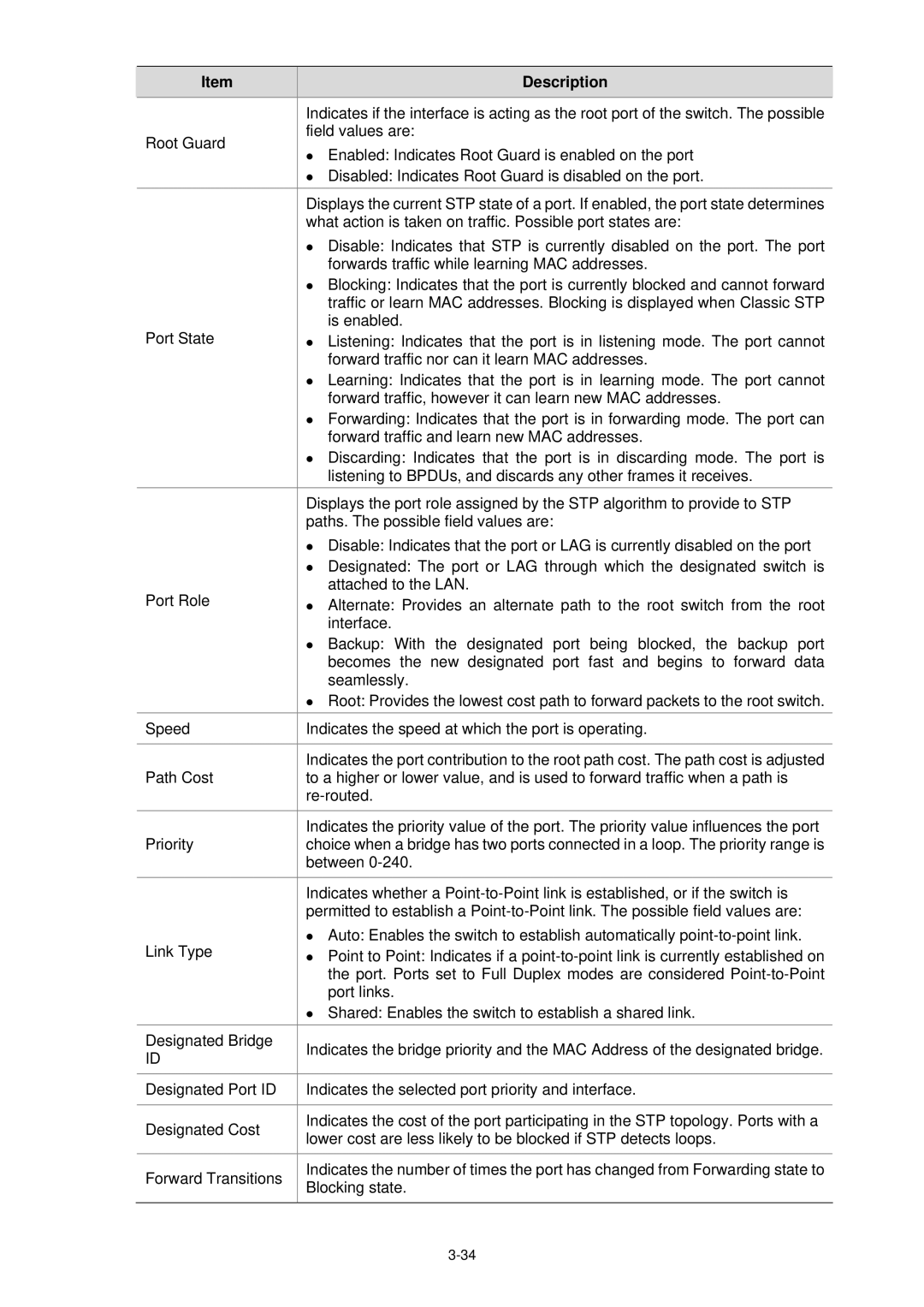
| Item |
| Description |
|
|
| Indicates if the interface is acting as the root port of the switch. The possible |
| Root Guard |
| field values are: |
|
| z Enabled: Indicates Root Guard is enabled on the port | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| z Disabled: Indicates Root Guard is disabled on the port. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines |
|
|
| what action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are: |
|
|
| z Disable: Indicates that STP is currently disabled on the port. The port |
|
|
| forwards traffic while learning MAC addresses. |
|
|
| z Blocking: Indicates that the port is currently blocked and cannot forward |
|
|
| traffic or learn MAC addresses. Blocking is displayed when Classic STP |
| Port State |
| is enabled. |
|
| z Listening: Indicates that the port is in listening mode. The port cannot | |
|
|
| forward traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses. |
|
|
| z Learning: Indicates that the port is in learning mode. The port cannot |
|
|
| forward traffic, however it can learn new MAC addresses. |
|
|
| z Forwarding: Indicates that the port is in forwarding mode. The port can |
|
|
| forward traffic and learn new MAC addresses. |
|
|
| z Discarding: Indicates that the port is in discarding mode. The port is |
|
|
| listening to BPDUs, and discards any other frames it receives. |
|
|
| Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP |
|
|
| paths. The possible field values are: |
|
|
| z Disable: Indicates that the port or LAG is currently disabled on the port |
|
|
| z Designated: The port or LAG through which the designated switch is |
| Port Role |
| attached to the LAN. |
|
| z Alternate: Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root | |
|
|
| interface. |
|
|
| z Backup: With the designated port being blocked, the backup port |
|
|
| becomes the new designated port fast and begins to forward data |
|
|
| seamlessly. |
|
|
| z Root: Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root switch. |
| Speed |
| Indicates the speed at which the port is operating. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted |
| Path Cost |
| to a higher or lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path is |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicates the priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port |
| Priority |
| choice when a bridge has two ports connected in a loop. The priority range is |
|
|
| between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicates whether a |
|
|
| permitted to establish a |
| Link Type |
| z Auto: Enables the switch to establish automatically |
|
| z Point to Point: Indicates if a | |
|
|
| the port. Ports set to Full Duplex modes are considered |
|
|
| port links. |
|
|
| z Shared: Enables the switch to establish a shared link. |
| Designated Bridge |
| Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated bridge. |
| ID |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Designated Port ID | Indicates the selected port priority and interface. | |
|
|
|
|
| Designated Cost |
| Indicates the cost of the port participating in the STP topology. Ports with a |
|
| lower cost are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Forward Transitions |
| Indicates the number of times the port has changed from Forwarding state to |
|
| Blocking state. | |
|
|
| |
|
| ||
Page 58
Image 58