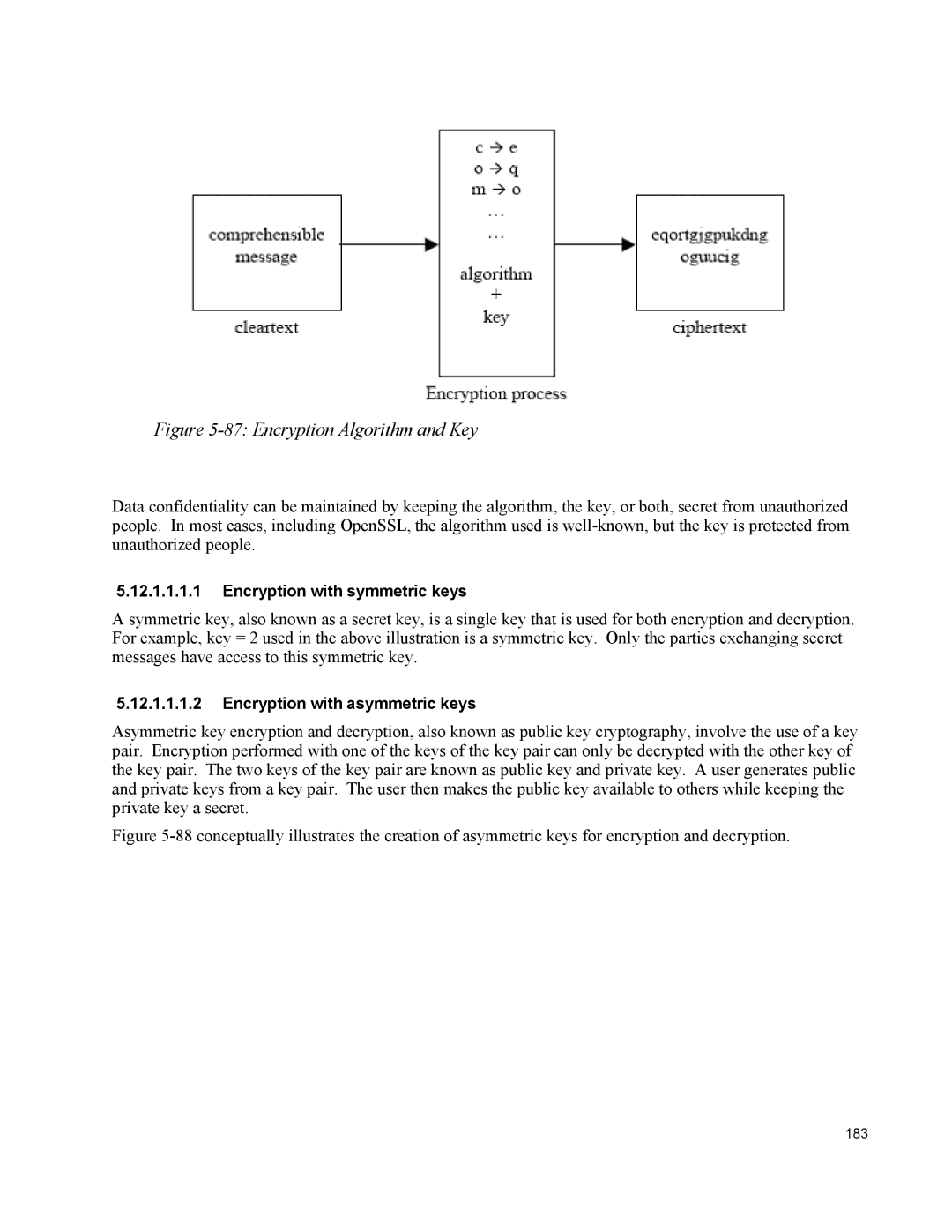
Figure 5-87: Encryption Algorithm and Key
Data confidentiality can be maintained by keeping the algorithm, the key, or both, secret from unauthorized people. In most cases, including OpenSSL, the algorithm used is
5.12.1.1.1.1Encryption with symmetric keys
A symmetric key, also known as a secret key, is a single key that is used for both encryption and decryption. For example, key = 2 used in the above illustration is a symmetric key. Only the parties exchanging secret messages have access to this symmetric key.
5.12.1.1.1.2Encryption with asymmetric keys
Asymmetric key encryption and decryption, also known as public key cryptography, involve the use of a key pair. Encryption performed with one of the keys of the key pair can only be decrypted with the other key of the key pair. The two keys of the key pair are known as public key and private key. A user generates public and private keys from a key pair. The user then makes the public key available to others while keeping the private key a secret.
Figure 5-88 conceptually illustrates the creation of asymmetric keys for encryption and decryption.
183