Programmers Guide
SPWU013A
Page
ThunderLANt Programmers Guide
Copyright 1996, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Important Notice
Iii
Read This First
Notational Conventions
If You Need Assistance
Trademarks
Contents
Physical Interface PHY
List Structures
Contentsix
Contents
Figures
Network Status Register Bits
Network Configuration Register Bits
Network Status Mask Register Bits
MAC Protocol Selection Codes
±25
Xiv
ThunderLAN Architecture Networking Protocols PCI Interface
ThunderLAN Overview
Fifo
ThunderLAN Architecture
PCI
Sram LAN
Networking Protocols
PCI Cycles
PCI Interface
Byte
Byte Ordering
Page
ThunderLAN Registers
Register Addresses
ThunderLAN Registers
PCI Nvram
PCI Configuration Space
±3. Configuration Eeprom Data Format
Word
Following example reads a byte of a PCI register
Pciint
Offset
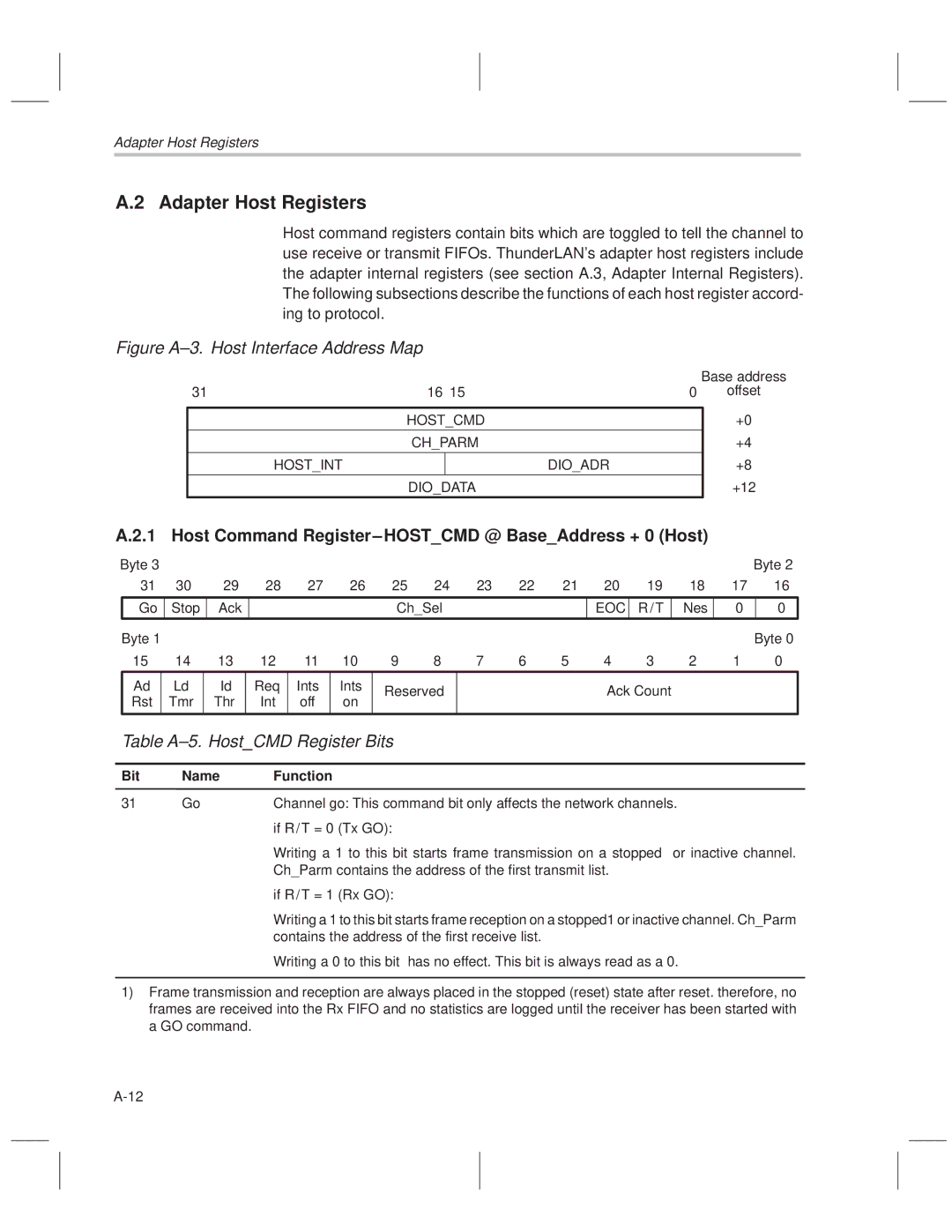
Host Registers
Hostcmd Chparm Hostint Dioadr
+12
Host Registers
HASH1 HASH2
Internal Registers
Internal Registers
Byte
Outpwbaseaddr+OFFDIOADDR, addr
±6. MII PHY Registers
MII PHY Registers
Mdata
Possible MII interfaces Parameters Baseaddr
Delay DioRdBytebaseaddr,NetSio SetNMRST
Device to read from
#define CritOn if CritLevel == 0 \ Asm cli CritLevel++
Is the read op code for an MII management operation
Ackn bit out
Get PHY Ack Ack = inpdiodata If !ack & Mdata
Tmp = 0xffff TogLH
LEDs
Bios ROM
External Devices
Eeprom
Registers
External Devices
Eeprom
±1. ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
Address Default Binary Bits Description
ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
±1. ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
±1. ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
±1. ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
±1. ThunderLAN Eeprom Map
Initializing Resetting
Initializing and Resetting
Finding the Network Interface Card NIC
Initializing
Word PciFindDevice
Pciiobaselo
Finding the Controller in Memory and I/O Space
#define Pciintline 0x3C
Finding Which Interrupt was Assigned
Turning on the I/O Port and Memory Address Decode
Setting the PCI Bus Latency Timer
Recovering the Silicon Revision Value
Hardware Reset
Resetting
Software Reset
Page
Interrupt Handling
Loading and Unloading an Interrupt Service Routine ISR
Code that gets executed is
Nic.OldNic = HwSetIntVectorBYTEnic.Irq, NicIsr
Prioritizing Adapter Interrupts
Acknowledging Interrupts Acking
Tx EOF Interrupt. Inttype = 001b
Interrupt Type Codes
No Interrupt Invalid Code. Inttype = 000b
Dummy Interrupt. Inttype = 100b
Statistics Overflow Interrupt. Inttype = 010b
Rx EOF Interrupt. Inttype = 011b
Network Status Interrupt. Inttype = 110b and IntVec = 00h
Tx EOC Interrupt. Inttype = 101b
Adapter Check Interrupt. Inttype = 110b and IntVec ≠ 00h
Bit Name Function
±1. Adapter Check Bit Definitions
±2. Adapter Check Failure Codes
Bit Name Channel List/Data
Rx EOC Interrupt. Inttype = 111b
EOC/EOF
07h IovErr
Page
List Structures
List Management
±2. Linked List Management Technique
List Management
Cstat Field Bit Requirements
One-Fragment Mode
±3. Receive List Format ± OneFrag =
Receive List Format
Field Definition
