Chapter 2: Capacity and Availability Management 25
your server becomes low on kernel memory, your system becomes unresponsive. To regain control of your server, you must restart it to free up the kernel memory.
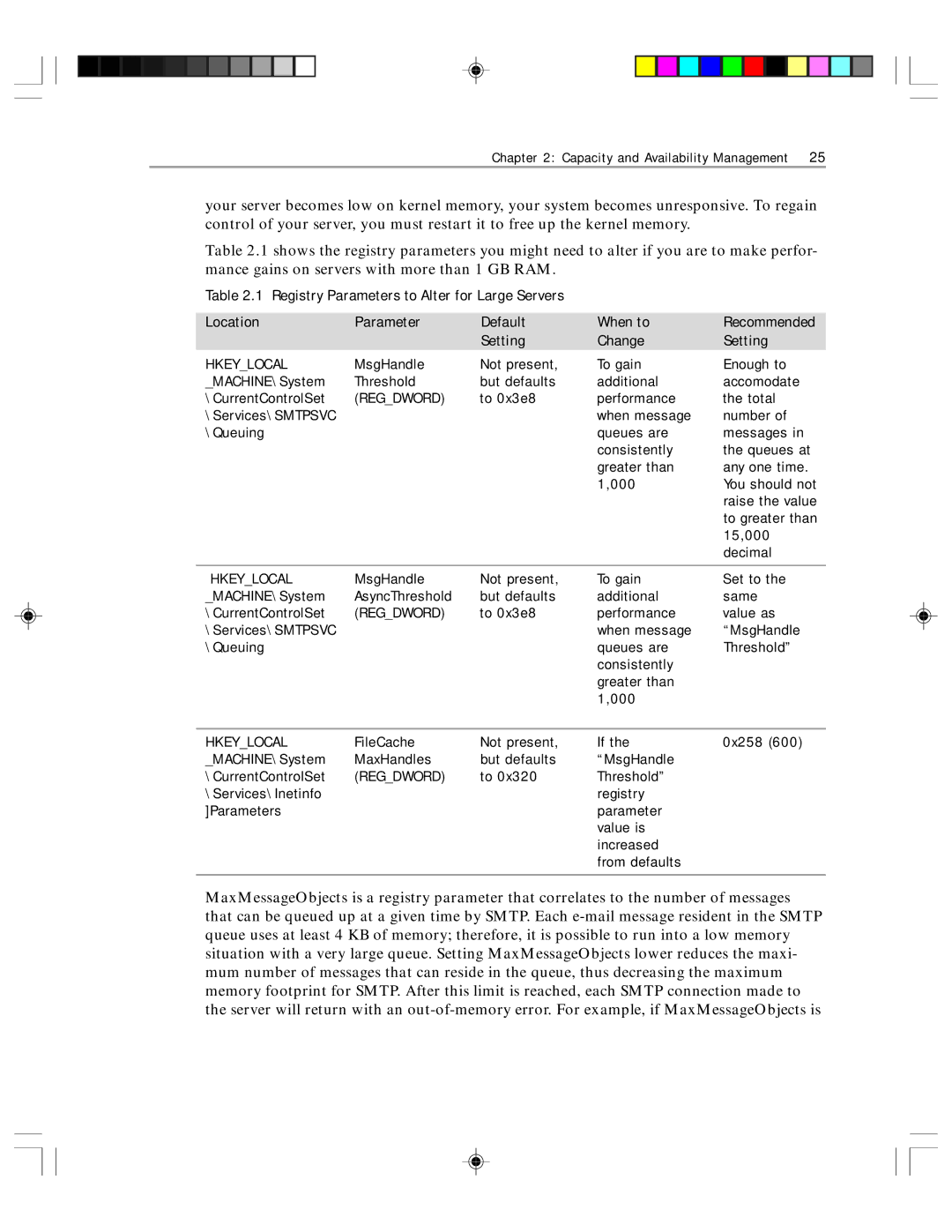
Table 2.1 shows the registry parameters you might need to alter if you are to make perfor- mance gains on servers with more than 1 GB RAM.
Table 2.1 Registry Parameters to Alter for Large Servers
Location | Parameter | Default | When to | Recommended |
|
| Setting | Change | Setting |
HKEY_LOCAL | MsgHandle | Not present, | To gain | Enough to |
_MACHINE\System | Threshold | but defaults | additional | accomodate |
\CurrentControlSet | (REG_DWORD) | to 0x3e8 | performance | the total |
\Services\SMTPSVC |
|
| when message | number of |
\Queuing |
|
| queues are | messages in |
|
|
| consistently | the queues at |
|
|
| greater than | any one time. |
|
|
| 1,000 | You should not |
|
|
|
| raise the value |
|
|
|
| to greater than |
|
|
|
| 15,000 |
|
|
|
| decimal |
|
|
|
|
|
HKEY_LOCAL | MsgHandle | Not present, | To gain | Set to the |
_MACHINE\System | AsyncThreshold | but defaults | additional | same |
\CurrentControlSet | (REG_DWORD) | to 0x3e8 | performance | value as |
\Services\SMTPSVC |
|
| when message | “MsgHandle |
\Queuing |
|
| queues are | Threshold” |
|
|
| consistently |
|
|
|
| greater than |
|
|
|
| 1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HKEY_LOCAL | FileCache | Not present, | If the | 0x258 (600) |
_MACHINE\System | MaxHandles | but defaults | “MsgHandle |
|
\CurrentControlSet | (REG_DWORD) | to 0x320 | Threshold” |
|
\Services\Inetinfo |
|
| registry |
|
]Parameters |
|
| parameter |
|
|
|
| value is |
|
|
|
| increased |
|
|
|
| from defaults |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaxMessageObjects is a registry parameter that correlates to the number of messages that can be queued up at a given time by SMTP. Each