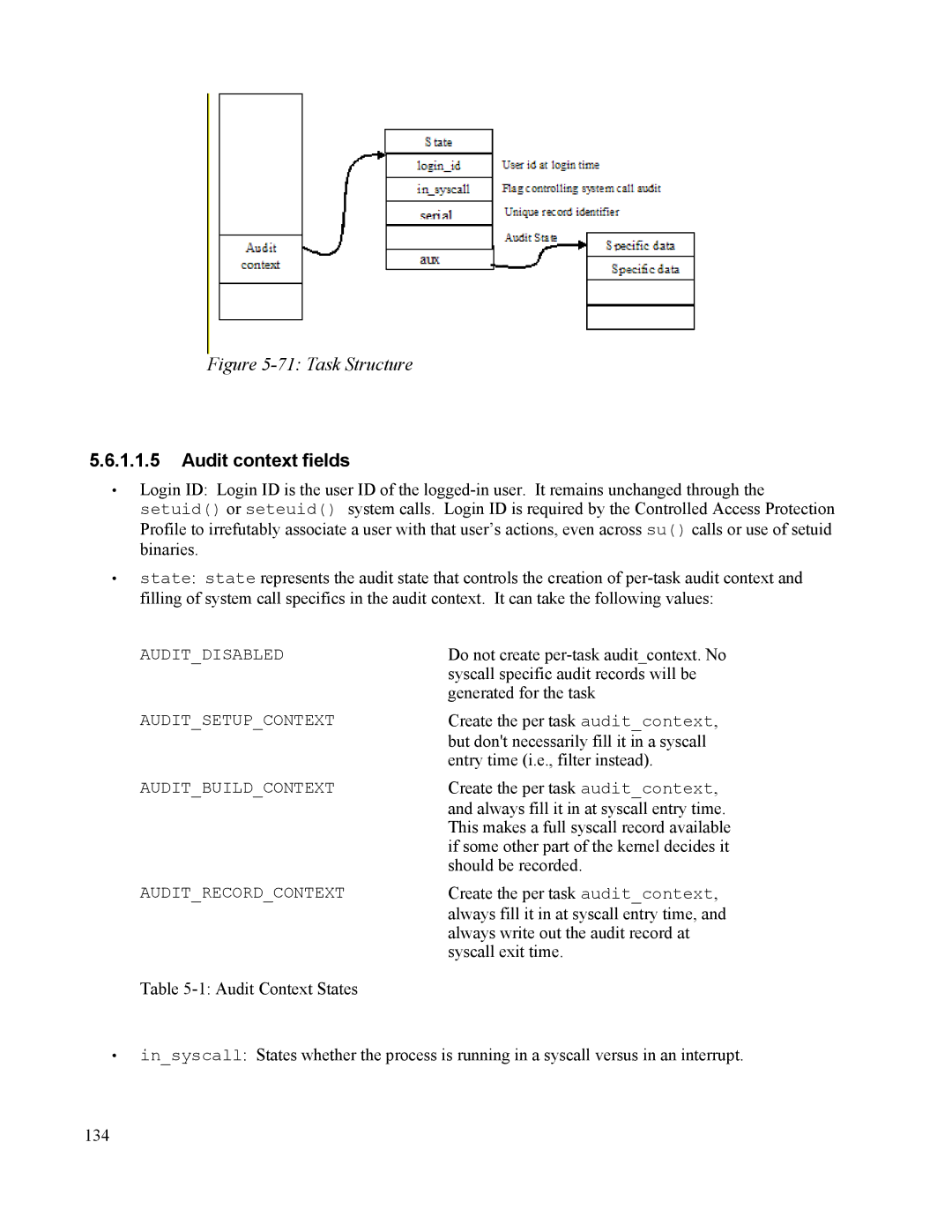
Figure 5-71: Task Structure
5.6.1.1.5Audit context fields
•Login ID: Login ID is the user ID of the
•state: state represents the audit state that controls the creation of
AUDIT_DISABLED
AUDIT_SETUP_CONTEXT
AUDIT_BUILD_CONTEXT
AUDIT_RECORD_CONTEXT
Table
Do not create
Create the per task audit_context, but don't necessarily fill it in a syscall entry time (i.e., filter instead).
Create the per task audit_context, and always fill it in at syscall entry time. This makes a full syscall record available if some other part of the kernel decides it should be recorded.
Create the per task audit_context, always fill it in at syscall entry time, and always write out the audit record at syscall exit time.
•in_syscall: States whether the process is running in a syscall versus in an interrupt.
134