User’s Guide
Adept SmartController
Page
00356-00100, Rev. E May
Page
Table of Contents
SmartController Operation
Table of Contents
SmartController Maintenance
SDIO Module
Using the Manual Control Pendant MCP 125
Index
Figure A-1
List of Figures
List of Figures
List of Tables
List of Tables
Adept SmartController CX
Introduction
Product Description
Adept SmartController CS
Introduction
How Can I Get Help?
Related Manuals
Adept Document Library
Reading and Training for Users and Operators
Safety
System Safeguards
Safety Features on the Front Panel
Computer Controlled Robots and Motion Devices
Other Computer-Controlled Devices
Safety
Program Security
Manually Controlled Robots and Motion Devices
Inappropriate Uses of the Adept SmartController
Standards Compliance
Stop Circuit
CAT-3 Version of SmartController
Identification
Functionality Changes
Operational Change in SmartModule Systems
Upon Unpacking
SmartController Installation
Controller Installation
Before Unpacking
Mounting the SmartController
SmartController Installation
Repacking for Relocation
Space Around the Chassis
Rack Mounting the SmartController
Controller Installation
Panel Mounting the SmartController
Panel Mounting the SmartController
Table Mounting the SmartController
Table Mounting the SmartController
CompactFlash Memory Card
Stacking Components
CompactFlash Memory Card Compartment
Installing CompactFlash
24VDC Power Specifications
Connecting Power
24VDC Power Cabling
Daisy-Chaining Power
Grounding
Grounding Point
Installing 24VDC Connectors
V Connectors
Ieee 1394 Cable Specifications
PDU2
System Cable Installation
System Cable Installation
Page
Green Indicates Red Indicates
SmartController CS Connectors and Indicators
SmartController Operation
Top Three Status LEDs
Bottom Three Status LEDs
LED Display Error # Description
SW1 DIP switches
DeviceNet connector
Xusr connector
Ethernet Eth 10/100 connector
RS-232 and RS-422/485 connectors
Xdio connector
SmartController CX Connectors and Indicators
Front Panel
System 5V Power On LED
Manual/Automatic Mode Switch
High Power On/Off Switch & Lamp
Emergency Stop Switch
Configuring the Controller
Factory Default Settings
DIP-Switch Settings
Ascii Terminal
Configuring the Controller
Row # Interpretation
AdeptWindows PC Graphical User Interface
Pin Signal Type
SmartController Serial I/O Connectors
RS-232 Connectors
Auto Boot
RS-422/485 Connector
SmartController Serial I/O Connectors
Controller Connector + Designation
Graphical Interface Using AdeptWindows
Installing the User Interface
Start = Programs = Accessories = HyperTerminal
Text Interface Using a PC with HyperTerminal Software
Installing the User Interface
Installation Procedure
Recommended Terminal for Text-Based Systems
Text Interface Using a Terminal
Pin Description Comments Shorted if Pairs Not Used
Connecting Equipment to the System
Description Comments
Pin Pairs
Pin Xmcp Pin MCP Description Pin D-Sub Pin CPC
CAT-3 E-Stop Circuit on Xusr and XFP Connectors
Stop, High Power On/Off and MANUAL/AUTO Controls
Emergency Stop Circuits
Adept Front Panel Schematic
Muted Safety Gate E-Stop Circuitry
User E-Stop Indication Remote Sensing of E-Stop
Line E-Stop Input
User High Power On Indication
Remote Manual Mode
Remote High Power On/Off Control
High Power On/Off Lamp
Remote Front Panel Usage
Remote MCP Usage
Connecting Customer-Supplied Digital I/O Equipment
Xdio Connector
Connecting Customer-Supplied Digital I/O Equipment
Input Signals
Fast Input Signals 1001 to
React Input Signals 1001 to
