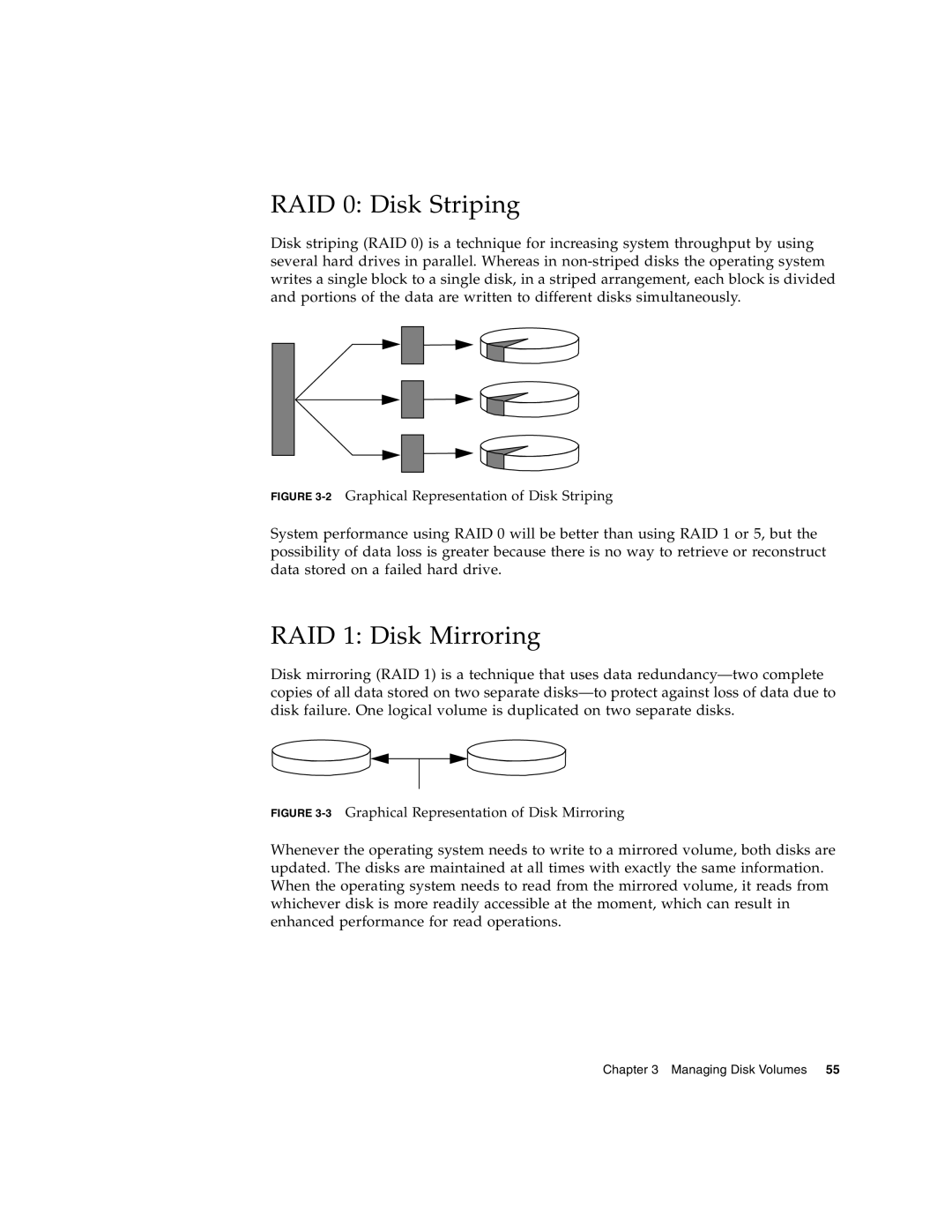
RAID 0: Disk Striping
Disk striping (RAID 0) is a technique for increasing system throughput by using several hard drives in parallel. Whereas in
FIGURE 3-2 Graphical Representation of Disk Striping
System performance using RAID 0 will be better than using RAID 1 or 5, but the possibility of data loss is greater because there is no way to retrieve or reconstruct data stored on a failed hard drive.
RAID 1: Disk Mirroring
Disk mirroring (RAID 1) is a technique that uses data
FIGURE 3-3 Graphical Representation of Disk Mirroring
Whenever the operating system needs to write to a mirrored volume, both disks are updated. The disks are maintained at all times with exactly the same information. When the operating system needs to read from the mirrored volume, it reads from whichever disk is more readily accessible at the moment, which can result in enhanced performance for read operations.