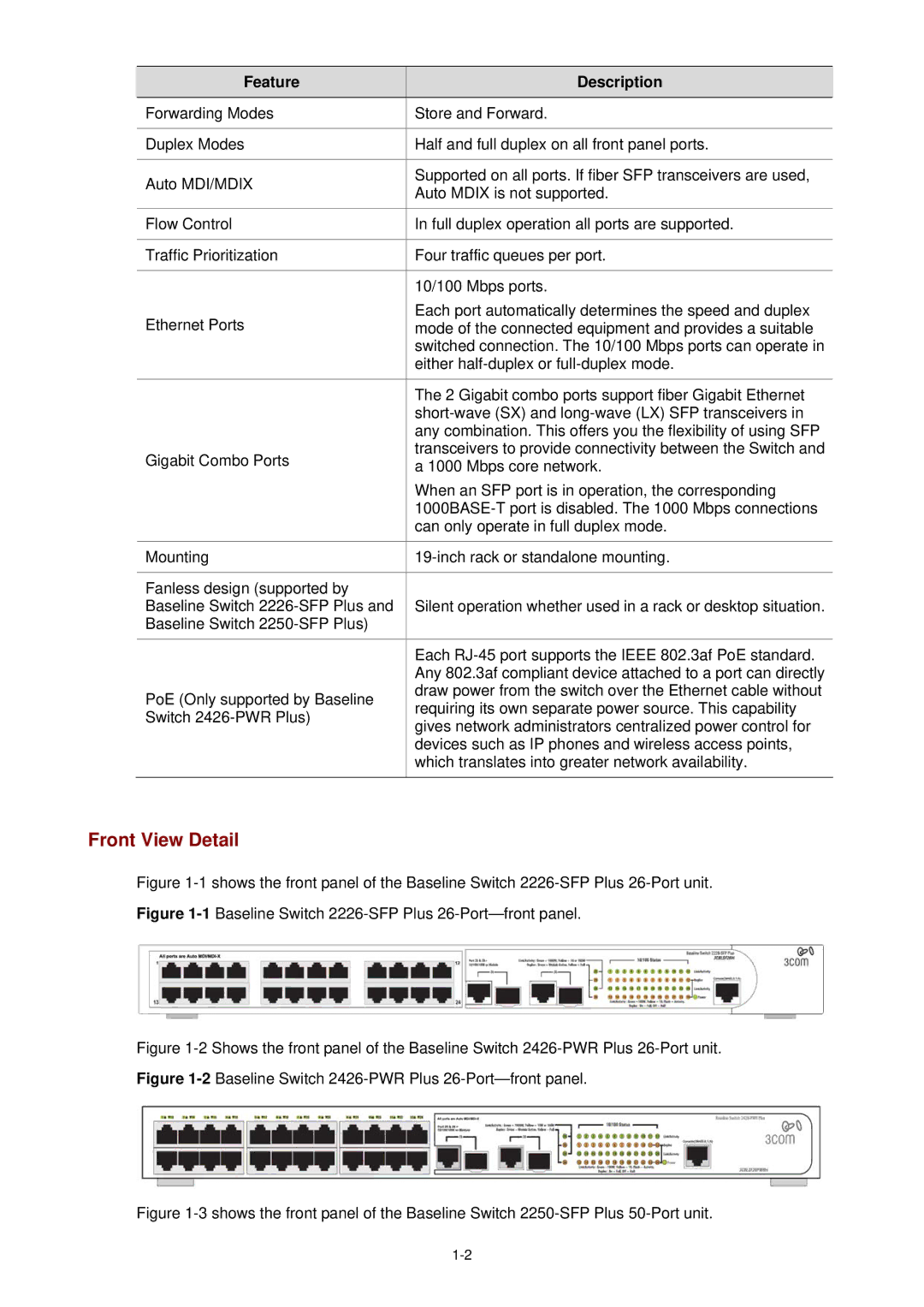
Feature
Description
Forwarding Modes | Store and Forward. | |
|
| |
Duplex Modes | Half and full duplex on all front panel ports. | |
|
| |
Auto MDI/MDIX | Supported on all ports. If fiber SFP transceivers are used, | |
Auto MDIX is not supported. | ||
| ||
|
| |
Flow Control | In full duplex operation all ports are supported. | |
|
| |
Traffic Prioritization | Four traffic queues per port. | |
|
| |
| 10/100 Mbps ports. | |
Ethernet Ports | Each port automatically determines the speed and duplex | |
mode of the connected equipment and provides a suitable | ||
| switched connection. The 10/100 Mbps ports can operate in | |
| either | |
|
| |
| The 2 Gigabit combo ports support fiber Gigabit Ethernet | |
| ||
| any combination. This offers you the flexibility of using SFP | |
Gigabit Combo Ports | transceivers to provide connectivity between the Switch and | |
a 1000 Mbps core network. | ||
| ||
| When an SFP port is in operation, the corresponding | |
| ||
| can only operate in full duplex mode. | |
|
| |
Mounting | ||
|
| |
Fanless design (supported by |
| |
Baseline Switch | Silent operation whether used in a rack or desktop situation. | |
Baseline Switch |
| |
|
| |
| Each | |
| Any 802.3af compliant device attached to a port can directly | |
PoE (Only supported by Baseline | draw power from the switch over the Ethernet cable without | |
requiring its own separate power source. This capability | ||
Switch | ||
gives network administrators centralized power control for | ||
| ||
| devices such as IP phones and wireless access points, | |
| which translates into greater network availability. | |
|
|