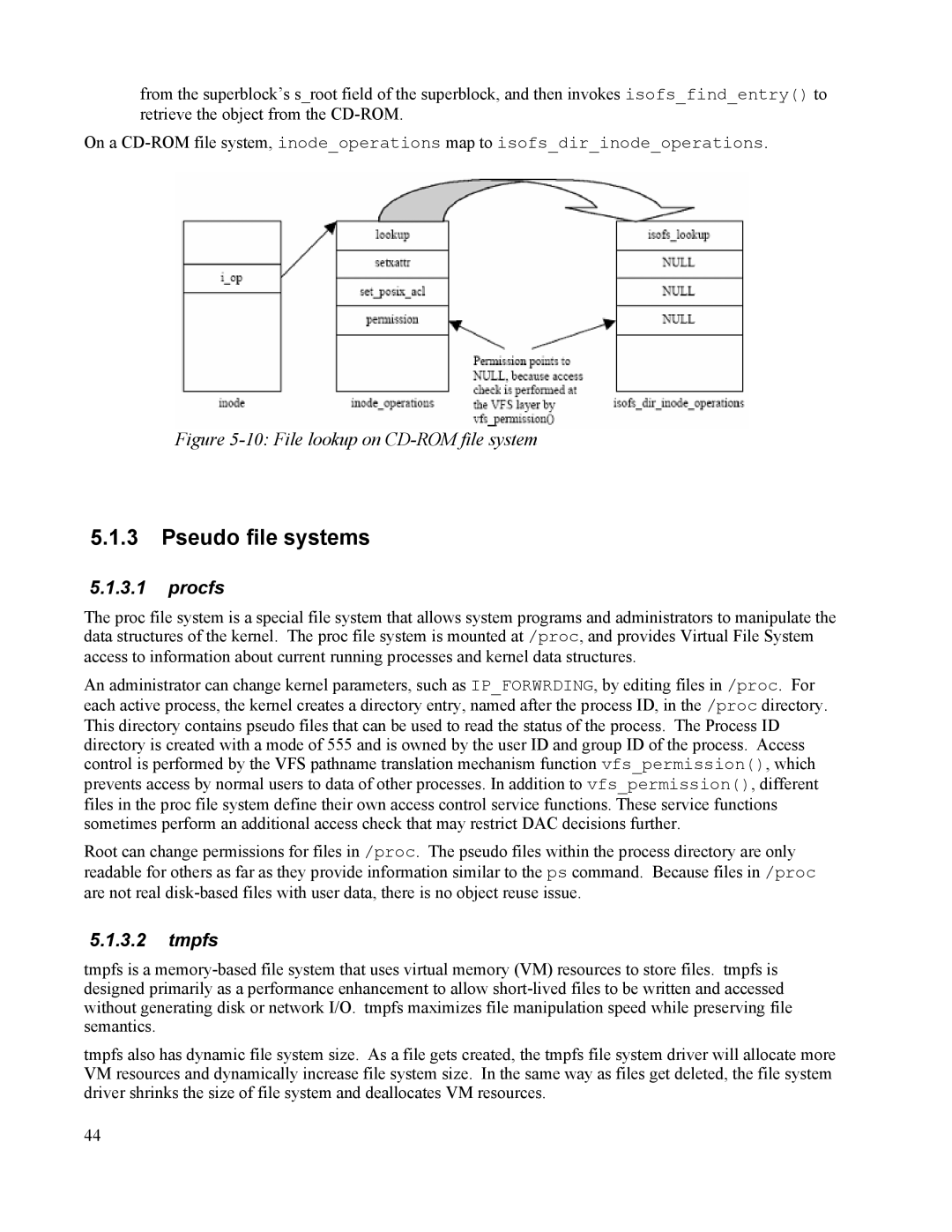
from the superblock’s s_root field of the superblock, and then invokes isofs_find_entry() to retrieve the object from the
On a
Figure 5-10: File lookup on CD-ROM file system
5.1.3Pseudo file systems
5.1.3.1procfs
The proc file system is a special file system that allows system programs and administrators to manipulate the data structures of the kernel. The proc file system is mounted at /proc, and provides Virtual File System access to information about current running processes and kernel data structures.
An administrator can change kernel parameters, such as IP_FORWRDING, by editing files in /proc. For each active process, the kernel creates a directory entry, named after the process ID, in the /proc directory. This directory contains pseudo files that can be used to read the status of the process. The Process ID directory is created with a mode of 555 and is owned by the user ID and group ID of the process. Access control is performed by the VFS pathname translation mechanism function vfs_permission(), which prevents access by normal users to data of other processes. In addition to vfs_permission(), different files in the proc file system define their own access control service functions. These service functions sometimes perform an additional access check that may restrict DAC decisions further.
Root can change permissions for files in /proc. The pseudo files within the process directory are only readable for others as far as they provide information similar to the ps command. Because files in /proc are not real
5.1.3.2tmpfs
tmpfs is a
tmpfs also has dynamic file system size. As a file gets created, the tmpfs file system driver will allocate more VM resources and dynamically increase file system size. In the same way as files get deleted, the file system driver shrinks the size of file system and deallocates VM resources.
44