5.12.1.1Concepts
SSL is used to authenticate endpoints and to secure the contents of the
SSL uses encryption with symmetric keys for data transfer, encryption with asymmetric keys for exchanging symmetric keys, and
5.12.1.1.1Encryption
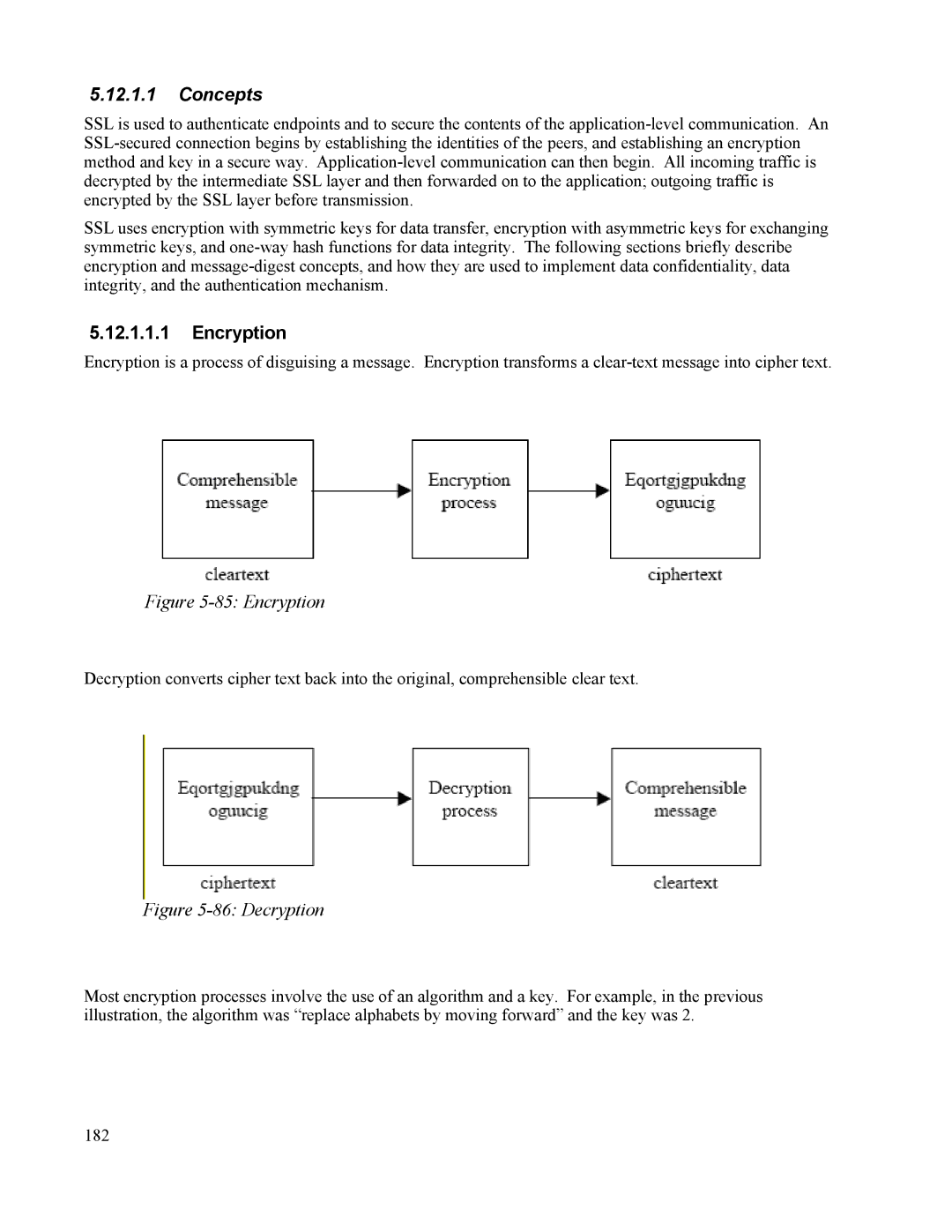
Encryption is a process of disguising a message. Encryption transforms a
Figure 5-85: Encryption
Decryption converts cipher text back into the original, comprehensible clear text.
Figure 5-86: Decryption
Most encryption processes involve the use of an algorithm and a key. For example, in the previous illustration, the algorithm was “replace alphabets by moving forward” and the key was 2.
182