word LD, and s1S==s2 Or s1S==s2
Command format
Condition Steps
Basic instructions-30
When WR0000 ≠ WR0002, R003 turns on
Relational box Relational BOX
26.8 Lower case DW
Double word LD, and s1Ss2 Or s1Ss2
BOX
Basic instructions-32
When WR0000 WR0002, R005 turns on
Word See Notes 37.5 Double word
S1 s2 Steps
Basic instructions-33
When DR0000 DR0002, R006 turns on signed
SignedRelational box Signed Relational BOX
Off
Basic instructions-34
When WR0000 ≤ WR0002, R007 turns on
≤ Relational box ≤ Relational BOX
S1 = s2
Double word LD, and s1S=s2 Or s1S=s2
Substitution statement Assignment Statement
Arithmetic instructions-1
= s
See following table
Designated by WR0000 + WM000
X00001
Substituted into WR0000 at the leading edge of input
Binary addition Binary Addition
Arithmetic instructions-2
Word Double word
Substitution destination Augend Addend
Word 177 Double word
Arithmetic instructions-3
115 Lower case DW
Binary subtraction Binary Subtraction
Arithmetic instructions-4
Substitution destination Minuend Subtrahend
Positive Negative
BCD subtraction BCD Subtraction
Arithmetic instructions-5
104 Lower case DW
Word 163 Double word
Binary multiplication Binary Multiplication
Arithmetic instructions-6
Word 112 Double word
Substitution destination Multiplicand Multiplier
BCD multiplication BCD Multiplication
Arithmetic instructions-7
164 Lower case DW
Word 447 Double word
Multiplication
Signed binary multiplication Signed Binary
143
Binary division Binary Division
Arithmetic instructions-9
= s1 / s2
= s1 / s2 Word 110 Double word
BCD division
Arithmetic instructions-10
= s1 B/ s2
152 Lower case DW
Signed binary division
Arithmetic instructions-11
= s1 S/ s2
101
Logical or
Arithmetic instructions-12
= s1 or s2
Upper case B
Logical
Arithmetic instructions-13
= s1 and s2
= s1 and s2 Bit, word Double word
Exclusive or
Arithmetic instructions-14
= s1 XOR s2
= s1 XOR s2 Bit, word Double word
= Relational expression
Arithmetic instructions-15
= s1 == s2
= s1 == s2 Is a word Is a double word
= s1 S== s2
Signed = Relational expression
108
= s1 S== s2 Is a double word
= s1 s2 Is a word Is a double Word Bit Double word
Arithmetic instructions-17
= s1 s2
= s1 S s2 Is a double word
Signed Relational expression
= s1 S s2
= s1 s2 Is a word Is a double word
Arithmetic instructions-19
Arithmetic instructions-20
≤ Relational expression
Arithmetic instructions-21
= s1 = s2
= s1 = s2 Is a word Is a double word
= s1 S= s2 Is a double word
Signed ≤ Relational expression
= s1 S= s2
Bit set
Application instructions-1
Bset d, n
Bit location to be set Constant is set Decimal
Bres d, n
Bit reset
Application instructions-2
BTS d, n
Application instructions-3
Bit test
Also, the 20th bit of DR0104 is checked by BTS
Also, the 20th bit of DR0102 is reset to 0 by Bres
Shift right
Application instructions-4
SHR d, n
After execution
DIF1
SHL d, n
Application instructions-5
Shift left
ROR d, n
Application instructions-6
Rotate right
ROL d, n
Application instructions-7
Rotate left
B31 DR0002
LSR d, n
Application instructions-8
Logical shift right
Logical shift left
Application instructions-9
LSL d, n
If d is a word
BSR d, n
Application instructions-10
BCD shift right
BSL d, n
Application instructions-11
BCD shift left
Block transfer Move
Application instructions-12
Below
If n is a word
Words of data are transferred
Copy
Application instructions-13
Copy d, s, n
Below Copy d, s, n
Default value H2020 is set in the range of WR0100 to WR01FE
Block exchange Exchange
Application instructions-14
