THEORY OF OPERATION | ||
| FIGURE E.2 - GENERAL DISCRIPTION |
|
Return to Section TOC
to Section TOC
P
o { w
e
r
W
a
v
e
4
0
5
o n l y
|
| Main Switch Board | |
Input switch | Input | Primary | |
Rectifier | |||
Current | |||
|
| Sensor | |
|
| Reconnect | |
|
| Switch | |
|
| Primary | |
|
| Current | |
|
| Sensor | |
|
| Fan |
220 VAC | Transformer |
| olntrCoFan | Primary Current Feedback(2) | IGBTDriveSig | |||
|
| 115VAC Fan Supply |
| Input Relay Control |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| Auxiliary |
|
| Soft Start Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| V/F Capacitor Feedback (2) |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| nal |
|
| 40VDC | Machine Control Supply |
|
|
| ||
|
| +15VDC, |
|
|
| |||
|
| Power |
|
|
| |||
|
| Board | RS232 Supply +5VDC |
|
| Control Board | ||
220 | 42VAC |
|
|
| ||||
|
| Can Supply +5VDC |
|
|
| |||
Receptacle | 65VAC |
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| DC |
|
| Arc |
| Electrode | ||
|
| Bus |
|
| Link | Wire | Sense | |
|
| Board | 40VDC |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Feeder |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| Recp. |
| Thermostats |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
Board | ||
| Feedbac | Curre nt |
| k |
|
Choke
ltagoV Se seen
Ou ttpu
21 Lead
Voltage
Sense
Recp.
Positive
Output
Terminal
Negative
Output
Terminal
Yellow
Thermal
LED
Status
Red/Green
LED
R232
Connector
Return
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
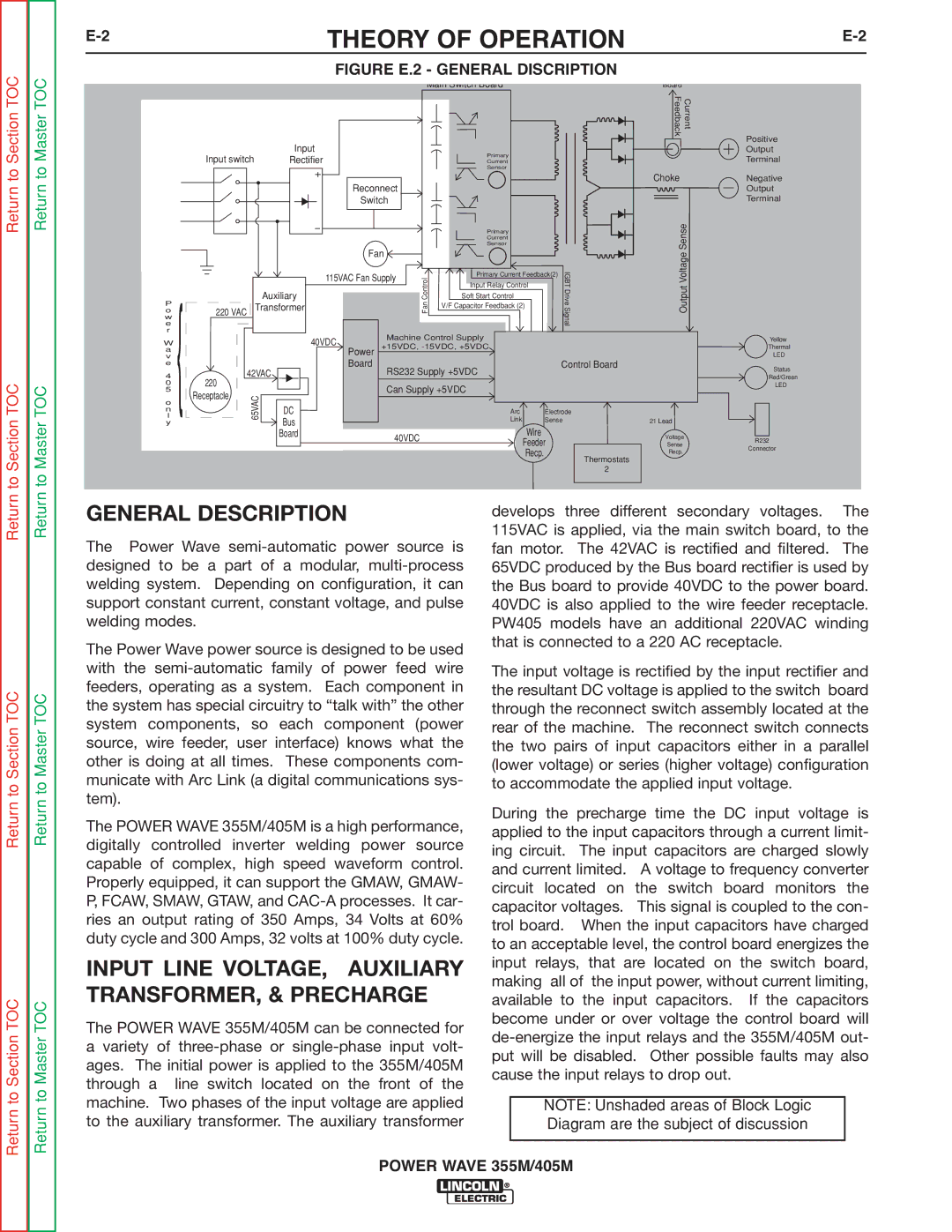
GENERAL DESCRIPTION | develops three different secondary voltages. | The | ||||||
The Power Wave | power source is | 115VAC is applied, via the main switch board, to the | ||||||
fan motor. The 42VAC is rectified and filtered. | The | |||||||
designed to be a part of a modular, | 65VDC produced by the Bus board rectifier is used by | |||||||
welding system. Depending on configuration, it can | the Bus board to provide 40VDC to the power board. | |||||||
support constant current, constant voltage, and pulse | 40VDC is also applied to the wire feeder receptacle. | |||||||
welding modes. |
| PW405 models have an additional 220VAC winding | ||||||
The Power Wave power source is designed to be used | that is connected to a 220 AC receptacle. |
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
with the | The input voltage is rectified by the input rectifier and | |||||||
feeders, operating as a system. Each component in | the resultant DC voltage is applied to the switch board | |||||||
