5.2Process control and management
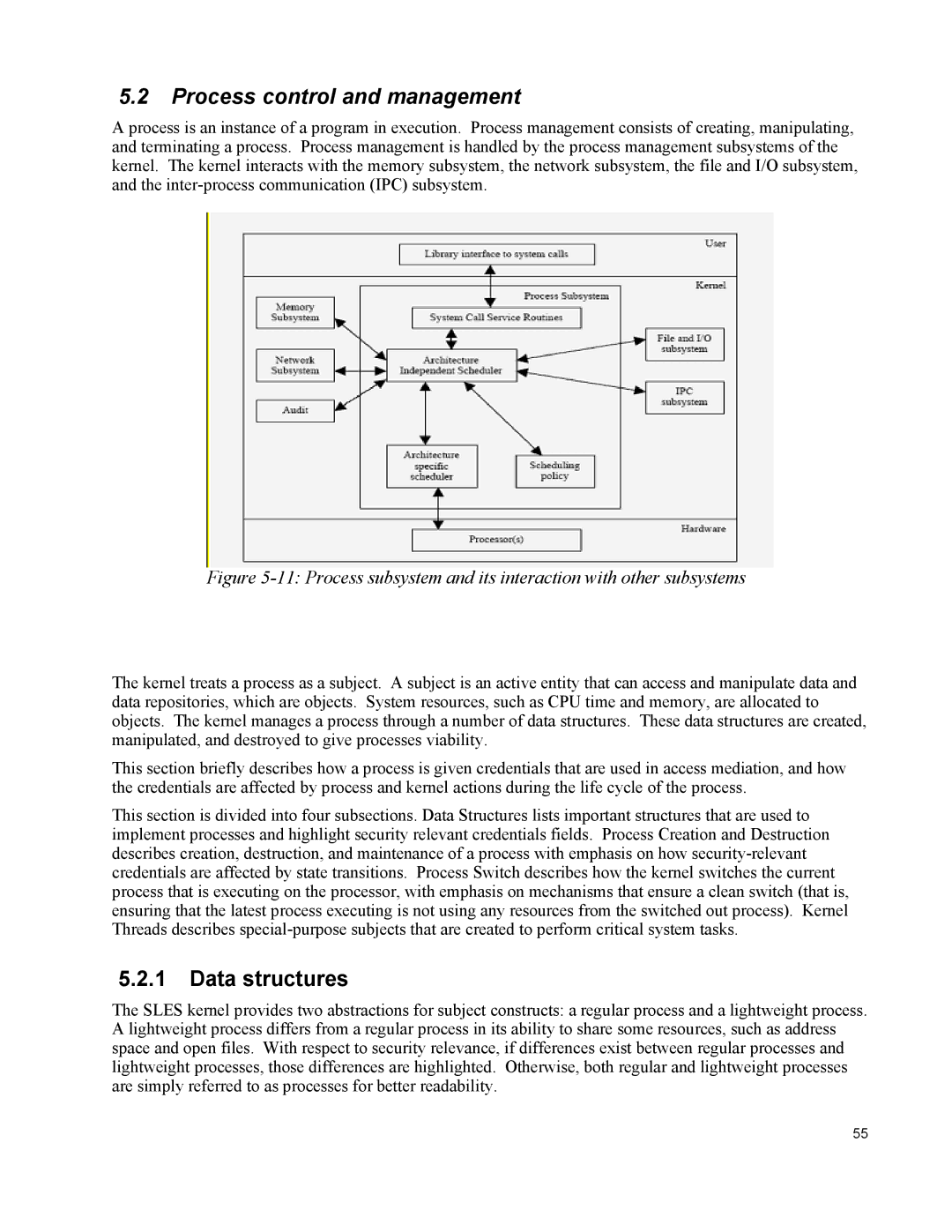
A process is an instance of a program in execution. Process management consists of creating, manipulating, and terminating a process. Process management is handled by the process management subsystems of the kernel. The kernel interacts with the memory subsystem, the network subsystem, the file and I/O subsystem, and the
Figure 5-11: Process subsystem and its interaction with other subsystems
The kernel treats a process as a subject. A subject is an active entity that can access and manipulate data and data repositories, which are objects. System resources, such as CPU time and memory, are allocated to objects. The kernel manages a process through a number of data structures. These data structures are created, manipulated, and destroyed to give processes viability.
This section briefly describes how a process is given credentials that are used in access mediation, and how the credentials are affected by process and kernel actions during the life cycle of the process.
This section is divided into four subsections. Data Structures lists important structures that are used to implement processes and highlight security relevant credentials fields. Process Creation and Destruction describes creation, destruction, and maintenance of a process with emphasis on how
5.2.1Data structures
The SLES kernel provides two abstractions for subject constructs: a regular process and a lightweight process. A lightweight process differs from a regular process in its ability to share some resources, such as address space and open files. With respect to security relevance, if differences exist between regular processes and lightweight processes, those differences are highlighted. Otherwise, both regular and lightweight processes are simply referred to as processes for better readability.
55