The segment selector specifies an entry in either the global or local descriptor table. The specified descriptor- table entry describes the segment location in
5.5.2.5.2Effective address
The offset into a memory segment is referred to as an effective address. Effective addresses are formed by adding together elements comprising a base value, a
Effective Address = Base + (Scale x Index) + Displacement Long mode supports
5.5.2.5.3Linear address
The linear address, which is also referred as virtual address, is a
5.5.2.5.4Physical address
A physical address is a reference into the
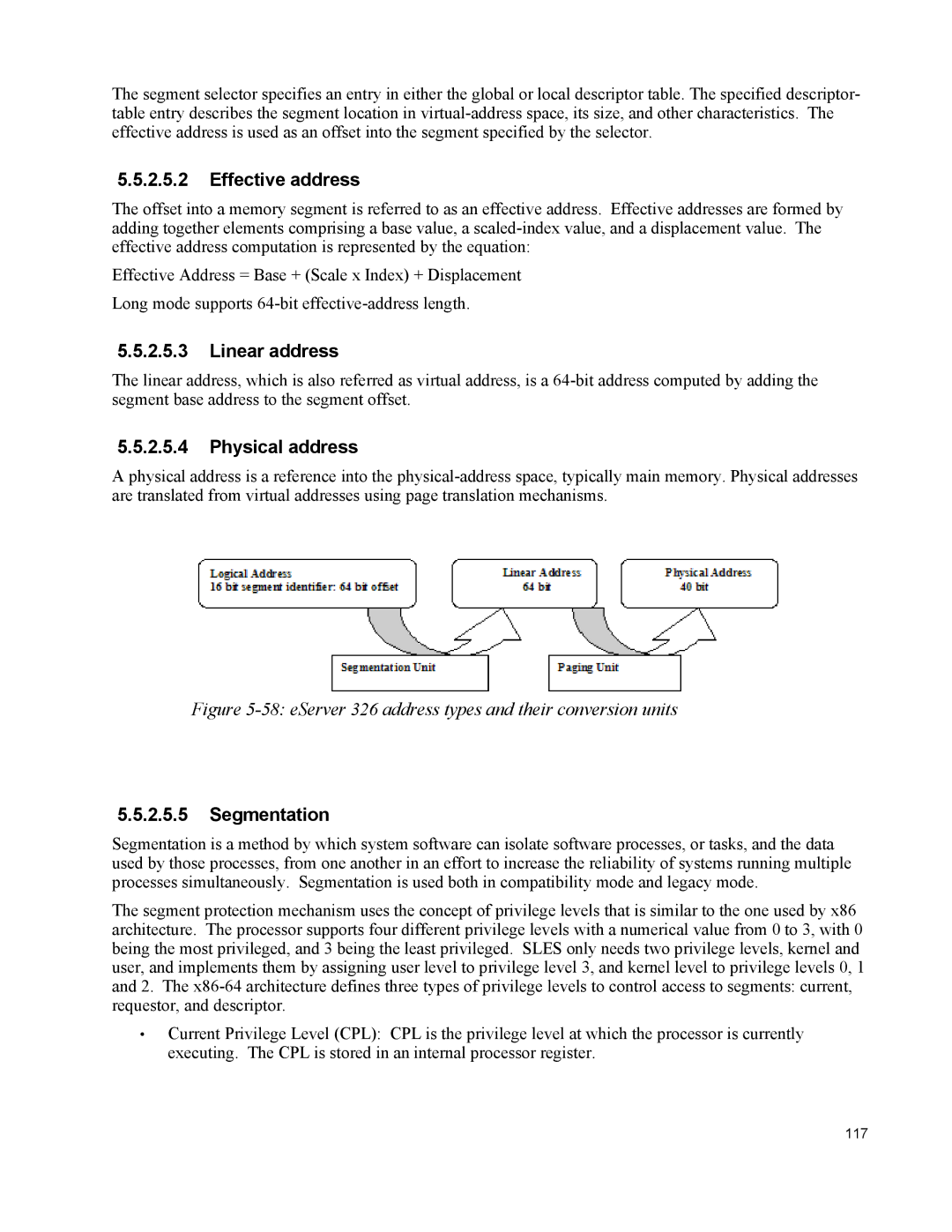
Figure 5-58: eServer 326 address types and their conversion units
5.5.2.5.5Segmentation
Segmentation is a method by which system software can isolate software processes, or tasks, and the data used by those processes, from one another in an effort to increase the reliability of systems running multiple processes simultaneously. Segmentation is used both in compatibility mode and legacy mode.
The segment protection mechanism uses the concept of privilege levels that is similar to the one used by x86 architecture. The processor supports four different privilege levels with a numerical value from 0 to 3, with 0 being the most privileged, and 3 being the least privileged. SLES only needs two privilege levels, kernel and user, and implements them by assigning user level to privilege level 3, and kernel level to privilege levels 0, 1 and 2. The
•Current Privilege Level (CPL): CPL is the privilege level at which the processor is currently executing. The CPL is stored in an internal processor register.
117