ActivMedia Robotics Operating System
|
|
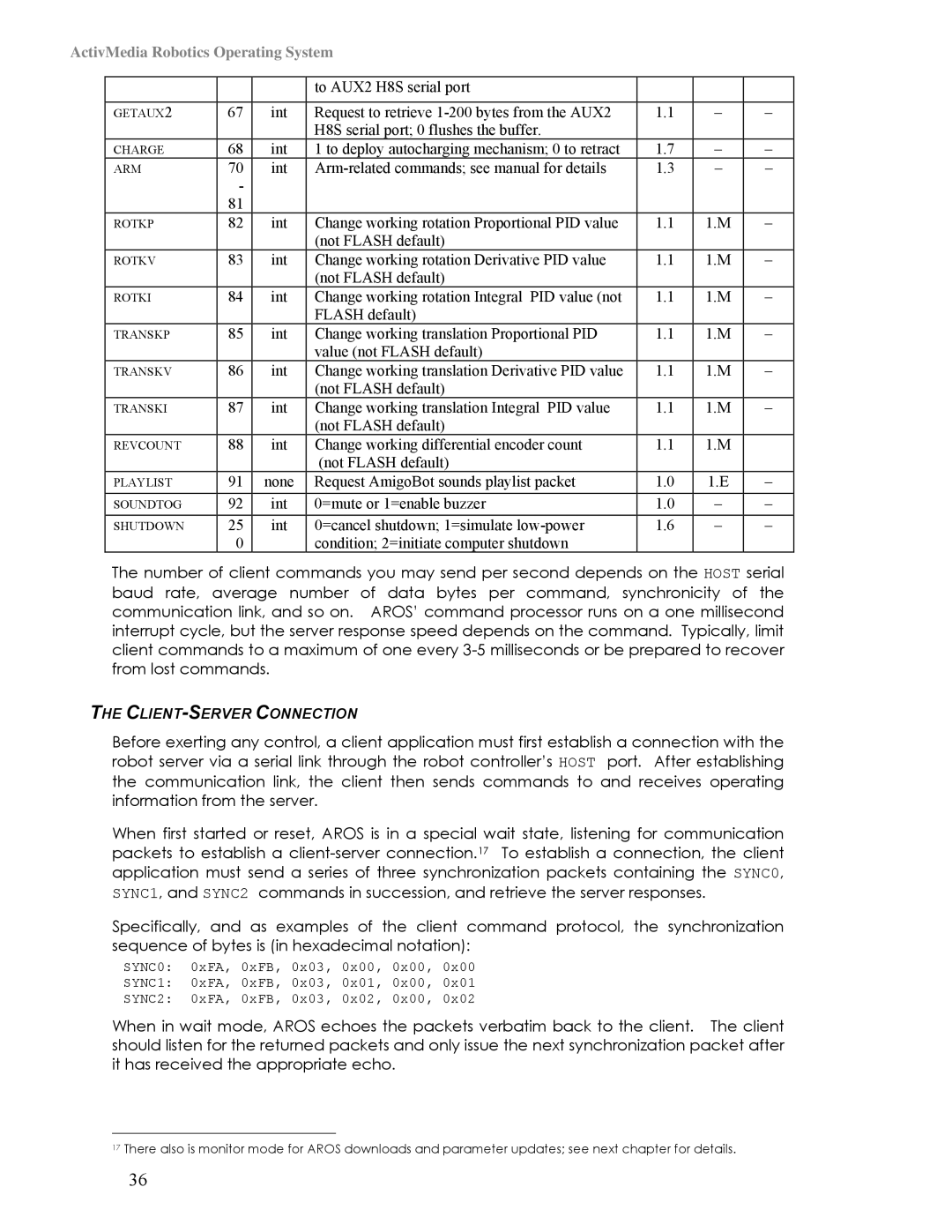
| to AUX2 H8S serial port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GETAUX2 | 67 | int | Request to retrieve | 1.1 | – | – |
|
|
| H8S serial port; 0 flushes the buffer. |
|
|
|
CHARGE | 68 | int | 1 to deploy autocharging mechanism; 0 to retract | 1.7 | – | – |
ARM | 70 | int | 1.3 | – | – | |
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| 81 |
|
|
|
|
|
ROTKP | 82 | int | Change working rotation Proportional PID value | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
ROTKV | 83 | int | Change working rotation Derivative PID value | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
ROTKI | 84 | int | Change working rotation Integral PID value (not | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| FLASH default) |
|
|
|
TRANSKP | 85 | int | Change working translation Proportional PID | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| value (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
TRANSKV | 86 | int | Change working translation Derivative PID value | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
TRANSKI | 87 | int | Change working translation Integral PID value | 1.1 | 1.M | – |
|
|
| (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
REVCOUNT | 88 | int | Change working differential encoder count | 1.1 | 1.M |
|
|
|
| (not FLASH default) |
|
|
|
PLAYLIST | 91 | none | Request AmigoBot sounds playlist packet | 1.0 | 1.E | – |
SOUNDTOG | 92 | int | 0=mute or 1=enable buzzer | 1.0 | – | – |
SHUTDOWN | 25 | int | 0=cancel shutdown; 1=simulate | 1.6 | – | – |
| 0 |
| condition; 2=initiate computer shutdown |
|
|
|
The number of client commands you may send per second depends on the HOST serial baud rate, average number of data bytes per command, synchronicity of the communication link, and so on. AROS’ command processor runs on a one millisecond interrupt cycle, but the server response speed depends on the command. Typically, limit client commands to a maximum of one every
THE CLIENT-SERVER CONNECTION
Before exerting any control, a client application must first establish a connection with the robot server via a serial link through the robot controller’s HOST port. After establishing the communication link, the client then sends commands to and receives operating information from the server.
When first started or reset, AROS is in a special wait state, listening for communication packets to establish a
Specifically, and as examples of the client command protocol, the synchronization sequence of bytes is (in hexadecimal notation):
SYNC0: 0xFA, 0xFB, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
SYNC1: 0xFA, 0xFB, 0x03, 0x01, 0x00, 0x01
SYNC2: 0xFA, 0xFB, 0x03, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02
When in wait mode, AROS echoes the packets verbatim back to the client. The client should listen for the returned packets and only issue the next synchronization packet after it has received the appropriate echo.
17There also is monitor mode for AROS downloads and parameter updates; see next chapter for details.
36