the system has special circuitry to “talk with” the other | through the reconnect switch assembly located at the | |||||||
system components, so each component (power | rear of the machine. The reconnect switch connects | |||||||
source, wire feeder, user interface) knows what the | the two pairs of input capacitors either in a parallel | |||||||
other is doing at all times. These components com- | (lower voltage) or series (higher voltage) configuration | |||||||
municate with Arc Link (a digital communications sys- | to accommodate the applied input voltage. |
|
| |||||
tem). |
| During the precharge time the DC input voltage is | ||||||
The POWER WAVE 355M/405M is a high performance, | ||||||||
applied to the input capacitors through a current limit- | ||||||||
digitally controlled inverter welding power source | ||||||||
ing circuit. The input capacitors are charged slowly | ||||||||
capable of complex, high speed waveform control. | ||||||||
and current limited. A voltage to frequency converter | ||||||||
Properly equipped, it can support the GMAW, GMAW- | ||||||||
circuit located on the switch board monitors |
| the | ||||||
P FCAW, SMAW, GTAW, and |
| |||||||
capacitor voltages. This signal is coupled to the con- | ||||||||
ries an output rating of 350 Amps, 34 Volts at 60% | ||||||||
trol board. When the input capacitors have charged | ||||||||
duty cycle and 300 Amps, 32 volts at 100% duty cycle. | ||||||||
to an acceptable level, the control board energizes the | ||||||||
|
| |||||||
INPUT LINE VOLTAGE, | AUXILIARY | input relays, | that are located on | the switch board, | ||||
making all of | the input power, without current limiting, | |||||||
TRANSFORMER, & PRECHARGE | ||||||||
available to the input capacitors. | If the capacitors | |||||||
The POWER WAVE 355M/405M can be connected for | become under or over voltage the control board will | |||||||
a variety of | ||||||||
put will be disabled. Other possible faults may also | ||||||||
ages. The initial power is applied to the 355M/405M | ||||||||
cause the input relays to drop out. |
|
|
| |||||
through a line switch located on the front of the |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
machine. Two phases of the input voltage are applied |
|
|
|
| ||||
| NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic |
|
| |||||
to the auxiliary transformer. The auxiliary transformer |
| Diagram are the subject of discussion |
|
| ||||