Sitrans
Safety Guidelines Qualified Personnel
Technical data subject to change
Technical Publications
Table of Contents
Maintenance
Iii
Appendix C Hart Documentation
113
Applications
Introduction
Safety Notes
Safety marking symbols
Manual
Abbreviations and Identifications
Short form
Long Form
Description
Power
Specifications
Environmental
Performance
Outputs
User Interface
Communications
Weight
Electrodes
Wetted Parts
Enclosure electronic
Process Conditions
Approvals
Sitrans LC 500 Transmitter
Operating Principles
Operation & Application
Capacitance measurement in a cylindrical metal tank
Non-conductive or conductive contents
Sitrans LC 500 electrode
A non-conductive or irregular tank
Stilling well
Active shield
Active
Measurement Section Probe seal
Inactive
Application Sitrans LC
Level Measurement
USL
Switch action
Interface Measurement
Fault Signalling
Via the loop current
Via Hart
Via the solid-state output
Sitrans LC 500 Probe Configuration
Probe Configuration
Electrode Assembly
Process Connections
Seal Types
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
Non-Standard Application Sitrans LC 500 Configuration
Non-standard applications
Sitrans LC 500 Installation
Installation
Handling Electrodes
Protection for solid-state switch
Mounting Instructions
Process Cautions
Sitrans LC 500 Standard Level Version
Wiring
Interconnection Sitrans LC
Supply
Interconnection
Cable
Selecting the correct instrumentation cable
Is applications maximum cable length
Multi-drop applications maximum cable length
Subtract the capacitance for the device
Which allows for 560 meters on that side
Connecting Sitrans LC
Connection Diagram
Terminals
Where the stilling well is welded to the tank 7ML19985GE01
Grounding instructions
Grounding Examples Sitrans LC
System Grounding referencing
Metal Tanks
Cathodically Protected Metal Tanks
Non-Conductive Tanks
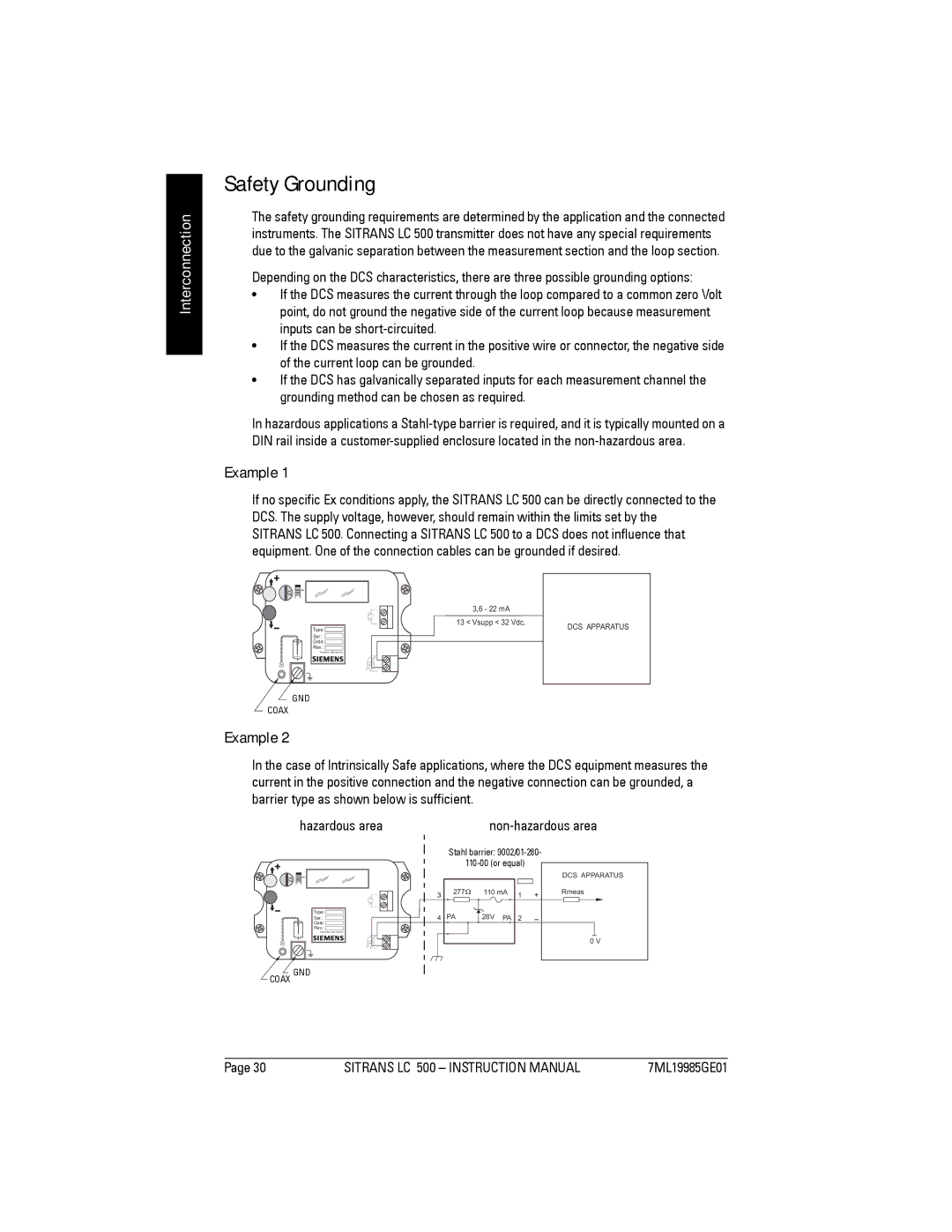
Safety Grounding
Example
Hazardous area Non-hazardous area
Diagnostics
Typical PLC configuration with Hart
Communications
Current values used as signals from digital transmitters
Applications for Solid-state Output
Factory Settings
Switch Protection Diode
Settings
Setting Description
Setting
Interconnection
Sitrans LC 500 User Interface
LCD display
User Interface
How to access the data
Menu Levels 00 to 0F and 10 to 1F
Description Menu Group Details
Rotary switch
Access to a menu item
Adjusting the value
Push-buttons
Transmitter Variables
Transmitter Variable User-defined Functions Units
Start-up Sitrans LC
Quick Start
Start Up
Quick Start Sequence
Rotary Switch Positions Quick Reference
Num
Menu levels 0
To change from menu 00 to menu
To change from menu 10 to menu
Calibration using push-button adjustment
Changing stepsize value menu
100% value is set
Current percent of span = 14/20 = 70%
Start Up
Calibration using Hart
Start Up
Number Description
Number
Maintenance
Maintenance
Test function
Inspections
Maintenance
Troubleshooting Sitrans LC
Troubleshooting
If you are unable to change settings
Error Messages and Error Codes
Error Messages push-button operation
Error Codes Hart
Error Description Cause Message
Appendix a Menu Groups
Transmitter Variable Settings menu level
Stepsize Update Value
Rotary Left Switch Description Values Position Arrow
Menu Items
Set the rotary switch to B
Damping
Lower Sensor Limit
Rotary Switch
Delta Range Setting
Upper Sensor Limit
Description Values Position
Affected Rotary Left Switch Mode Description
Affected Rotary Left Switch Mode
Lower Range Value
Transmitter Variable Values menu level
Upper Range Value
Dynamic Value, Primary Variable PV menu 00 and menu
Rotary Left Description Values Switch
Rotary Switch Left Arrow Description Position
