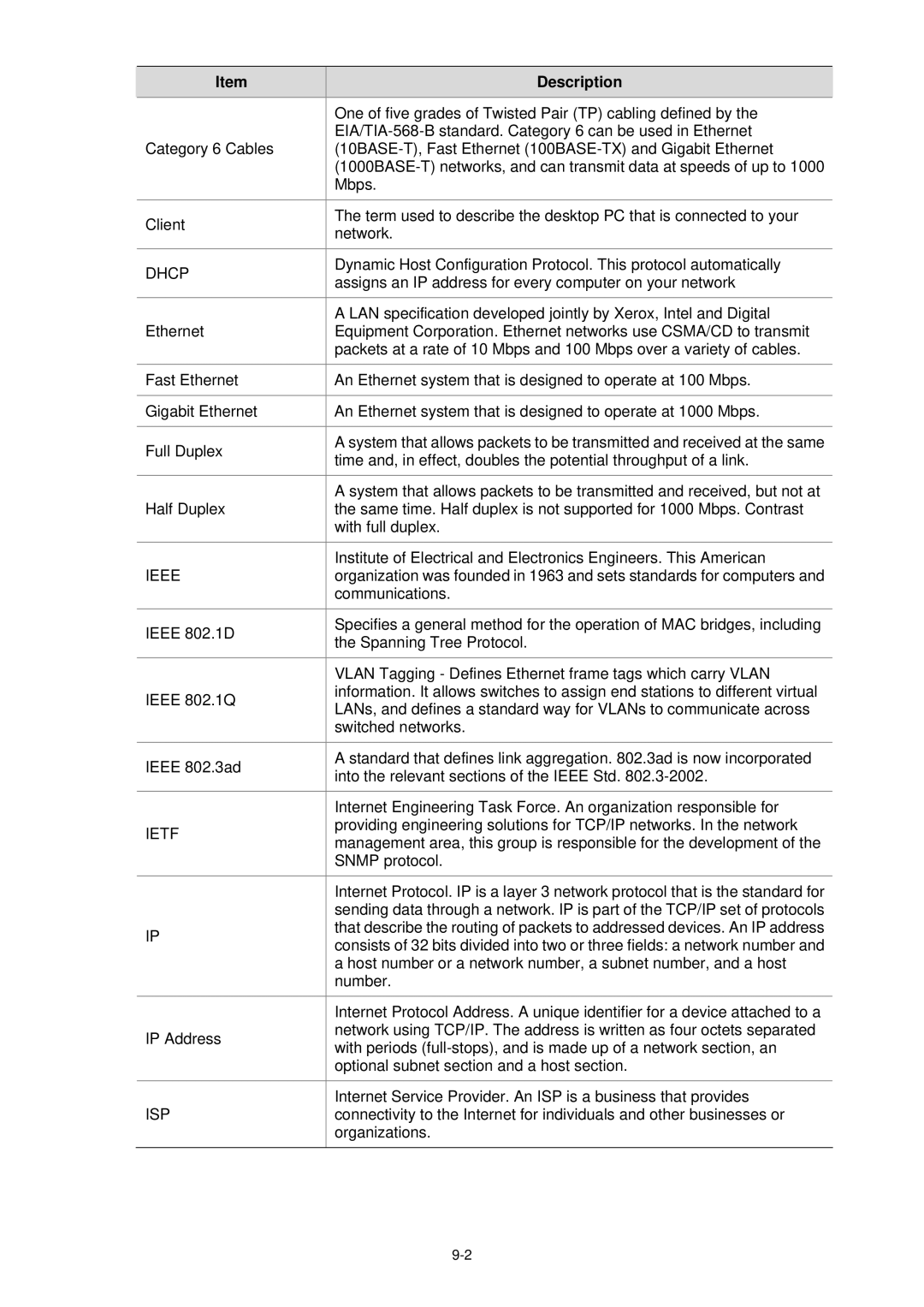
| Item |
| Description |
|
|
| One of five grades of Twisted Pair (TP) cabling defined by the |
| Category 6 Cables |
| |
|
| ||
|
|
| |
|
|
| Mbps. |
|
|
|
|
| Client |
| The term used to describe the desktop PC that is connected to your |
|
| network. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| DHCP |
| Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol automatically |
|
| assigns an IP address for every computer on your network | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A LAN specification developed jointly by Xerox, Intel and Digital |
| Ethernet |
| Equipment Corporation. Ethernet networks use CSMA/CD to transmit |
|
|
| packets at a rate of 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps over a variety of cables. |
|
|
| |
| Fast Ethernet | An Ethernet system that is designed to operate at 100 Mbps. | |
|
|
| |
| Gigabit Ethernet | An Ethernet system that is designed to operate at 1000 Mbps. | |
|
|
|
|
| Full Duplex |
| A system that allows packets to be transmitted and received at the same |
|
| time and, in effect, doubles the potential throughput of a link. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A system that allows packets to be transmitted and received, but not at |
| Half Duplex |
| the same time. Half duplex is not supported for 1000 Mbps. Contrast |
|
|
| with full duplex. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. This American |
| IEEE |
| organization was founded in 1963 and sets standards for computers and |
|
|
| communications. |
|
|
|
|
| IEEE 802.1D |
| Specifies a general method for the operation of MAC bridges, including |
|
| the Spanning Tree Protocol. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VLAN Tagging - Defines Ethernet frame tags which carry VLAN |
| IEEE 802.1Q |
| information. It allows switches to assign end stations to different virtual |
|
| LANs, and defines a standard way for VLANs to communicate across | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| switched networks. |
|
|
|
|
| IEEE 802.3ad |
| A standard that defines link aggregation. 802.3ad is now incorporated |
|
| into the relevant sections of the IEEE Std. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internet Engineering Task Force. An organization responsible for |
| IETF |
| providing engineering solutions for TCP/IP networks. In the network |
|
| management area, this group is responsible for the development of the | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| SNMP protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internet Protocol. IP is a layer 3 network protocol that is the standard for |
|
|
| sending data through a network. IP is part of the TCP/IP set of protocols |
| IP |
| that describe the routing of packets to addressed devices. An IP address |
|
| consists of 32 bits divided into two or three fields: a network number and | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| a host number or a network number, a subnet number, and a host |
|
|
| number. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internet Protocol Address. A unique identifier for a device attached to a |
| IP Address |
| network using TCP/IP. The address is written as four octets separated |
|
| with periods | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| optional subnet section and a host section. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internet Service Provider. An ISP is a business that provides |
| ISP |
| connectivity to the Internet for individuals and other businesses or |
|
|
| organizations. |
|
|
|
|
Page 133
Image 133