5.SCSI Interface
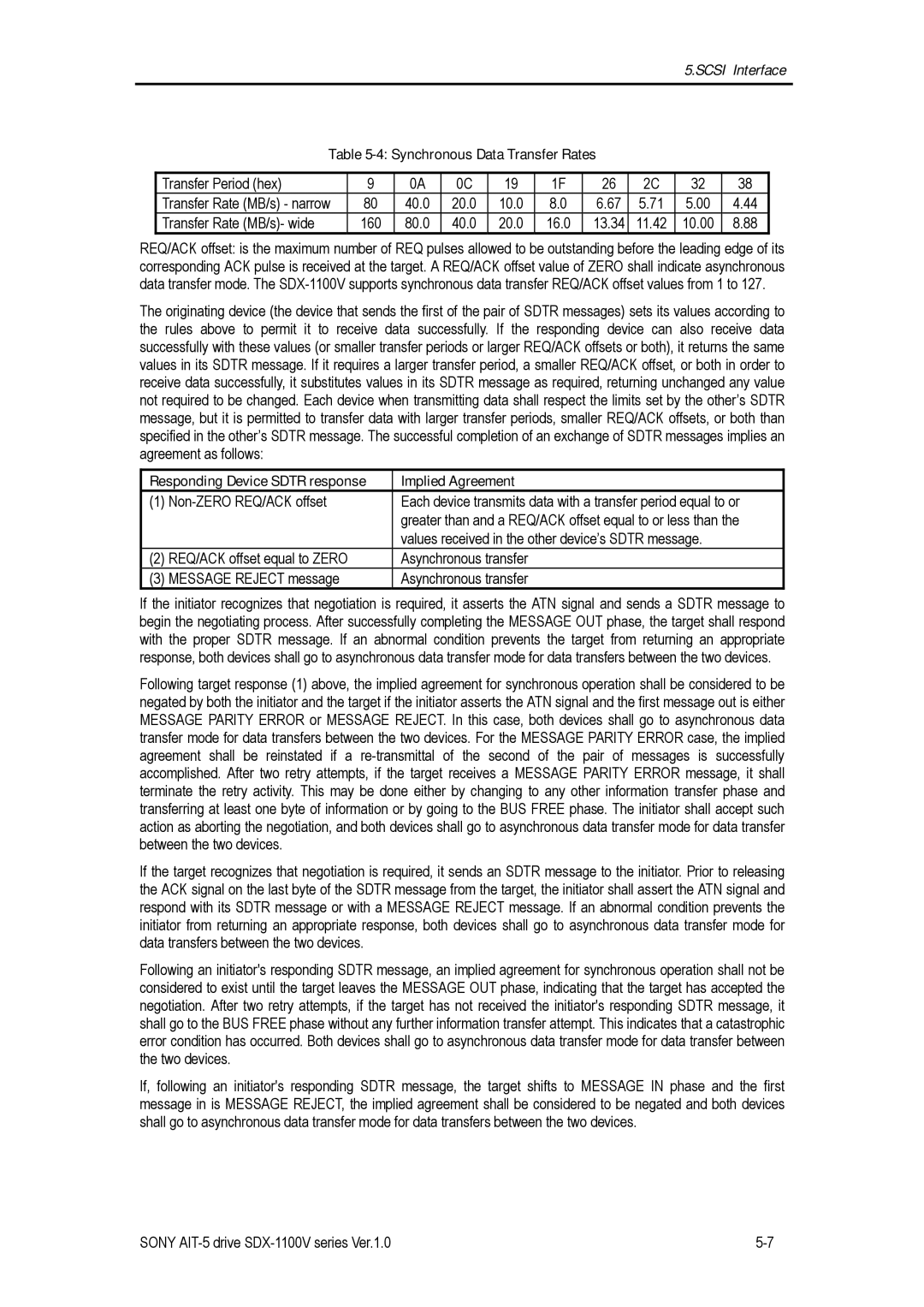
Table 5-4: Synchronous Data Transfer Rates
Transfer Period (hex) | 9 | 0A | 0C | 19 | 1F | 26 | 2C | 32 | 38 |
Transfer Rate (MB/s) - narrow | 80 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 6.67 | 5.71 | 5.00 | 4.44 |
Transfer Rate (MB/s)- wide | 160 | 80.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 16.0 | 13.34 | 11.42 | 10.00 | 8.88 |
REQ/ACK offset: is the maximum number of REQ pulses allowed to be outstanding before the leading edge of its corresponding ACK pulse is received at the target. A REQ/ACK offset value of ZERO shall indicate asynchronous data transfer mode. The
The originating device (the device that sends the first of the pair of SDTR messages) sets its values according to the rules above to permit it to receive data successfully. If the responding device can also receive data successfully with these values (or smaller transfer periods or larger REQ/ACK offsets or both), it returns the same values in its SDTR message. If it requires a larger transfer period, a smaller REQ/ACK offset, or both in order to receive data successfully, it substitutes values in its SDTR message as required, returning unchanged any value not required to be changed. Each device when transmitting data shall respect the limits set by the other’s SDTR message, but it is permitted to transfer data with larger transfer periods, smaller REQ/ACK offsets, or both than specified in the other’s SDTR message. The successful completion of an exchange of SDTR messages implies an agreement as follows:
Responding Device SDTR response | Implied Agreement | |
(1) | Each device transmits data with a transfer period equal to or | |
|
| greater than and a REQ/ACK offset equal to or less than the |
|
| values received in the other device’s SDTR message. |
(2) | REQ/ACK offset equal to ZERO | Asynchronous transfer |
(3) MESSAGE REJECT message | Asynchronous transfer | |
If the initiator recognizes that negotiation is required, it asserts the ATN signal and sends a SDTR message to begin the negotiating process. After successfully completing the MESSAGE OUT phase, the target shall respond with the proper SDTR message. If an abnormal condition prevents the target from returning an appropriate response, both devices shall go to asynchronous data transfer mode for data transfers between the two devices.
Following target response (1) above, the implied agreement for synchronous operation shall be considered to be negated by both the initiator and the target if the initiator asserts the ATN signal and the first message out is either MESSAGE PARITY ERROR or MESSAGE REJECT. In this case, both devices shall go to asynchronous data transfer mode for data transfers between the two devices. For the MESSAGE PARITY ERROR case, the implied agreement shall be reinstated if a
If the target recognizes that negotiation is required, it sends an SDTR message to the initiator. Prior to releasing the ACK signal on the last byte of the SDTR message from the target, the initiator shall assert the ATN signal and respond with its SDTR message or with a MESSAGE REJECT message. If an abnormal condition prevents the initiator from returning an appropriate response, both devices shall go to asynchronous data transfer mode for data transfers between the two devices.
Following an initiator's responding SDTR message, an implied agreement for synchronous operation shall not be considered to exist until the target leaves the MESSAGE OUT phase, indicating that the target has accepted the negotiation. After two retry attempts, if the target has not received the initiator's responding SDTR message, it shall go to the BUS FREE phase without any further information transfer attempt. This indicates that a catastrophic error condition has occurred. Both devices shall go to asynchronous data transfer mode for data transfer between the two devices.
If, following an initiator's responding SDTR message, the target shifts to MESSAGE IN phase and the first message in is MESSAGE REJECT, the implied agreement shall be considered to be negated and both devices shall go to asynchronous data transfer mode for data transfers between the two devices.
SONY |