To change from menu 10 to menu Set the rotary switch to
Display the Highest / Lowest Recorded Value
Rotary Left Switch Mode Description Action Values
Transmitter Variables Dynamic Value menu level
Analog Output Signalling proportional or 2-state menu level
Upper Threshold Delay 2-state mode
Rotary Left Added Switch Arrow
Indicator
Rotary Left Added Switch
Arrow Indicator
Upper Threshold Setting 2-state mode
Mode Description Values Position
Analog Signalling Mode 2-state menu level
Lower Threshold Setting 2-state mode
Rotary Left Mode
State High
State State Low
Analog Fault Signalling 2-state
State mode must be selected at menu
For detailed information, see Fault Signalling on
22.0 mA
Digital Output Signalling solid-state output menu level
Upper Threshold Delay solid-state output
Rotary Left Des Switch
Identifier Cription
Lower Threshold Delay solid-state output
Upper Threshold Setting solid-state output
Value
Rotary Left Des Switch Mode
Lower Threshold Setting solid-state output
Rotary Left Added Des Switch Mode
Indicator Cription
Digital Signalling Mode solid-state output
Rotary Left Des Switch Arrow Mode Cription Action
= cc
Digital Fault Signalling
Rotary Left Switch Mode
Action Values
Output Signal Processing Test
Factory Settings
Switch Left Arrow Description Display Meaning Position
Miscellaneous
Rotary Switch Left Arrow Description Mode Values Position
Protection Display Switch Local
Settings
Range Inversion
Appendix B LCD display examples
LCD alphanumeric display examples
Appendix B
Appendix C Hart Documentation
Hart information
Hart Device Descriptor DD
Simatic Process Device Manager PDM
Sitrans LC 500 DD Menu/Variable Organization
Hart Response Code Information
Hart Conformance and Command Class
Command Description Usage Number
Command Description Usage
General Transmitter Information
Damping information
Non-volatile Memory Data Storage
Additional Universal Command Specifications
Burst mode
MultiDrop operation
Units conversions
Appendix D Block Diagram, and Correlation table, mA to %
Sitrans LC 500 Block Diagram
Correlation % 100% to 4-20 mA or 20-4 mA
Range 0 100 % Current in mA
Appendix D
Standard Version
Standard Version S-Series, Threaded
Series Threaded
Appendix E
Features Standard Version S-Series, Threaded
Series Cable Version With weight With anchor
Features Standard Version S-Series, Flanged
Series, Welded Flange
Features Standard Version D-Series
Features Standard Version DD-Series
Standard Version D-Series, Machined Flange
Series
Features Standard Version, Probe/ Thermal Isolator
SD-Series Probe/Thermal Isolator
All wetted parts made of PFA
Thermal isolator to prevent
Interface Version
Interface Version, threaded optional sanitary and flanged
Features Sanitary Version, Tri-Clamp
Sanitary Version
Flanges
Flange Standards
Examples using dimensions above Capacitance in air
Applications Examples
Generic Application Calculations
Capacitance in oil
Larger tank, dimensions in feet
PF = 33.2 pF
Device settings
CAn
90.0
08.0
Application Analog fault signalling 2-state output
Current loop is in 2-state mode C Hi selected
State fault signalling enabled F Hi selected
CHi
USL is set to 83.50 pF
LSL is set to 7.3 pF
Appendix F Approvals
CE Certificate
Sitrans LC 500 / Pointek CLS
Appendix F
CE Bescheinigung
Wir erklären hiermit auf eigene Verantwortung, dass der
Hinweis
Instrument label Sitrans LC
Kema certificate and schedules
Appendix F
Appendix F
Appendix F
Appendix F
Appendix F
Appendix F
Appendix F
Application Specifications
Certificates and Approvals
Namur recommendation NE
Approval
Glossary
Glossary
7ML19985GE01
Index
Numerics
Index
Wiring
Index
Quick Reference Sitrans LC
Quick Reference
Rotary Switch Positions Quick Reference
Page
7ml19985GE01