11. DIO Output Specifications Xdio connector
Output Signals
Digital Output Wiring for Xdio Connector
Pin Signal
Screw-Terminal Field-Wiring Adapter Blocks
Digital I/O Connector Ordering Details Third-Party Sources
Channel Signal Pin
Belt Encoder Interface on SmartController CX
Belt Encoder Interface on SmartController CX
Belt Encoder Typical Input Circuit
SAVI Board System Requirements and Restrictions
SAVI Board Features
AdeptVision sAVI Option
Introduction
Guidelines for Cameras
Camera Compatibility
Pixel Format
AdeptVision sAVI Inspection System Limitations
Camera Compatibility
Standard Resolution Cameras
High Resolution Cameras
Cameras Supported
Two-Camera Breakout Cable for RS-170 Cameras
Camera Cables
Four-Camera Breakout Cable for RS-170 Cameras
Meter Camera Extension Cables
Camera Cables
Connecting the Cables to the RS-170 Standard Camera
Installing Camera Cables
Camera Cable Installation Drawing RS-170
Installing Camera Cables
Camera Cable Pin and Signal Information
Pin Function
Camera Cable Pin and Signal Information
Pin Function
Pin Locations for Camera Cable Connector 12-Pin Hirose Male
From Pin Function
From Pin Function
Str/Pwr User +12 V to cameras User power return
Pin
Pin
SAVI Board Specifications
SAVI Board Specifications
Page
Changing the Lamp in the High Power Indicator
SmartController Maintenance
Lamp Body Contact Alignment
SmartController Maintenance
SmartController Dimensions
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
SDIO Dimensions
Adept Front Panel Dimensions
Adept Front Panel Dimensions
Adept Front Panel Back View
Adept MCP Dimensions
Adept MCP Dimensions
MCP Cradle Dimensions
Mounting the sDIO
SDIO Module a
Appendix a sDIO Module
Rack Mounting the sDIO
Mounting the sDIO
Panel Mounting the sDIO
Installing the sDIO
Table Mounting the sDIO
Stack Mounting
Input Signal Block Byte Output Signal Numbers
Configuring a Single sDIO
Default sDIO I/O Configuration
Configuring a Single sDIO
Modifying the Default sDIO Configuration
Assigning sDIO Signal Blocks
Configure 1394 DIO
Do you want to save these changes?
Assigning I/O Signal Numbers
+ System Configuration Data Then, press Enter to continue
Enter new value
100 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Edit system configuration Then, press Enter to continue
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 101
SDIO Signal Mapping Example
102 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Using Multiple sDIO Modules
Status LEDs
SDIO Module Connectors and Indicators
Configuring a System with an sDIO and a RIO
SDIO Module Connectors and Indicators
SDIO Digital I/O Signals
SDIO Inputs
104 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 105
SDIO Digital I/O Signals
106 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Testing sDIO Outputs
SDIO Outputs
SDIO LEDs
SDIO Output Power Supply Current Selection
Illumination Upper LED Link Lower LED OK SF
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 107
108 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Parameter Value
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 109
Smart-DIO
Optional DIO Cables
Labeling Cables
110 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Input and Output Cable Wiring Information
Pin Signal Wire Number Group Color Locations
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 111
112 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 113
Pin Group Signal name Wire Number Color Pin Locations
114 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 115
DeviceNet Specifications