R7F4 R7F3 R7F2 R7F1
XCG d1, d2, n
To be reversed
Reverses the contents of d
Application instructions-15
Twos complement Negate
Application instructions-16
NEG d
To take complement
Absolute value
Application instructions-17
ABS d, s
ABS d, s Word Double word
Binary → BCD conversion
Application instructions-18
Before conversion
BIN
BCD → Binary conversion
Application instructions-19
After conversion BIN Before conversion
BCD
Decode
Application instructions-20
Average
105 115 195 317 481 829 1586
128 187 126
Application instructions-21
Encode
Number of bits set to That counts the bits Set to
Application instructions-22
Bit count
Swap
Application instructions-23
Swap d
Swaps the upper 8 bits and lower 8 bits contained in d
Application instructions-24
When n=0, it is not executed When n5, it is not executed
Unit
Unity result write Destination I/O
Input Point type Output
Distribute
When n=0, it is not executed
Application instructions-25
X01001 DIF0 Dist WR0000, WX0000 LD X00001 and DIF0
Normal scan end
Control instructions-1
714
Instruction for use
101
102
Special internal output Error code Error description
Conditional jump
Control instructions-4
CU, CT
Code number To 255 Decimal Jump condition
104
Syntax of JMP, Cjmp
Nesting of JMP instructions is allowed
Label
Control instructions-5
LBL n
WRF001 H0001 Duplicate definition of LBL
Code number To 49 Decimal
Control instructions-6
For the instruction instruction, see Next n
106
107
Control instructions-7
Next
108
Syntax of for to Next
109
Start subroutine program
Control instructions-9
SB n
WRF001 H0004 Duplicate definition of SB H0013 SB undefined
111
RTS DER ERR
RTS
Start interrupt scan program Interrupt
Control instructions-11
To 2 , 16 to 19
To 27 Decimal
113
Control instructions-12
End interrupt scan program Return Interrupt
114
Syntax of SB n, RTS, INT n and RTI
Nesting of subroutines is allowed up to 5 levels
Usable I/O Others
Baud rate Value
+C H0000
+A Data length Byte +B H80 †† ††=Start code
118
R7E3
Sample program
WR0
DIF0
Name Description Countermeasure
TRNS/RECV command return code table
064
Transfer command-2
Recv 0 d, s, t
122
123
FUN instructions-1
General purpose port switching
Argument
124
Refresh All points
FUN instructions-2
432
Argument dummy
Refresh Input/output
FUN instructions-3
244
Input type
127
128
High-speed Counter Operation Control
FUN instructions-5
147
Argument Counter Number, operation Control value
High-speed Counter Coincidence Output Control
FUN instructions-6
138
Argument Counter Number, output Instruction
131
Argument counter Number Replacement value Storage area
High-speed Counter Current Value Replacement
FUN instructions-8
Rewrite the count value of the counter No to
High-speed counter current value reading
FUN instructions-9
132
Argument counter Number Current value storage Area
134
FUN instructions-11
High-speed counter preset
162
135
136
137
138
FUN instructions-13
173
139
Pulse output control
FUN instructions-14
149
Argument Pulse output Number
FUN instructions-15
Pulse frequency output setting changes
217
141
142
Pulse output with acceleration/deceleration
FUN instructions-16
919
143
144
145
146
Usable I/O classifications and point types
Type Assignment Point
I/O Assignment
External I/O Numbers
Shows a diagram outlining this series of operations
Classification Data type Remarks
List of external I/O classification and data type
List of I/O number conventions for external I/O
Data type Numbering convention Example
WR0
Internal Output Numbers
