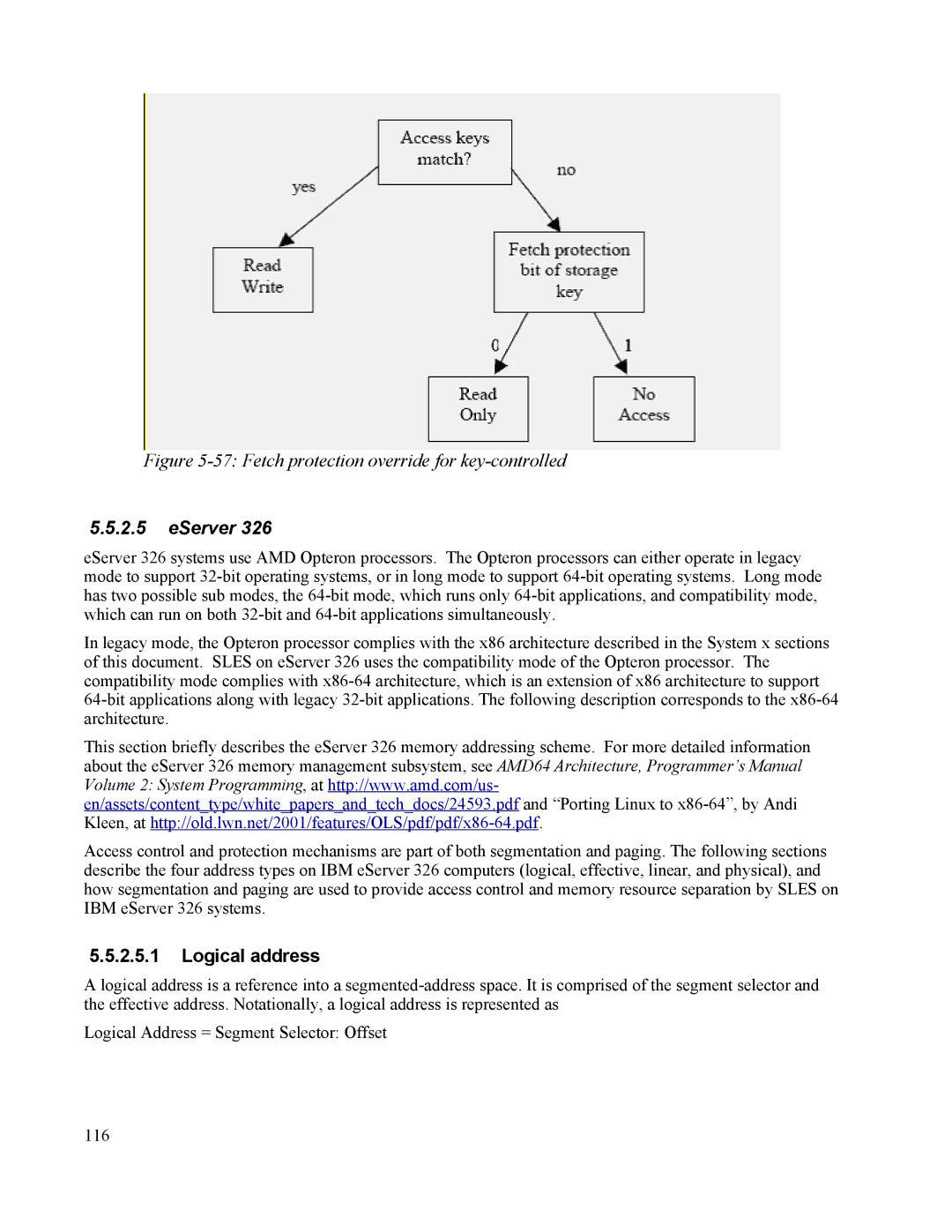
Figure 5-57: Fetch protection override for key-controlled
5.5.2.5eServer 326
eServer 326 systems use AMD Opteron processors. The Opteron processors can either operate in legacy mode to support
In legacy mode, the Opteron processor complies with the x86 architecture described in the System x sections of this document. SLES on eServer 326 uses the compatibility mode of the Opteron processor. The compatibility mode complies with
This section briefly describes the eServer 326 memory addressing scheme. For more detailed information about the eServer 326 memory management subsystem, see AMD64 Architecture, Programmer’s Manual Volume 2: System Programming, at http://www.amd.com/us- en/assets/content_type/white_papers_and_tech_docs/24593.pdf and “Porting Linux to
Access control and protection mechanisms are part of both segmentation and paging. The following sections describe the four address types on IBM eServer 326 computers (logical, effective, linear, and physical), and how segmentation and paging are used to provide access control and memory resource separation by SLES on IBM eServer 326 systems.
5.5.2.5.1Logical address
A logical address is a reference into a
Logical Address = Segment Selector: Offset
116