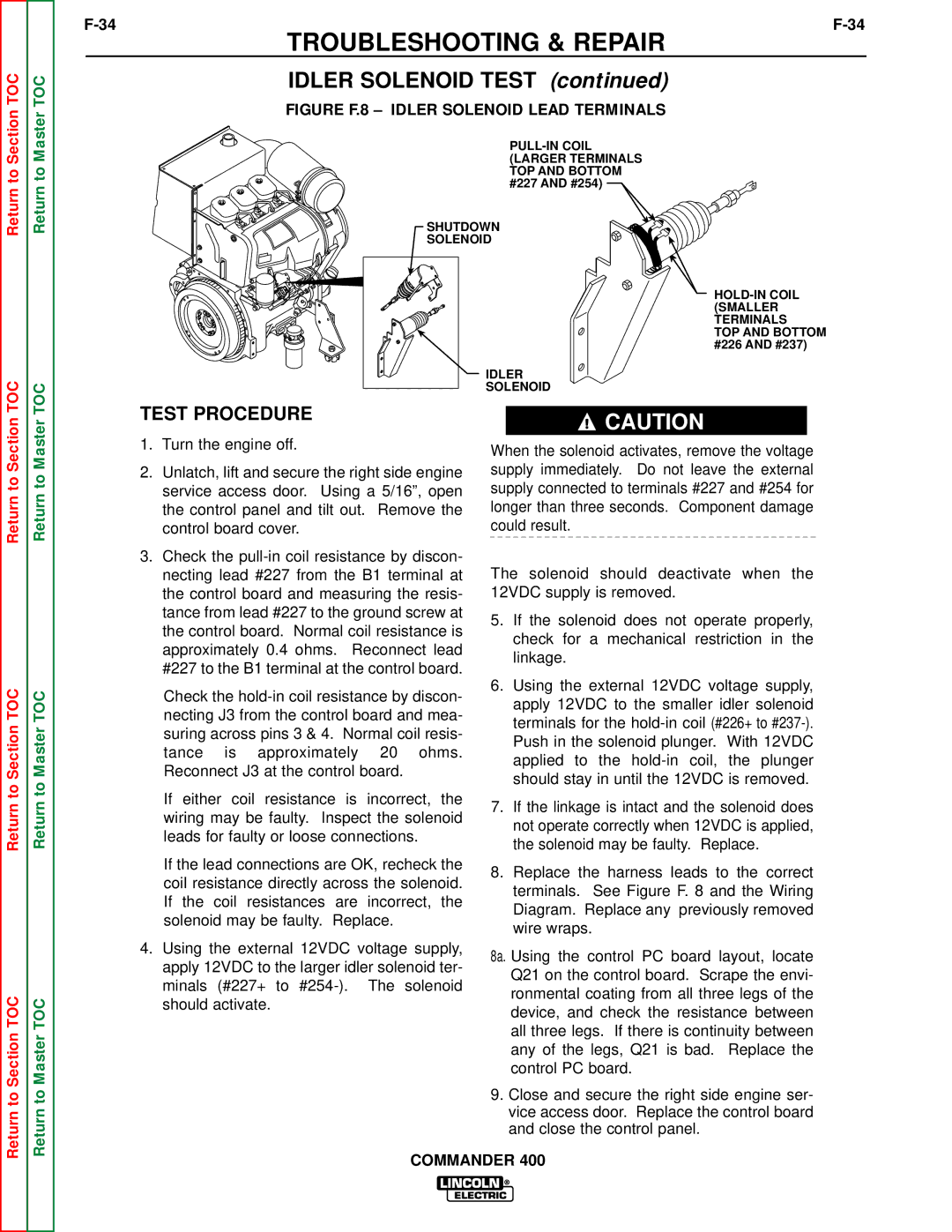
SVM133-B specifications
The Lincoln Electric SVM133-B is an innovative welding machine designed to meet the diverse needs of welders and fabrication shops. This versatile equipment combines state-of-the-art technology with user-friendly features, making it ideal for both novice and professional welders.One of the main features of the SVM133-B is its advanced inverter technology. This allows for a more efficient power delivery, which translates into reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs. The machine is capable of delivering optimal welding performance across a range of materials, from thin sheets to heavier sections, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as automotive, construction, and repair.
The SVM133-B supports multiple welding processes, including MIG, stick, and TIG welding. This flexibility ensures that users can adapt to various job requirements without needing multiple machines. The intuitive control panel allows users to switch between modes effortlessly, providing a seamless welding experience.
Another notable characteristic of the SVM133-B is its compact and lightweight design. Weighing significantly less than traditional welding machines, it is highly portable, making it easy to transport to different job sites. Additionally, its rugged construction ensures durability, allowing it to withstand tough working conditions.
The SVM133-B is equipped with advanced safety features, such as overheat and overload protection, which safeguard both the machine and the user during operation. It also includes a digital display that provides real-time feedback on settings, voltage, and amperage, which enhances precision and control during welding tasks.
Lincoln Electric has prioritized ease of use in the SVM133-B, with quick setup guides and clear instructions. This user-centric approach not only facilitates a smoother learning curve for beginners but also optimizes the workflow for experienced welders, enabling them to maximize productivity.
One of the standout features is the capability to weld aluminum with ease, thanks to its spool gun compatibility. This feature sets the SVM133-B apart from many competitors, providing added value for users who require flexibility in their welding projects.
In summary, the Lincoln Electric SVM133-B stands out in the welding machine market due to its inverter technology, multi-process capabilities, portability, and robust safety measures. It embodies the perfect blend of innovation and practicality, making it a top choice for welders looking to enhance their skills and productivity across a wide array of applications. Whether for professional use or hobbyist projects, the SVM133-B offers a reliable solution for high-quality welding tasks.