±1. Receive Parameter List Fields
Bit Name Function Ignored by adapter. Set to
±2. Receive Cstat Request Bits
MSB LSB
RX EOC
±3. Receive Cstat Complete Bits
EOC
±7. Transmit List Format
Transmit List Format
±4. Transmit Parameter List Fields
When nine or less fragments are used
Transmit Cstat
Mand
Priority
±5. Transmit Cstat Request Bits
Ignored by adapter. Should be set to
Ing transmission requests
TX EOC
±6. Transmit Cstat Complete Bits
Transmitting and Receiving Frames
Frame Format GO Command
Receive Rx Frame Format
Frame Format
±3. Token Ring Logical Frame Format Tx
Transmit Tx Frame Format
Starting Frame Reception Rx GO Command
GO Command
GO Command
Starting Frame Transmission Tx GO Command
GO Command
GO Command
Physical Interface PHY
PCI Tlan
MII-Enhanced Interrupt Event Feature
802.3u MII
Tlan MII TNETE211
Name Type Function
±1. ThunderLAN MII Pins 100M-bps CSMA/CD
Start Operation
Register Turn Data Delimiter Code
±3. MII Frame Format Write
±2. Possible Sources of MII Event Interrupts
Tion also disables the counter event function
Name Function
Link
SOF
Qcyc Mint
Mdclk Mdio
Nonmanaged MII Devices
Mcol
Bit-Rate Devices
PHY Initialization
Page
Register Definitions
PCI Configuration Registers
Size
PCI Autoconfiguration from External 24C02 Serial Eeprom
Byte Device ID Vendor ID
PCI Device ID Register @ 02h Default = 0500h
PCI Vendor ID Register @ 00h Default = 104Ch
SER
PCI Command Register @ 04h
Table A±1. PCI Command Register Bits
Table A±2. PCI Status Register Bits
PCI Status Register @ 06h
Devsel FBB
PDEVSEL#
PCI Base Class Register @ 0Bh
PCI Latency Timer Register @ 0Dh
PCI Subclass Register @ 0Ah
PCI Program Interface Register @ 09h
PCI Memory Base Address Register @ 14h
PCI Bios ROM Base Address Register @ 30h
PCI Nvram Register @ 34h
Memory Base Address 12 LSBs Memory Base Address 16 MSBs
PCI Interrupt Pin Register @ 3Dh
Table A±3. PCI Nvram Register Bits
PCI Interrupt Line Register @ 3Ch
Table A±4. PCI Reset Control Register Bits
PCI Reset Control Register @ 40h
PCI MinGnt @ 3Eh and MaxLat @ 3Fh Registers
Srdis
CardBus CIS Pointer @ 28h
Adapter Host Registers
Host Command Register±HOSTCMD @ BaseAddress + 0 Host
Table A±5. HostCMD Register Bits
Hostcmd
Table A±5. HostCMD Register Bits
If Nes = 1, EOC = 1, and R/T = 1 Rx EOC Ack
Cated in ChSel
If Nes = 1, EOC = 0, and R/T = 0 Tx EOF Ack
Raised
Be issued in a single write cycle
Lected otherwise statistics commands are selected
To be issued in a single write cycle Nes
Lected. If set to a 0, EOF operations are selected
LdThr
LdTmr
ChSel must indicate the selected transmit channel
ReqInt
Channel Parameter Register±CHPARM @ BaseAddress + 4 Host
Table A±6. Hostint Register Bits
Host Interrupt Register±HOSTINT @ BaseAddress + 10 Host
Table A±7. Dioadr Register Bits
DIO Address Register±DIOADR @ BaseAddress + 8 Host
DIO Data Register±DIODATA @ BaseAddress + 12 Host
Adapter Internal Registers
HASH2 HASH1
ManTest NetConfig
Tx underrun
Late
Table A±8. Network Command Register Bits
Network Command Register±NetCmd @ 0x00 DIO
Table A±9. Network Serial I/O Register Bits
Network Serial I/O Register±NetSio @ 0x00 DIO
Table A±10. Network Status Register Bits
