Back to Contents
Specifications
Controls and Lights
Connectors
Environmental
Physical
System Setup Screens
System Setup
Entering System Setup
System Setup Options
Drives
System
Onboard Devices
Performance
LED Control
Security
Power Management
Post Behavior
Off Do not use the Auto Power Time
Maintenance
Time
Setup & Boot Menu default
Boot Sequence
Option Settings
Changing Boot Sequence for the Current Boot
Changing Boot Sequence for Future Boots
Clearing Forgotten Passwords
¡ In Windows XP, click Start→ Turn Off Computer→ Turn off
Cleaning Your Computer
Clearing Cmos Settings
Computer, Keyboard, and Monitor
CDs and DVDs
FCC Notices U.S. Only
Mouse
Floppy Drive
Class B
Contacting Dell
FCC Identification Information
Technical Support 0011
Argentina Buenos Aires
Aruba
Australia Sydney
Chile Santiago
Brunei
Canada North York, Ontario
Cayman Islands
Dominican Republic
Czech Republic Prague
Denmark Copenhagen
Dominica
Guatemala
Germany Frankfurt
Greece
Grenada
Sales Ireland Cherrywood
Customer Service
Sales
Business computers
Support.ap.dell.com
Korea Seoul
Latin America
Luxembourg
Panama
New Zealand Support.ap.dell.com
Nicaragua
Norway Lysaker
09/091
Singapore Singapore
Slovakia Prague
South Africa Johannesburg
Trinidad/Tobago
Customer Service Bracknell
Taiwan
Thailand
Venezuela
Financial Services
A. Austin, Texas
Virgin Islands
Support.dell.com
Find It Here
Click Help and Support
¡ In Windows XP, click Start and click Help and Support
Glossary
Docking device See APR
Device driver See driver
Page
Page
NIC See network adapter
Module bay See media bay
Page
Video resolution See resolution
Back to Contents
Windows XP, click Start→ Turn Off Computer→ Turn off
Before You Begin
Recommended Tools
Preparing to Work Inside Your Computer
Inside View of Your Computer
Removing the Computer Cover
Frntusb
System Board Components
DDR2 Memory Overview
Memory
Installing Memory
Addressing Memory Configurations
Removing Memory
Cards
Removing PCI and PCI Express Cards
Installing PCI and PCI Express Cards
Page
Page
Page
Page
Drives
Network Adapter and Sound Card Settings
Removing a Hard Drive
General Drive Installation Guidelines
Hard Drive
About Serial ATA Drives
Page
Installing a Hard Drive
Removing the Drive Panel
Drive Panel
Replacing the Drive Panel
Floppy Drive
Removing a Floppy Drive
Installing a Floppy Drive
Removing a Media Card Reader
Media Card Reader
Installing a Media Card Reader
Optical Drive
Removing an Optical Drive
