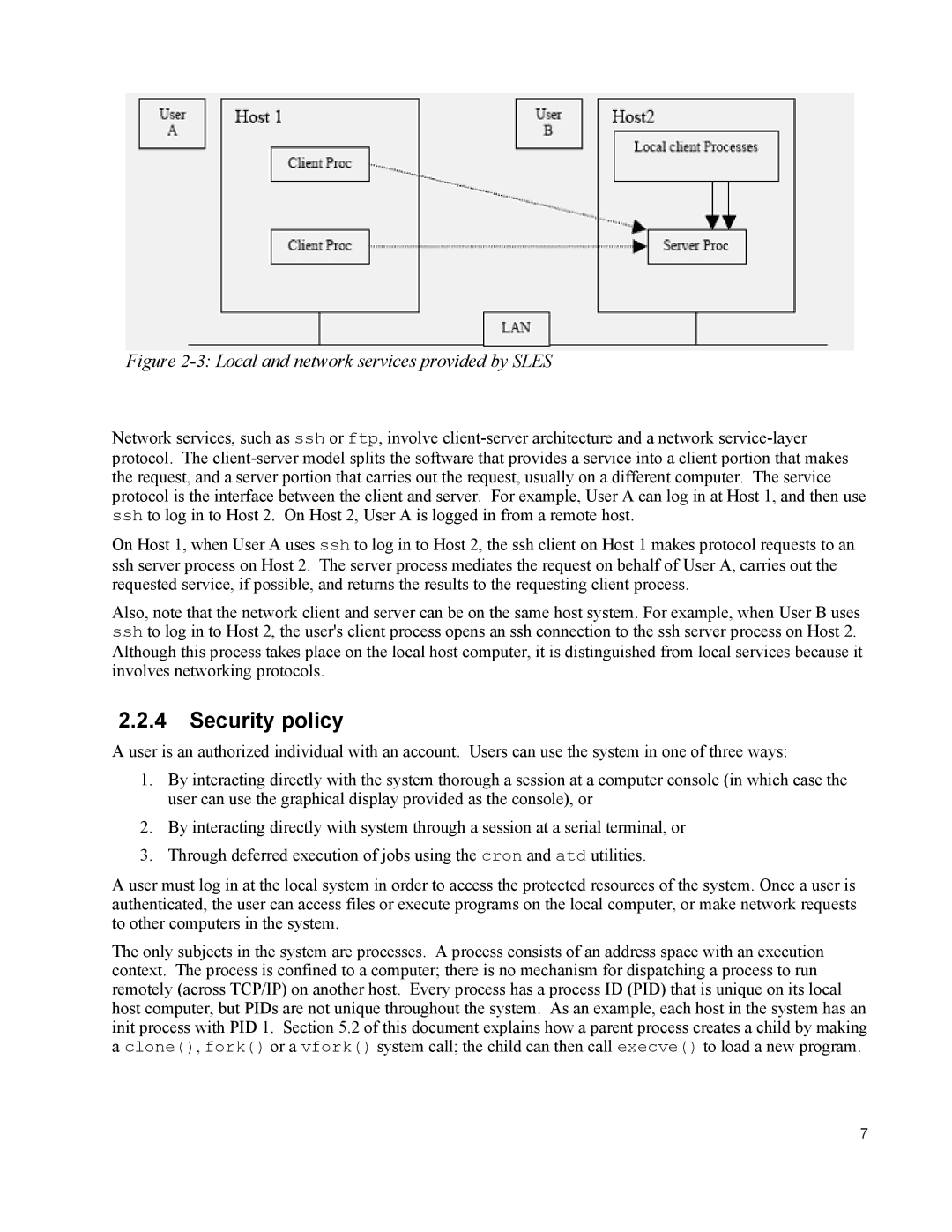
Figure 2-3: Local and network services provided by SLES
Network services, such as ssh or ftp, involve
On Host 1, when User A uses ssh to log in to Host 2, the ssh client on Host 1 makes protocol requests to an ssh server process on Host 2. The server process mediates the request on behalf of User A, carries out the requested service, if possible, and returns the results to the requesting client process.
Also, note that the network client and server can be on the same host system. For example, when User B uses ssh to log in to Host 2, the user's client process opens an ssh connection to the ssh server process on Host 2. Although this process takes place on the local host computer, it is distinguished from local services because it involves networking protocols.
2.2.4Security policy
A user is an authorized individual with an account. Users can use the system in one of three ways:
1.By interacting directly with the system thorough a session at a computer console (in which case the user can use the graphical display provided as the console), or
2.By interacting directly with system through a session at a serial terminal, or
3.Through deferred execution of jobs using the cron and atd utilities.
A user must log in at the local system in order to access the protected resources of the system. Once a user is authenticated, the user can access files or execute programs on the local computer, or make network requests to other computers in the system.
The only subjects in the system are processes. A process consists of an address space with an execution context. The process is confined to a computer; there is no mechanism for dispatching a process to run remotely (across TCP/IP) on another host. Every process has a process ID (PID) that is unique on its local host computer, but PIDs are not unique throughout the system. As an example, each host in the system has an init process with PID 1. Section 5.2 of this document explains how a parent process creates a child by making a clone(), fork() or a vfork() system call; the child can then call execve() to load a new program.
7