Network Status Register±NetSts @ 0x00 DIO
Table A±11. Network Status Mask Register Bits
Network Status Mask Register±NetMask @ 0x00 DIO
BIT PEF
Network Configuration Register±NetConfig @ 0x04 DIO
Table A±12. Network Configuration Register Bits
Mtest
Table A±13. MAC Protocol Selection Codes
Default PCI Parameter Registers±@ 0x08±0x0C DIO
Manufacturing Test Register±ManTest @ 0x04 DIO
Code MAC Protocol Selected
All-Nodes Broadcast Address
General Address Registers±Areg0-3 @ 0x10±0x24 DIO
Hash Address Registers±HASH1/HASH2 @ 0x28±0x2C DIO
0x3C Single collision Tx frames
Network Statistics Registers±@ 0x30±0x40 DIO
Good Tx frames 0x34 Rx overrun
Counter Definition
Table A±14. Ethernet Error Counters
Adapter Commit Register±Acommit @ 0x40 DIO Byte
Table A±15. Demand Priority Error Counters
LED Register±LEDreg @ 0x44 DIO Byte
Table A±16. Adapter Commit Register Bits
31±28 Tx commit
Level
Table A±17. Burst Size Register Bits
Burst Size Register±BSIZEreg @ 0x44 DIO Byte
Byte Maximum Rx frame size in units of 8 bits
Maximum Rx Frame Size Register±MaxRx @ 0x44 DIO Bytes 2+3
Table A±18. Demand Priority Error Counters
Interrupt Disable Register Intdis @ 0x48 DIO Byte
Disabled. Default value is
RX EOF
Figure A±8 Base-T PHY Registers
10Base-T PHY Registers
Table A±19. PHY Generic Control Register Bits
PHY Generic Control Register±GENctl @
Fect on PHY operation
Nal Mcol whenever the transmit enable Mtxen pin is asserted
Coltest
Reserved Read as
Table A±20. PHY Generic Status Register Bits
PHY Generic Status Register±GENsts @
Autocomplt Rflt Link Jabber
Autocmplt
Jabber
OUI Manufacturers model number Revision number
PHY Generic Identifier±GENidhi/GENidlo @ 0x2/0x3
Tlrflt
Autonegotiation Advertisement Register±ANadv @
Table A±21. Autonegotiation Advertisement Register Bits
Lprflt
Autonegotiation Link Partner Ability Register±ANlpa @
Lpnxtpage
Table A±23. Autonegotiation Expansion Register Bits
Autonegotiation Expansion Register±ANexp @
Pardetflt Lpnpable Pagerx Lpanable
Pardetflt
ThunderLAN PHY Identifier High/Low±TLPHYid @
Table A±24. ThunderLAN PHY Control Register Bits
ThunderLAN PHY Control Register±TLPHYctl @
Table A±25. ThunderLAN PHY Status Register Bits
ThunderLAN PHY Status Register±TLPHYsts @
Inten
Mint Phok Polok
Inverted link pulses has been detected
POLOK²
Tpenergy
Set.²
Page
100VG-AnyLAN Training TNETE211 Register Descriptions
PMI Interface
Figure B±1 .12 Training Frame Format
100VG-AnyLAN Training
100VG-AnyLAN Training
Figure B±2. Training Flowchart
100VG-AnyLAN Training
TNETE211 Register Descriptions
Autoconfiguration enable Not implemented
Reset Loopbk Pdown Isolate
Table B±1. PHY Generic Control Register Bits
0x01 PHY generic status register 0x02
Rflt Link Jabber
PHY Generic Status Register ±GENsts @
Table B±2. PHY Generic Status Register Bits
Trfail Tridle Npmdw Nfew Inten Tint
Iglink Mcrs Ptlswen Prlsren
Table B±3. ThunderLAN PHY Control Register Bits
Table B±4. ThunderLAN PHY Status Register Bits
Mint Phok Config Retrain Lstate Trfrto Rtridl Lrcv Lsil
Retrain
Lstate
Inten bit is also set, this causes an MII interrupt
Trfrto
Rtridl
Lrcv
TNETE100PM/TNETE110PM