Overview, Continued
DataNET Hub Hierarchy
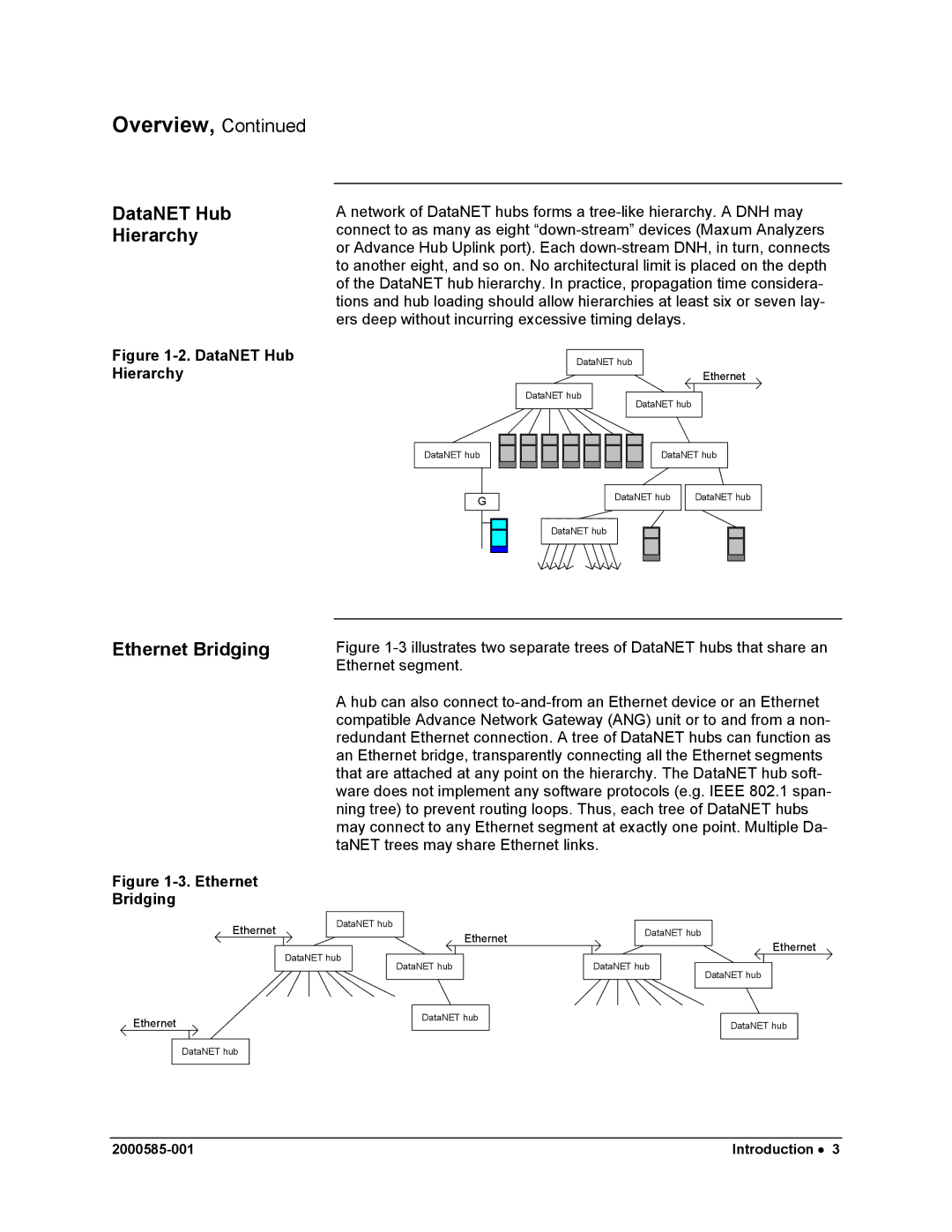
A network of DataNET hubs forms a
Figure 1-2. DataNET Hub Hierarchy
DataNET hub
G
DataNET hub
Ethernet
DataNET hub
DataNET hub
DataNET hub | |
DataNET hub | DataNET hub |
DataNET hub
Ethernet Bridging
Figure 1-3 illustrates two separate trees of DataNET hubs that share an Ethernet segment.
A hub can also connect to-and-from an Ethernet device or an Ethernet compatible Advance Network Gateway (ANG) unit or to and from a non- redundant Ethernet connection. A tree of DataNET hubs can function as an Ethernet bridge, transparently connecting all the Ethernet segments that are attached at any point on the hierarchy. The DataNET hub soft- ware does not implement any software protocols (e.g. IEEE 802.1 span- ning tree) to prevent routing loops. Thus, each tree of DataNET hubs may connect to any Ethernet segment at exactly one point. Multiple Da- taNET trees may share Ethernet links.
Figure 1-3. Ethernet
Bridging
Ethernet | DataNET hub | |
Ethernet | ||
|
DataNET hub
| DataNET hub |
| DataNET hub |
Ethernet | DataNET hub |
| |
| DataNET hub |
DataNET hub
Ethernet
DataNET hub
DataNET hub
Introduction • 3 |