DR0
WM0
Memory Size and Memory Assignment
Lists the programming specifications for the MICRO-EH
Sram
Flash
Following methods are used to create the user programs
Programming Devices
Programming Methods
System configuration using a personal computer
Ladder Editor
WVCB02H WPCB02H
List of procedures for creating a program
Out-line of opera-ting procedure Situation Point
Modify Test operation, adjustment
On-line On-direct
Size of one circuit
Example when using a processing box
Example when using loop symbols
Program Transfer
WRF03C
WRF01A
WRF03D
WRF06B
Input/Output Function
Initial Setting for Special Input/Output Function
Change individual setting Store the settings in the memory
Operation mode list
Operation Mode
Special internal output for setting detailed function
Input/Output Setting
„ In/output setting
Y100 Group „ Mode setting Y101 Y102 Group 2 Group
„ Outline
„ Example
Special Output Operation in CPU Stop Status
Pulse / PWM Output adjustment
R7FC toR7FF
Counter output
Basic operation
High-Speed Counter Single-Phase
Operation of Single-Phase Counter
Current value clear instruction operation
Preload input operation
Setting of Single-Phase Counter
Individual counter setting
At abnormal setting
WRF058 Counter
WRF059 Counter
Phase counting mode
High-Speed Counter Two-Phase Counter
Operation of Two-Phase Counters
↓ Falling edge Low ↑ Rising edge High
High ↓ Falling edge
↑ Rising edge Low
↓ Falling edge High
High ↓ Falling edge Low
↑ Rising edge High
Diagnostic error
Setting of Two-Phase Counter
WRF072
WRF076
Bit Description
WRF058 Two-phase counter
Operation of PWM Output
PWM Output
Setting the PWM output on-duty value
Setting the PWM Output
Setting the PWM output frequency
Individual PWM output setting
Setting abnormality
WRF058 PWM output
WRF059 PWM output WRF05A PWM output
Operation of Pulse Output
Pulse Train Output
Setting the pulse output frequency
Setting of Pulse Output
Setting the number of output pulses
Number of output pulses for pulse output
WRF059 Pulse output
Individual setting of pulse outputs
WRF058 Pulse output
Digital Filter
Interrupt Input
Interrupt input correspondence table Terminal INT No
Input sampling number
Potentiometers
Analogue Output
Analogue Input
Analogue Expansion unit
Sw6 Conversion mode Remarks
Sw1 Sw2 Range Remarks
Sw3 Sw4 Range Remarks
Specification. a 10-point type CPU becomes
Switch Stop or
RUN mode when the RUN input is On
Input on
Program classification Description Expression
RUN Start
Definition and operation
Normal Scan
RTI RTI INT0INT0
Causes of congestion errors at normal scan
Scan time Congestion check time
Periodical Scan
10 Congestion error at periodical scan 10 ms
Stop
Continuation of operation after a congestion error
Interrupt Scan
Interrupt contact on Congestion check time
Scan Program execution Interrupt contact on
List of interrupt label Interrupt label Cause of startup
Relationship of Each Scan Type
INT16 INT17 INT18 INT27
CPU Halt time
Online Change in RUN
Conditions for performing program change while running
Powering on
Instantaneous Power Failure
Instantaneous power failure actions
RUN OFF
Operation Parameter
Function Description When to use the function
Forced Output
Forced Set/Reset
Test Operation
Installation location and environment
Installation
Installing the unit
Mounting to a DIN rail
10-2
10-3
Wiring
Separation of the power system
10-4
Wiring to the power module
Unit Screw Clamping
10-5
Wiring to the input terminals DC input AC input
Transistor output