Installing an Optical Drive
Safety Instructions for Liquid Cooling Assembly
Liquid Cooling Assembly
Removing the Liquid Cooling Assembly
Tecpump
Processor
Installing the Liquid Cooling Assembly
Removing the Processor
Installing the Processor
Removing the Card Fan
Fans
Installing the Card Fan
Removing the System Board
Installing the Optional Hard Drive Fan
System Board
Removing the Optional Hard Drive Fan
Installing the System Board
Power Supply PSU DC Connector Pin Assignments
Power Supply
KW Power Supply Pin Number Signal name AWG Wire Color
DC Power Connector P1
DC Power Connector P3 Graphics Card
DC Power Connector P2
DC Power Connectors P8 and P9 HDD0 and HDD1
DC Power Connector P4 Graphics Card
DC Power Connector P5 FD1
DC Power Connector P6 and P7 BAY1 and Bay2
DC Power Connectors P14 Peripheral
DC Power Connectors P10-P13 HDD2 and HDD5
DC Power Connector P15 Graphics Card 1-KW PSU Only
DC Power Connector P16 Graphics Card 1-KW PSU Only
Removing the Power Supply
Pin Number Signal Name AWG Wire Color
Installing the Power Supply
Front I/O-Panel Components
Front I/O Panel
Removing the Front I/O Panel
Installing the I/O Panel
Replacing the Battery
Battery
Removing the Computer Stand
Replacing the Computer Cover
Back to Contents
Understanding CPU Overclocking
Understanding Dual-Graphics Technology
Dell QuickSet
Front View
Front and Back View of the Computer
Resulting in bodily injury or damage to the computer
Front I/O Connectors
To ensure maximum system stability. Failure to install
Back View
Back I/O Connectors
RCA S/PDIF
Attaching the Computer Stand
Installing Your Computer in an Enclosure
Connecting Monitors
Connecting a Monitor With an Adapter
Connecting a Monitor Without an Adapter
Connecting a Monitor in a Dual Graphics Card Configuration
Connecting a TV
Connecting Two or More Monitors
RAID Level 0 Configuration
About Your RAID Configuration
RAID Level 0+1 Configuration
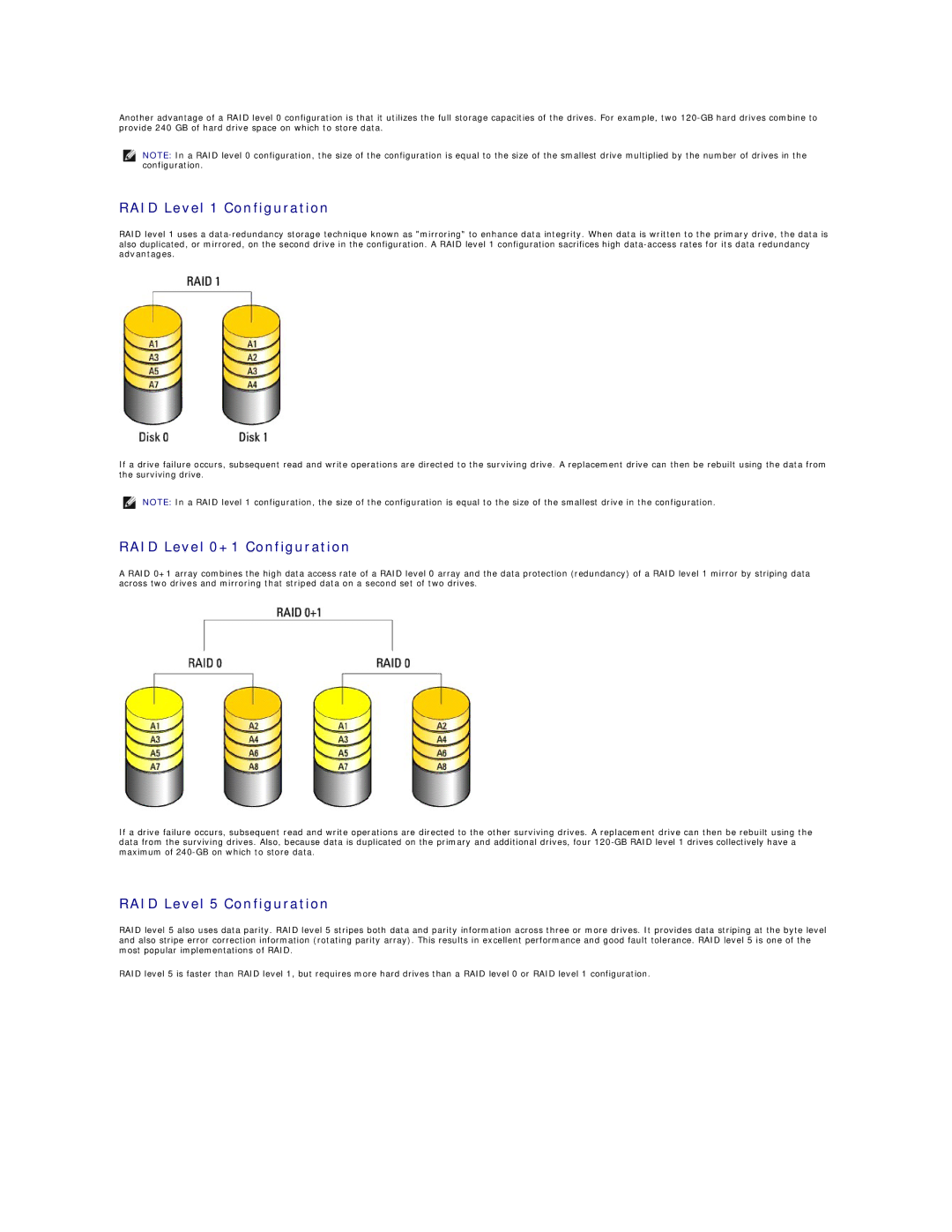
RAID Level 1 Configuration
RAID Level 5 Configuration
Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode
Configuring Your Hard Drives for RAID
Using the Nvidia MediaShield ROM Utility
Creating a RAID Array
Using Nvidia MediaShield
Click Create under System Tasks
Free Disk Selection window appears
Deleting a RAID Array
Clearing System Data window appears
Rebuilding a RAID Configuration
Using Multimedia
Copying CD, DVD, and Blu-ray Disc BD Media
How to Copy a CD, DVD, or BD