Volume
Adept DeviceNet B
Appendix B Adept DeviceNet
Pin Signal Name
Limitations of the Adept DeviceNet Scanner
Adept Supplied DeviceNet Hardware
DeviceNet Physical Layer and Media
DeviceNet Physical Layer and Media
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 117
118 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 119
Data Rates Kbps
120 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Figure B-2. DeviceNet Thick Cable
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 121
DeviceNet Connectors
Connector Description
Termination of the DeviceNet Network
Power Supply and the DeviceNet Bus
Power Capabilities of a DeviceNet Cable System
122 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 123
Length of Dropline Maximum Current
124 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Figure B-6. DeviceNet Connector Pinouts
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 125
Using the Manual C Control Pendant MCP
MCP Enable Switch Function on CAT-3 SmartController
Manual Control Pendant Basics
Appendix C Using the Manual Control Pendant MCP
Position Enable Switch
126 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Manual Control Pendant Basics
MCP-4 Compatibility
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 127
CMD
128 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 129
Connecting the MCP
130 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
MCP Layout
Soft Buttons
Function Buttons
Speed Bars and Slow Button
Mode Control and Joint/Axis Control Buttons
Emergency Stop From the MCP
Data Entry Buttons
132 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Re-Enabling Power After Enable Switch Released
Original SmartController
CAT-3 SmartController
Predefined Function Buttons
Background Mode
MCP Predefined Functions
Introduction
134 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Edit Function
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 135
Display Function
136 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Clear Error Function
CMD Function
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 137
138 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Figure C-10. Command CMD Function Button
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 139
Prog Set Function
Mode Control Buttons
Moving a Robot or Motion Device With the MCP
140 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
MAN/HALT Button
Emergency Stop Switch
Moving a Robot or Motion Device With the MCP
COMP/PWR Button
Joint/Axis Control Buttons
Speed Bars
142 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
World State
Comp Mode
Slow Button
Robot States
144 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Tool State
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 145
+RZ
146 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Figure C-16. Tool State Six-Axis Robot
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 147
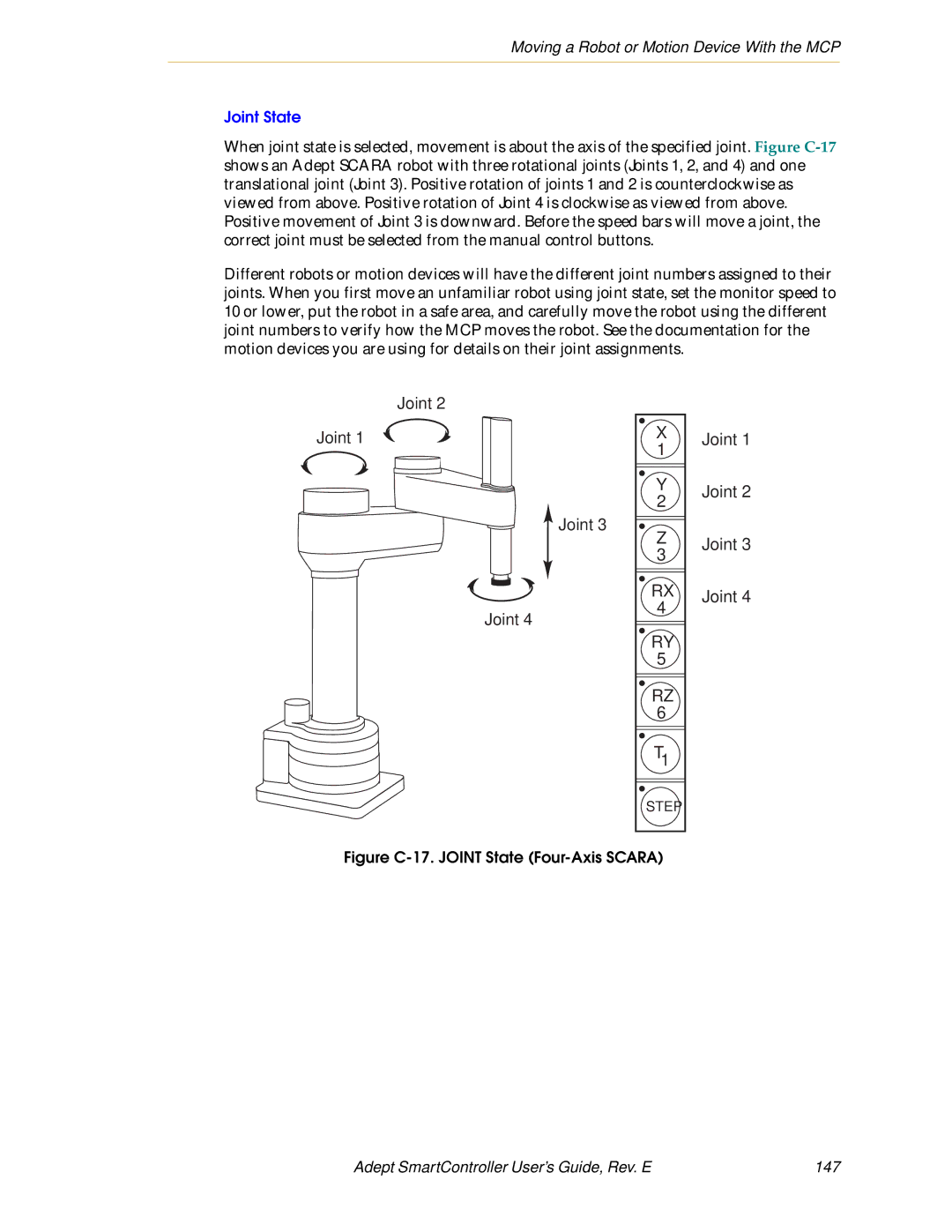
Joint State
148 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Free State
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 149
Controlling More Than One Robot
Joint/Axis LED state Joint range
DEV LED state Robot selected by pendant
Robots With Fewer Than Six Joints
Robots With More Than Six Joints
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 151
Index
152 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Index
Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E 153
143
154 Adept SmartController User’s Guide, Rev. E
Page
Triad Drive