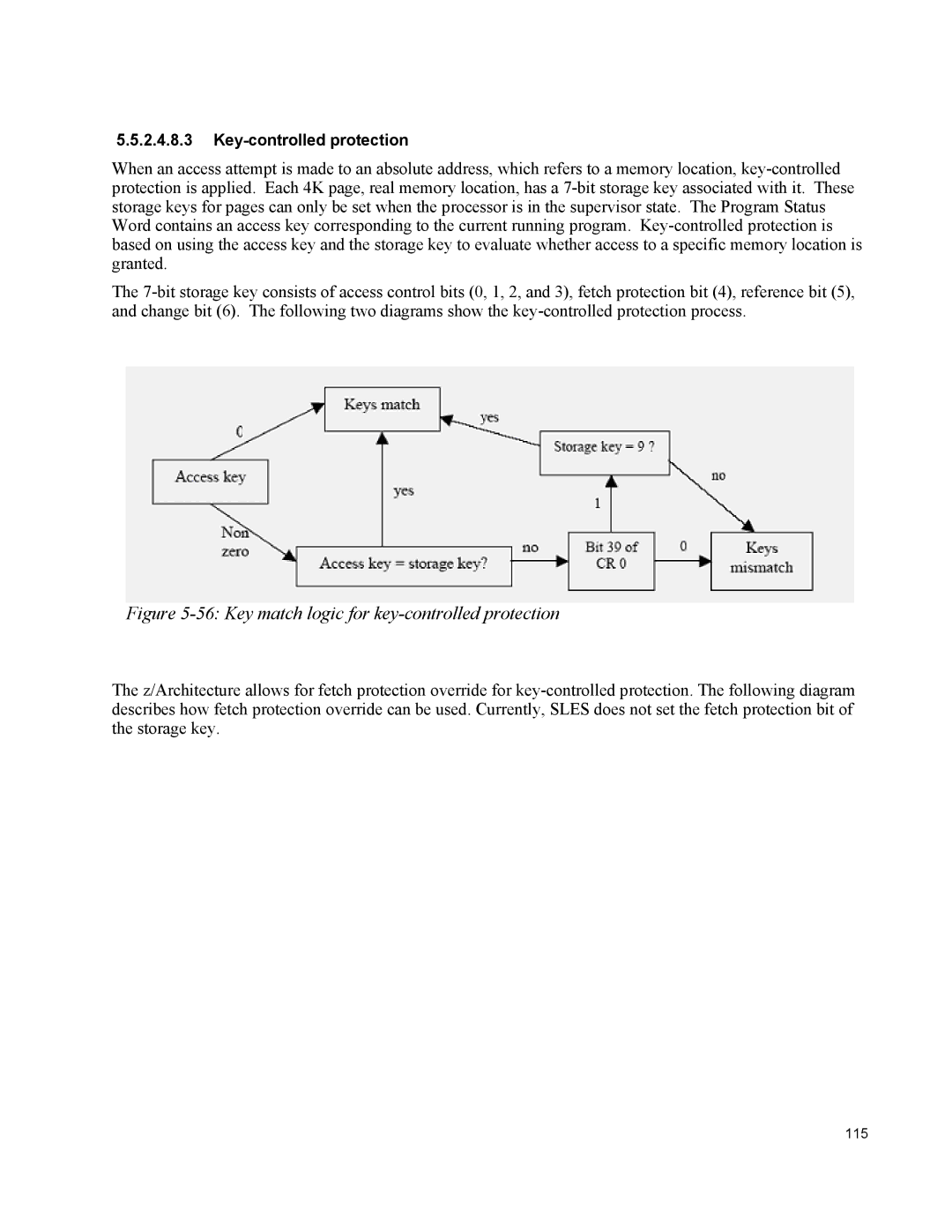
5.5.2.4.8.3
When an access attempt is made to an absolute address, which refers to a memory location,
The
Figure 5-56: Key match logic for key-controlled protection
The z/Architecture allows for fetch protection override for
115