Helpful Tips
Using Blank CD, DVD, and BD Media
Media Type Read Write Rewritable
MMC/RS-MMC
Using a Media Card Reader Optional
Click Checklist for creating a network
Network Setup Wizard
Transferring Information to a New Computer
Standby Mode
Power Management Options in Windows XP
Hibernate Mode
Hibernate Tab
Power Options Properties
Power Schemes Tab
Advanced Tab
Sleep Mode
Power Management Options in Windows Vista
Configuring Power Management Settings
Click Start and click My Computer
Solving Problems
Battery Problems
Drive Problems
Hard drive problems
Mail, Modem, and Internet Problems
Optical drive problems
Problems writing to an optical drive
Click Start→ All Programs→ Modem Helper
Error Messages
Click Start → All Programs→ Modem Diagnostic Tool
Click Uninstall
Keyboard Problems
Ieee 1394 Device Problems
Lockups and Software Problems
Solid blue screen appears
Memory Problems
Mouse Problems
Other software problems
Click Start → Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Mouse
Network Problems
Power Problems
Click Start→ Control Panel→ Mouse
Click Properties and click Ports
Printer Problems
Scanner Problems
Click Start → Control Panel→ Hardware and Sound→ Printer
No sound from headphones
Sound and Speaker Problems
No sound from speakers
Click Start→ Control Panel→ Appearance and Themes
Video and Monitor Problems
Screen is blank Screen is difficult to read
3D image quality is poor
Diagnostic Lights
Power Lights
Problem Description Suggested Resolution
Code Cause
Beep Codes
Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
System Messages
When to Use Dell Diagnostics
Dell Diagnostics
Starting Dell Diagnostics From Your Hard Drive
Option Function
Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
Tab Function
Click Start → Computer.→ System Properties→ Device Manager
What Is a Driver?
Drivers
Identifying Drivers
Manually Reinstalling Drivers
Using the Drivers and Utilities Media
Starting System Restore
Using Microsoft Windows System Restore
Restoring Your Operating System
Windows XP Dell PC Restore
Using Dell PC Restore and Dell Factory Image Restore
Undoing the Last System Restore
Enabling System Restore
Select Repair Your Computer
Windows Vista Dell Factory Image Restore
Before you Begin
Using the Operating System Media
Reinstalling Windows XP or Windows Vista
Click Dell Factory Image Restore
Click Start and click Help and Support
Troubleshooting Software and Hardware Problems