Wiring to the output terminals Relay output
EH-*XXDT
Transistor output Source type
10-7
Life characteristics 125 V AC
10-8
Wiring to the unit terminals
Port function
Communication port specification
Port
Ascii
11-2
Off H8000 Transmission procedure 4800 bps
Remarks
Setting port
Port 2 specifications
Bit WRF03D Initial value
11-3
1n station communication on RS-485
General purpose port Port 1,2
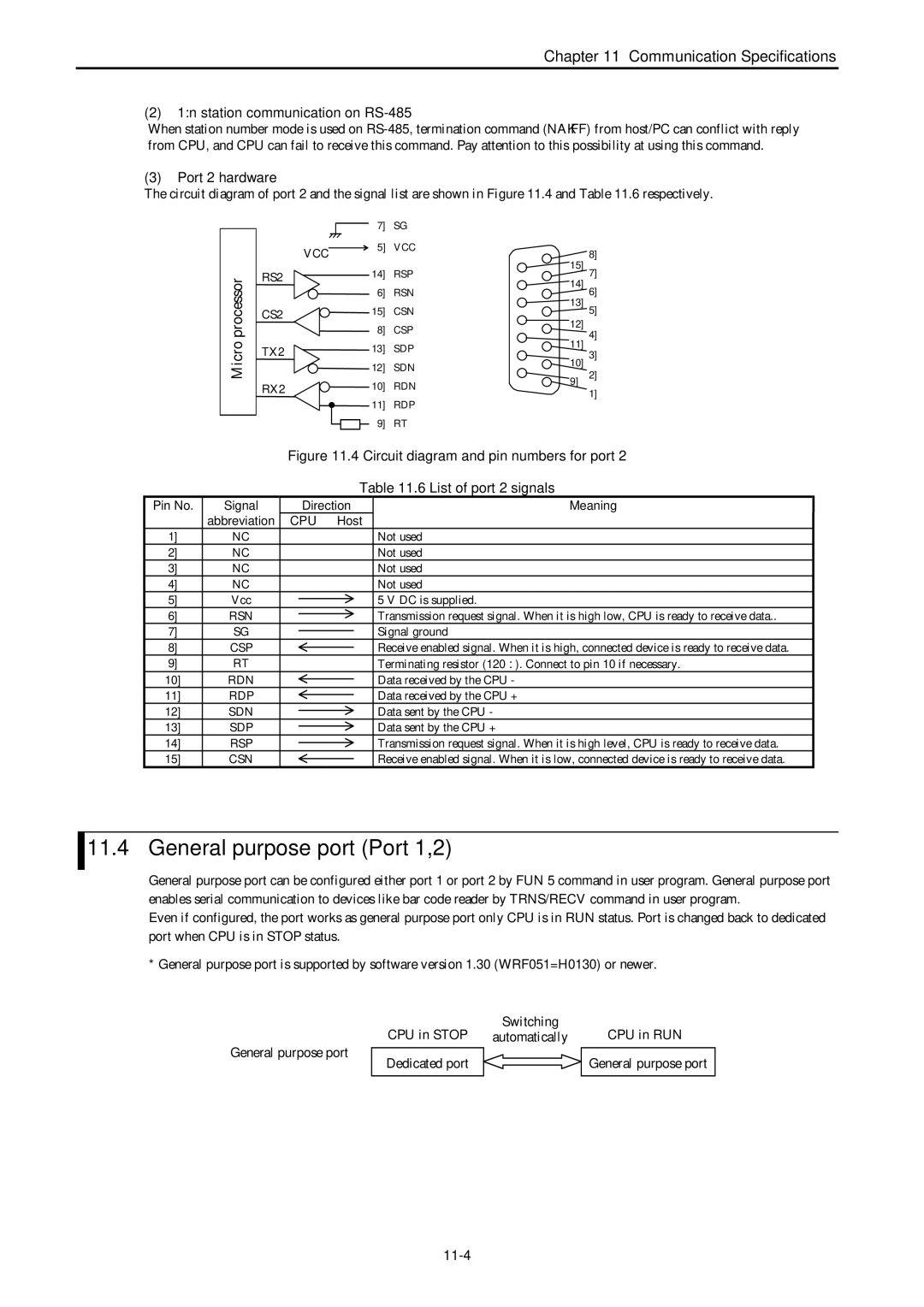
Port 2 hardware
11-4
Modem Control Function
Configuration
AT Commands
Command Function overview Example
List of commands extract
Register Set value Function
Number format Word format
11-7
Sequence
Port
Connecting to the Ports
Connection for 1n station communication by RS-485 11-9
Case of RS-422
11-10
Error Codes
Code Detection timing Cation
Error Error name Classifi
R7CF
Failure detection
LBL
Syntax and Assembler Error Codes
For
INT
CAL
Operation Error Codes
JMP
Cjmp
Bit Special Internal Output Area
Name Meaning Description Setting Resetting Condition
R7CB
R7CE
12-6
12-7
Special internal output Function That can be stored
List of special internal outputs that can be stored
WRF07B
WRF07C WRF07D WRF07E
12.5
Setting Resetting Condition
Name Storage data
12-9
12-10
Name Storage data Description Setting
12-11
PI/O function Individual setting Request
Name Stored data Description
12-12
Name Stored data Description Setting Resetting
Ladder Editor
Error Display and Actions
13-1
13-2
13-3
Process flow when an error occurred is shown below
Error code Error name Corrective action
13-4
13-5
Checklist when Abnormality Occurred
13-6
Procedures to Solve Abnormality
CPU LED, I/O LED
13-7
Power supply check
13-8
13-9
13-10
13-11
Assignment error is generated, but data is read
Data cannot be entered
13-12
13-13
13-14
CPU operates, but output signals are not detected
Assignment error occurred, but output is normal
13-15
13-16
Peripheral unit name Form
Operation verification procedures
Detailed operation example
14-1
14-2
E P 1 Starting the Ladder Editor for Windows
E P 2 Initialization
Select H-302 for the CPU type setting
Menu bar
14-3
14-4
Assign in the Menu bar
14-5
Setting from the I/O Assign List
14-6
Setting from the Slot Setting Status
14-7
E P 3 Program Input
Click the OK button. The dialogue closes
14-8
Click the OK button in the Processing Box
14-9
Input I/O No., time base, and the first setting value
M, Y, TD, SS, WDT, MS, TMR, CU, RCU, CTU, CTD, CL
14-10
Input comparison expression and comment Click the OK button
Click the circuit write icon Tool bar
14-11
E P 4 Checking Program Errors
14-12
E P 5 Saving the Program
14-13
E P 6 Program Transfer to CPU
14-14
Click File → CPU write in the Menu bar
14-15
E P 7 Monitoring Verifying the Operation
I/O Monitor dialogue box is displayed
I/O monitor can be specified in the following two ways
Click the icon in the Symbol bar
Monitor and display 16 points from Y100
14-16
Life of the power module
Normal status Main cause of error
Daily inspection
Items for daily inspection
15-2
Life of the battery
How to replace the battery
ANI
LDI
ORI
Not
EH-150 200 250 252 2000 2002 4010 700 1002 300 702 302
Arithmetic instructions Instruction Instruction name
Free
Application instructions 2/2 Instruction Instruction name
FUN instructions 1/5 Instruction Instruction name
FUN instructions 2/5 Instruction Instruction name
FUN instructions 3/5 Instruction Instruction name
FUN instructions 4/5 Instruction Instruction name
FUN instructions 5/5 Instruction Instruction name
Standards
Appendix 2 Standards