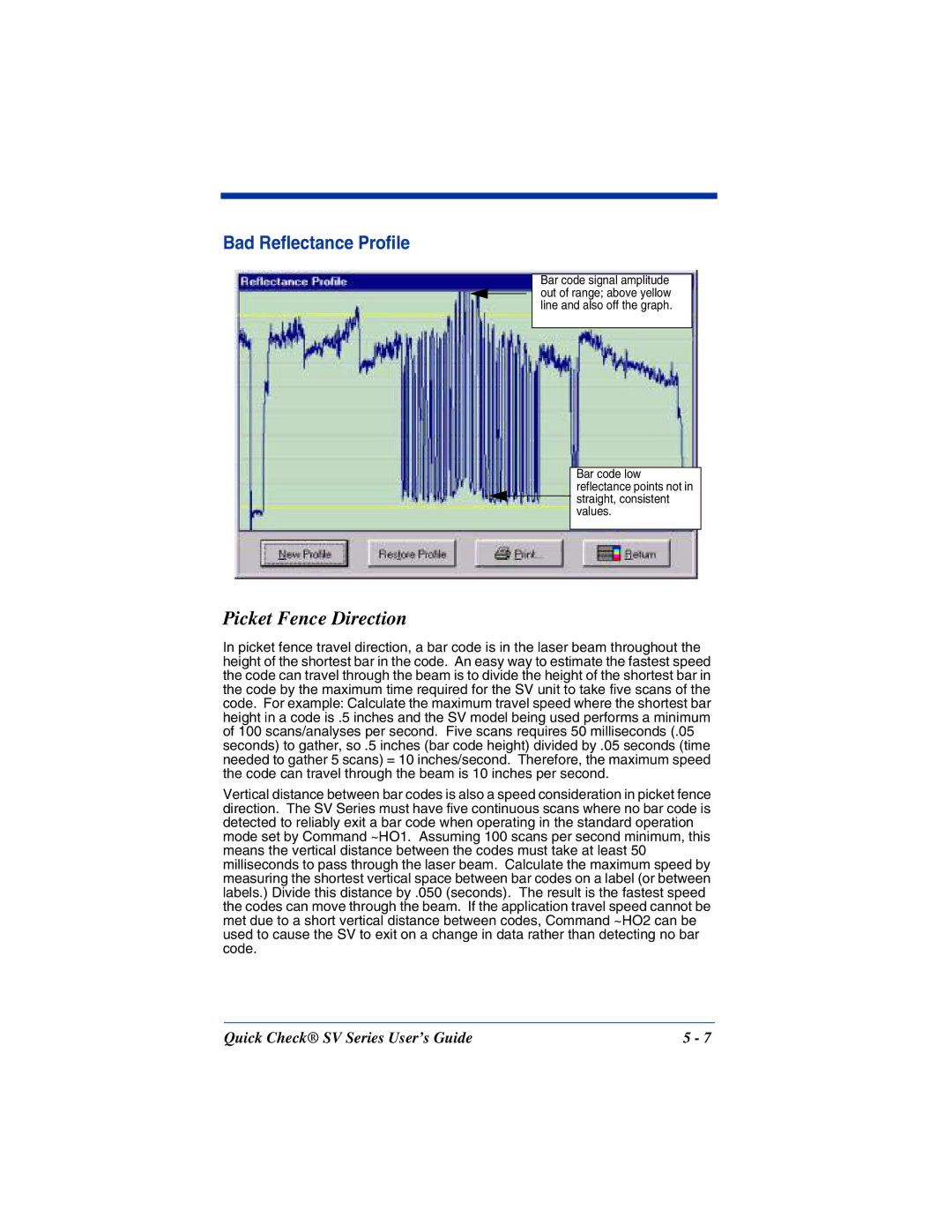
Bad Reflectance Profile
Bar code signal amplitude out of range; above yellow line and also off the graph.
Bar code low reflectance points not in ![]() straight, consistent values.
straight, consistent values.
Picket Fence Direction
In picket fence travel direction, a bar code is in the laser beam throughout the height of the shortest bar in the code. An easy way to estimate the fastest speed the code can travel through the beam is to divide the height of the shortest bar in the code by the maximum time required for the SV unit to take five scans of the code. For example: Calculate the maximum travel speed where the shortest bar height in a code is .5 inches and the SV model being used performs a minimum of 100 scans/analyses per second. Five scans requires 50 milliseconds (.05 seconds) to gather, so .5 inches (bar code height) divided by .05 seconds (time needed to gather 5 scans) = 10 inches/second. Therefore, the maximum speed the code can travel through the beam is 10 inches per second.
Vertical distance between bar codes is also a speed consideration in picket fence direction. The SV Series must have five continuous scans where no bar code is detected to reliably exit a bar code when operating in the standard operation mode set by Command ~HO1. Assuming 100 scans per second minimum, this means the vertical distance between the codes must take at least 50 milliseconds to pass through the laser beam. Calculate the maximum speed by measuring the shortest vertical space between bar codes on a label (or between labels.) Divide this distance by .050 (seconds). The result is the fastest speed the codes can move through the beam. If the application travel speed cannot be met due to a short vertical distance between codes, Command ~HO2 can be used to cause the SV to exit on a change in data rather than detecting no bar code.
Quick Check® SV Series User’s Guide | 5 - 7 |