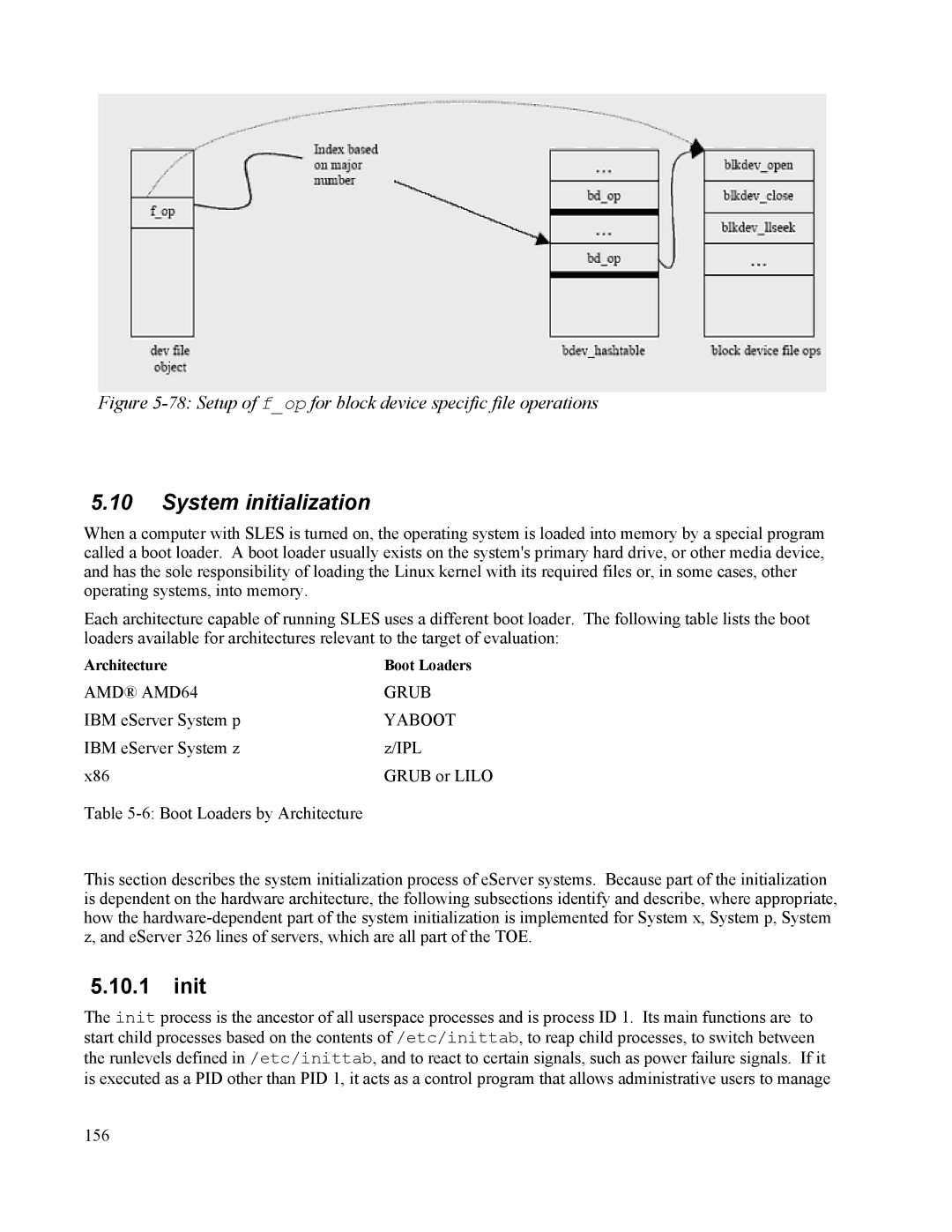
Figure 5-78: Setup of f_op for block device specific file operations
5.10System initialization
When a computer with SLES is turned on, the operating system is loaded into memory by a special program called a boot loader. A boot loader usually exists on the system's primary hard drive, or other media device, and has the sole responsibility of loading the Linux kernel with its required files or, in some cases, other operating systems, into memory.
Each architecture capable of running SLES uses a different boot loader. The following table lists the boot loaders available for architectures relevant to the target of evaluation:
Architecture | Boot Loaders |
AMD® AMD64 | GRUB |
IBM eServer System p | YABOOT |
IBM eServer System z | z/IPL |
x86 | GRUB or LILO |
Table |
|
This section describes the system initialization process of eServer systems. Because part of the initialization is dependent on the hardware architecture, the following subsections identify and describe, where appropriate, how the
5.10.1init
The init process is the ancestor of all userspace processes and is process ID 1. Its main functions are to start child processes based on the contents of /etc/inittab, to reap child processes, to switch between the runlevels defined in /etc/inittab, and to react to certain signals, such as power failure signals. If it is executed as a PID other than PID 1, it acts as a control program that allows administrative users to manage
156