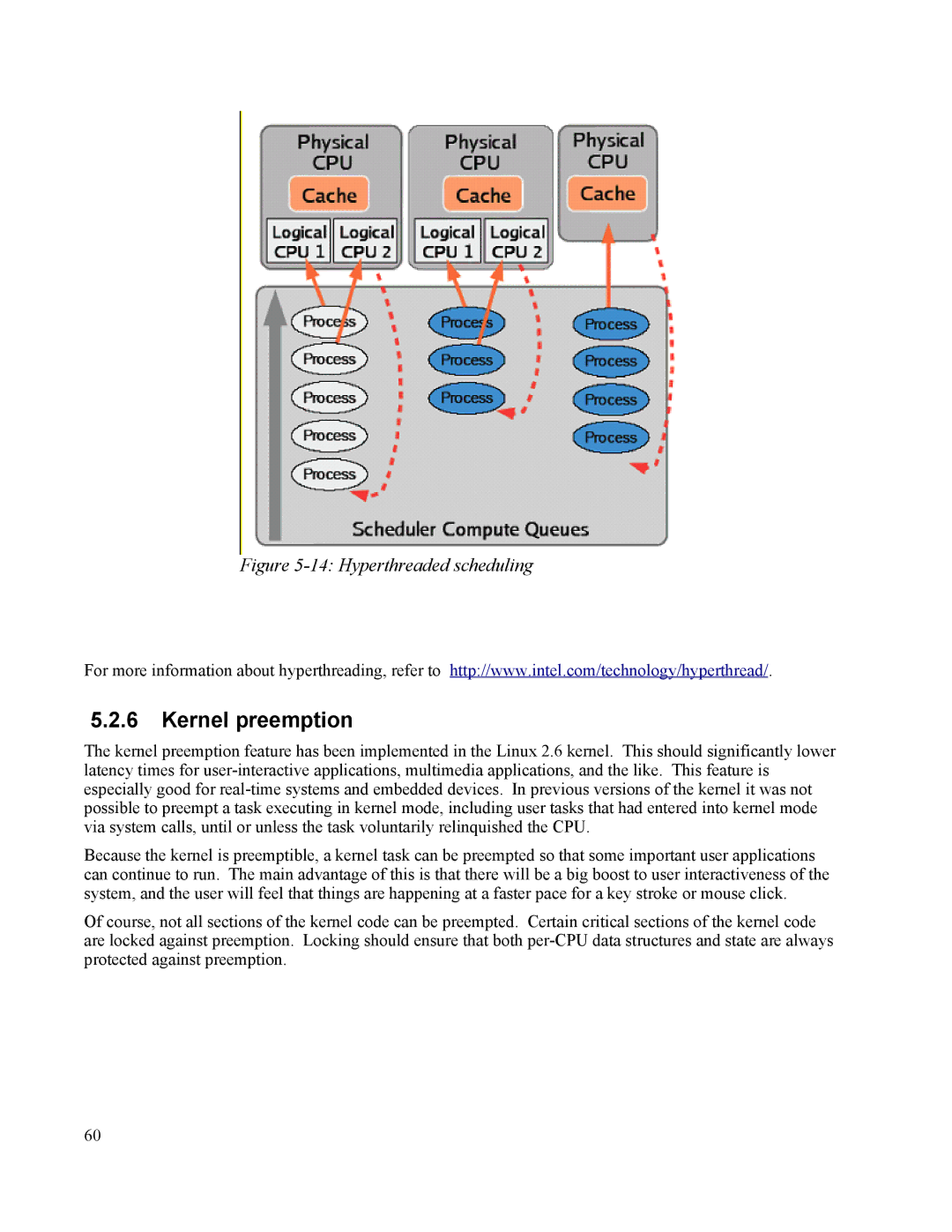
Figure 5-14: Hyperthreaded scheduling
For more information about hyperthreading, refer to http://www.intel.com/technology/hyperthread/.
5.2.6Kernel preemption
The kernel preemption feature has been implemented in the Linux 2.6 kernel. This should significantly lower latency times for
Because the kernel is preemptible, a kernel task can be preempted so that some important user applications can continue to run. The main advantage of this is that there will be a big boost to user interactiveness of the system, and the user will feel that things are happening at a faster pace for a key stroke or mouse click.
Of course, not all sections of the kernel code can be preempted. Certain critical sections of the kernel code are locked against preemption. Locking should ensure that both
60