Security
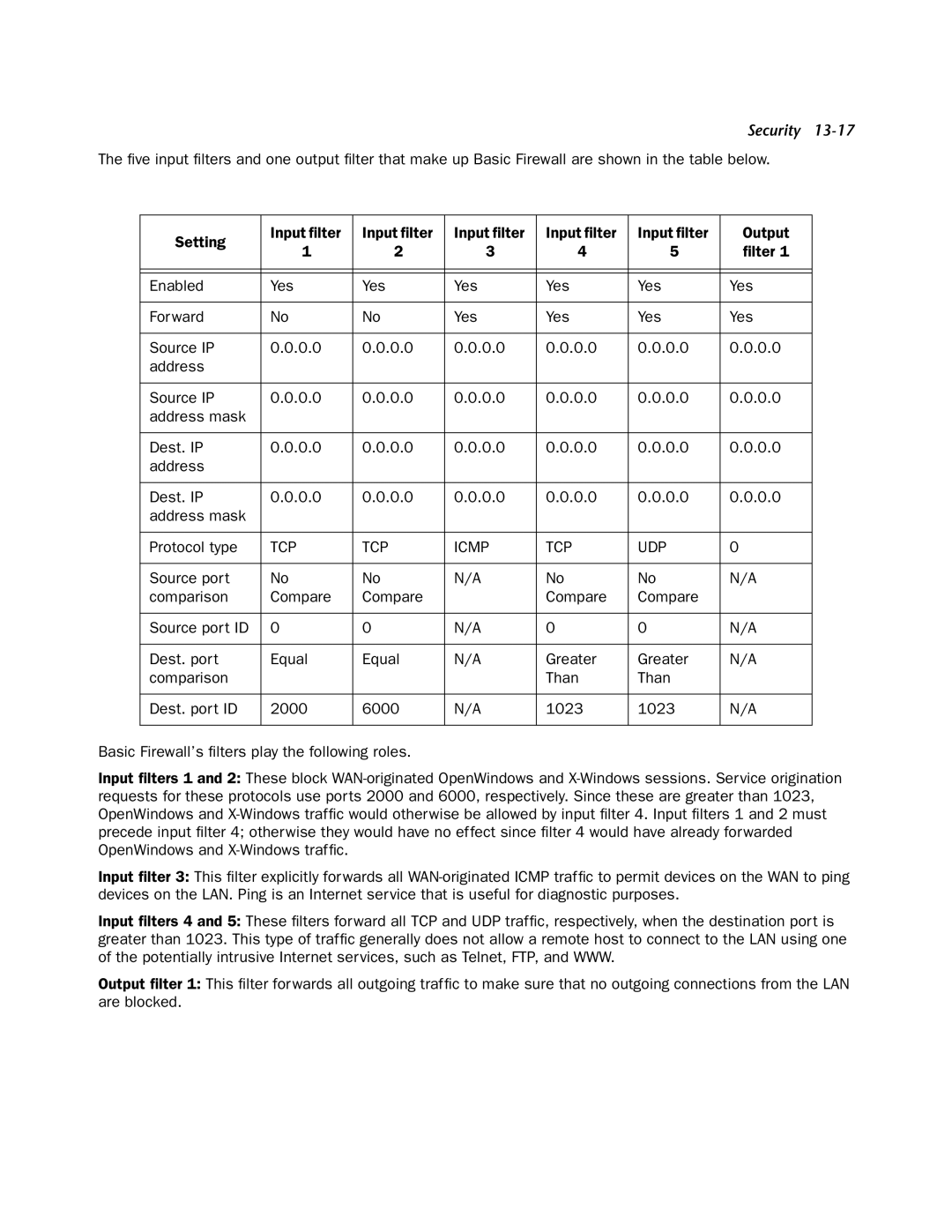
The five input filters and one output filter that make up Basic Firewall are shown in the table below.
Setting | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Output | |
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | filter 1 | ||
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Enabled | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Forward | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address mask |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address mask |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Protocol type | TCP | TCP | ICMP | TCP | UDP | 0 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source port | No | No | N/A | No | No | N/A | |
comparison | Compare | Compare |
| Compare | Compare |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source port ID | 0 | 0 | N/A | 0 | 0 | N/A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. port | Equal | Equal | N/A | Greater | Greater | N/A | |
comparison |
|
|
| Than | Than |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. port ID | 2000 | 6000 | N/A | 1023 | 1023 | N/A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Firewall’s filters play the following roles.
Input filters 1 and 2: These block
Input filter 3: This filter explicitly forwards all
Input filters 4 and 5: These filters forward all TCP and UDP traffic, respectively, when the destination port is greater than 1023. This type of traffic generally does not allow a remote host to connect to the LAN using one of the potentially intrusive Internet services, such as Telnet, FTP, and WWW.
Output filter 1: This filter forwards all outgoing traffic to make sure that no outgoing connections from the LAN are blocked.